IB Definitions
... The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The atomic number is equivalent to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes are atoms which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (due to the presence of different numbers of neutro ...
... The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The atomic number is equivalent to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes are atoms which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (due to the presence of different numbers of neutro ...
Properties of Matter Power Point
... Neutron- A sub-atomic particle in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are neutral, meaning that they have no charge, and a mass of 1 amu. Electron- A sub-atomic particle orbiting outside the nucleus of an atom. Electrons have a negative electrical charge and no mass. Atoms in their most stable state ha ...
... Neutron- A sub-atomic particle in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are neutral, meaning that they have no charge, and a mass of 1 amu. Electron- A sub-atomic particle orbiting outside the nucleus of an atom. Electrons have a negative electrical charge and no mass. Atoms in their most stable state ha ...
Origin of the Atom
... 3) An atom is held together by electric forces. This is from the attractive force of the electrons(-) and the ...
... 3) An atom is held together by electric forces. This is from the attractive force of the electrons(-) and the ...
Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... 68. q = mHf (melting), q = mHv(vaporizing), q = mC(change in temperature) (raising/lowering) *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. ...
... 68. q = mHf (melting), q = mHv(vaporizing), q = mC(change in temperature) (raising/lowering) *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. ...
Atomic Structure and Elements
... models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
... models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
Unit 3 Atomics Review SCIENTIFIC THEORIES Dalton theorized that
... The atomic number is the identity of an element. The periodic table and table S are arranged according to the atomic number. It tells you how many protons an atom has. a. Which element has 36 protons? _____________ b. How many protons does chlorine have? ___________ The mass number of an element is ...
... The atomic number is the identity of an element. The periodic table and table S are arranged according to the atomic number. It tells you how many protons an atom has. a. Which element has 36 protons? _____________ b. How many protons does chlorine have? ___________ The mass number of an element is ...
Corpuscles to Chemical Atomic Theory (The
... Rodriguez, M. (2015). The Periodic Table: Classification as a Means of Understanding. [Powerpoint slides]. Robert Boyle. (2015). Retrieved October 10, 2015 from http://www.chemheritage.org/discover/online-resour... earlychemistry-and-gases/boyle.aspx Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier: The Chemical Revolutio ...
... Rodriguez, M. (2015). The Periodic Table: Classification as a Means of Understanding. [Powerpoint slides]. Robert Boyle. (2015). Retrieved October 10, 2015 from http://www.chemheritage.org/discover/online-resour... earlychemistry-and-gases/boyle.aspx Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier: The Chemical Revolutio ...
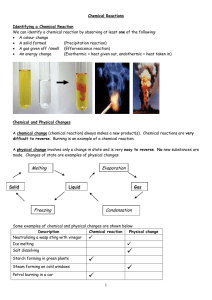
Chemical Reactions
... The reactants are separated from each other by a plus sign and the products are separated from each other by a plus sign. There should be an arrow in the middle. Examples: When sodium is mixed with water, a purple alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide is produced and hydrogen gas is evolved. Sodium ...
... The reactants are separated from each other by a plus sign and the products are separated from each other by a plus sign. There should be an arrow in the middle. Examples: When sodium is mixed with water, a purple alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide is produced and hydrogen gas is evolved. Sodium ...
Chapter 3 Review
... 14. Why do nuclei need neutrons to be stable? (ANS: neutrons are like glue that holds positive protons together.) 15. What are the symbols for the three types of radiation? (ANS: 42, 01, and ) 16. Describe two types of nuclear reactions other than radioactive decay. Where do they occur? (ANS: (1 ...
... 14. Why do nuclei need neutrons to be stable? (ANS: neutrons are like glue that holds positive protons together.) 15. What are the symbols for the three types of radiation? (ANS: 42, 01, and ) 16. Describe two types of nuclear reactions other than radioactive decay. Where do they occur? (ANS: (1 ...
What are X
... How many electrons can be in each shell (continued)? The shells are identified by a number n = 1,2,3…. with the n=1 shell being closest to the nucleus and a number l , giving the Angular Momentum of an electron in the shell. l has values 0,1,2,3,4 … up to the value (n-1) There can be maximum of 2( ...
... How many electrons can be in each shell (continued)? The shells are identified by a number n = 1,2,3…. with the n=1 shell being closest to the nucleus and a number l , giving the Angular Momentum of an electron in the shell. l has values 0,1,2,3,4 … up to the value (n-1) There can be maximum of 2( ...
02 The structure of the periodic table II
... This occurred 2 years after Rutherford proposed the nuclear model of the atom ...
... This occurred 2 years after Rutherford proposed the nuclear model of the atom ...
File - Science by Shaw
... Protons and Neutrons All of an atom’s positive charge Almost all of an atom’s mass. ...
... Protons and Neutrons All of an atom’s positive charge Almost all of an atom’s mass. ...
Electron configuration From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... atoms and molecules. For atoms, the notation consists of a sequence of atomic orbital labels (e.g. for phosphorus the sequence 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p) with the number of electrons assigned to each orbital (or set of orbitals sharing the same label) placed as a superscript. For example, hydrogen has one ...
... atoms and molecules. For atoms, the notation consists of a sequence of atomic orbital labels (e.g. for phosphorus the sequence 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p) with the number of electrons assigned to each orbital (or set of orbitals sharing the same label) placed as a superscript. For example, hydrogen has one ...
Ch. 4 Notes – THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM NOTE
... a) adapted model with subatomic particles: protons and electrons b) “plum pudding” model—electrons stuck in a proton lump 3) E. Rutherford (1871-1937); model in 1911 a) nucleus as the dense center with p+ and n0; e- outside it b) the atom is mostly space (gold foil experiment) 4) Niels Bohr (1885-19 ...
... a) adapted model with subatomic particles: protons and electrons b) “plum pudding” model—electrons stuck in a proton lump 3) E. Rutherford (1871-1937); model in 1911 a) nucleus as the dense center with p+ and n0; e- outside it b) the atom is mostly space (gold foil experiment) 4) Niels Bohr (1885-19 ...
Atomic Structure -
... capital letter with lower cap letters. The symbols represent the element’s name in Latin, so that is why some of the symbols don’t “match” the English term! (i.e., potassium = K) ...
... capital letter with lower cap letters. The symbols represent the element’s name in Latin, so that is why some of the symbols don’t “match” the English term! (i.e., potassium = K) ...
Synthesis of elements by helium and oxygen building blocks Bohr
... gives the hydrogen and helium isotopes enough kinetic energy to overcome the long-range repulsive Coulomb force and come within the short-range of the attractive strong nuclear force. The processes described above produce only nuclei of the elements: In the infernal heat of about 107 K atoms cannot ...
... gives the hydrogen and helium isotopes enough kinetic energy to overcome the long-range repulsive Coulomb force and come within the short-range of the attractive strong nuclear force. The processes described above produce only nuclei of the elements: In the infernal heat of about 107 K atoms cannot ...
The Atom
... Dalton’s Theory • A Summary of Dalton’s Atomic Theory: 1) An element is composed of tiny, indivisible, indestructible particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of an element are identical and have the same properties. 3) Atoms of different elements combine to form compounds. 4) Compounds contain atoms i ...
... Dalton’s Theory • A Summary of Dalton’s Atomic Theory: 1) An element is composed of tiny, indivisible, indestructible particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of an element are identical and have the same properties. 3) Atoms of different elements combine to form compounds. 4) Compounds contain atoms i ...
Finding the Amounts of Subatomic Particles
... properties as the element. The nucleus is the central part of an atom. It is made up of protons and neutrons and contains most of the atom’s mass. The nucleus was discovered by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. ...
... properties as the element. The nucleus is the central part of an atom. It is made up of protons and neutrons and contains most of the atom’s mass. The nucleus was discovered by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. ...
Atomic Theory – Matter Book pgs 83
... Discovered that the atom is divisible and negatively charged particles he called __________________. Today they are known as ___________. He also reasoned that positive charges existed in the atom to make the atom neutral, but could not find them. Describe the Plum Pudding Model Thomson proposed: __ ...
... Discovered that the atom is divisible and negatively charged particles he called __________________. Today they are known as ___________. He also reasoned that positive charges existed in the atom to make the atom neutral, but could not find them. Describe the Plum Pudding Model Thomson proposed: __ ...
energy levels
... • An electron in an atom can move from one energy level to another when the atom gains or loses energy. • Electrons can move up multiple energy levels at a time if it gains the right amount of energy. The size of the jump between energy levels determines the amount of energy gained or lost. ...
... • An electron in an atom can move from one energy level to another when the atom gains or loses energy. • Electrons can move up multiple energy levels at a time if it gains the right amount of energy. The size of the jump between energy levels determines the amount of energy gained or lost. ...