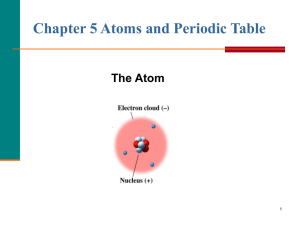
Atomic Theory
... 3. All atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. The atoms of one element are different in mass and size from the atoms of other elements. 4. Compounds are created when atoms of different elements link together in specific proportions. ...
... 3. All atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. The atoms of one element are different in mass and size from the atoms of other elements. 4. Compounds are created when atoms of different elements link together in specific proportions. ...
15.2 Electrons and Chemical Bonds
... numbers combines with other atoms to make a compound. Therefore, we say that sodium has an oxidation number of 1+. An oxidation number indicates the charge on the remaining atom (ion) when electrons are lost, gained, or shared in chemical bonds. Table 15.1 shows the oxidation numbers for some elemen ...
... numbers combines with other atoms to make a compound. Therefore, we say that sodium has an oxidation number of 1+. An oxidation number indicates the charge on the remaining atom (ion) when electrons are lost, gained, or shared in chemical bonds. Table 15.1 shows the oxidation numbers for some elemen ...
Symbols of Elements - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
... He then arranged columns so that elements with most similar properties were next to each other – First Periodic table Blank spaces left bc/ no known elements with mass and properties that fit ...
Bohr model
... Shell model of the atom Bohr extended the model of Hydrogen to give an approximate model for heavier atoms. This gave a physical picture which reproduced many known atomic properties for the first time. Heavier atoms have more protons in the nucleus, and more electrons to cancel the charge. Bohr's i ...
... Shell model of the atom Bohr extended the model of Hydrogen to give an approximate model for heavier atoms. This gave a physical picture which reproduced many known atomic properties for the first time. Heavier atoms have more protons in the nucleus, and more electrons to cancel the charge. Bohr's i ...
Unit-2.-Objectives
... Be able to use the Atomic # and Mass # of an isotope to calculate the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons present Know what the term isotope means and be able to perform simple calculations relating to isotopic data Understand Coulombic attraction and its affect on the force of charged partic ...
... Be able to use the Atomic # and Mass # of an isotope to calculate the numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons present Know what the term isotope means and be able to perform simple calculations relating to isotopic data Understand Coulombic attraction and its affect on the force of charged partic ...
Atoms
... 1, then it has 0 neutrons. It will have 1 proton to account for its mass number. An atom can lose or gain electrons to alter its charge and it can have different numbers of neutrons to change its mass, but the number of protons is always equal to its atomic number. On the other hand if Hydrogen has ...
... 1, then it has 0 neutrons. It will have 1 proton to account for its mass number. An atom can lose or gain electrons to alter its charge and it can have different numbers of neutrons to change its mass, but the number of protons is always equal to its atomic number. On the other hand if Hydrogen has ...
Chapter 4: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... gain energy, but it can move to a higher energy orbit by gaining an amount of energy equal to the difference in energy between the higherenergy orbit and the initial lower-energy orbit. When hydrogen is in an excited state, its electron is in a higher-energy orbit. ...
... gain energy, but it can move to a higher energy orbit by gaining an amount of energy equal to the difference in energy between the higherenergy orbit and the initial lower-energy orbit. When hydrogen is in an excited state, its electron is in a higher-energy orbit. ...
Atoms molecules Slide Guide Atoms ~ Atoms are the general term
... ~ Because electrons move so quickly, it is impossible to see where they are at a _________ __________ in time. After years of experimentation, scientists discovered ___________ areas where electrons are likely to be found. ~ The overall shape of the shells _______________ depending on how many elect ...
... ~ Because electrons move so quickly, it is impossible to see where they are at a _________ __________ in time. After years of experimentation, scientists discovered ___________ areas where electrons are likely to be found. ~ The overall shape of the shells _______________ depending on how many elect ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE - New York Science Teacher
... As the science of spectroscopy grew and the resolution of the bright-line spectra of an element improved and the dual nature of the electron was explored scientists formulated a new picture of the atom. This new model of the atom retains some of the original features but changes the concept of elect ...
... As the science of spectroscopy grew and the resolution of the bright-line spectra of an element improved and the dual nature of the electron was explored scientists formulated a new picture of the atom. This new model of the atom retains some of the original features but changes the concept of elect ...
Test 5: Chapter 5 – Electrons in Atoms
... time farther from the nucleus. Therefore, n specifies the atom’s major energy levels, called principal energy levels. ...
... time farther from the nucleus. Therefore, n specifies the atom’s major energy levels, called principal energy levels. ...
Ch-03 Notes ppt
... Elements are put in order of increasing atomic number on the periodic table, identifies an element. ...
... Elements are put in order of increasing atomic number on the periodic table, identifies an element. ...
The Atom - South Dade Senior High
... separate samples of neon gas, the same element, but they had different masses, how could this be? • The answer again is isotopes, if the number of neutrons is different the mass will be as well. ...
... separate samples of neon gas, the same element, but they had different masses, how could this be? • The answer again is isotopes, if the number of neutrons is different the mass will be as well. ...
The Atom - Magoffin County Schools
... • Within this space, ELECTRONS move around the nucleus of the atom much like a swarm of bees around a hive. • This area is known as the ELECTRON CLOUD. ...
... • Within this space, ELECTRONS move around the nucleus of the atom much like a swarm of bees around a hive. • This area is known as the ELECTRON CLOUD. ...
Sub-Atomic Particles and the Nuclear Atom - Chemistry-at-PA
... 34) How many protons in calcium? Ca’s atomic # is 20, so there are 20 protons 35) How many neutrons in an atom of lithium-7? Li’s atomic # is 3, so there are 3 protons, its mass is 7, so 3 + no = 7 the # of no must be 4. 36) How many electrons in every atom of magnesium? Mg’s atomic number is 12, so ...
... 34) How many protons in calcium? Ca’s atomic # is 20, so there are 20 protons 35) How many neutrons in an atom of lithium-7? Li’s atomic # is 3, so there are 3 protons, its mass is 7, so 3 + no = 7 the # of no must be 4. 36) How many electrons in every atom of magnesium? Mg’s atomic number is 12, so ...
gp - fc2009goran
... radioisotopes were used in what is now called nuclear medicine. The most common, stable form of iodine has an atomic number of 53 (protons) and an atomic weight of 127 (53 protons plus 74 neutrons). Because its nucleus has the "correct" number of neutrons, it is stable and is not radioactive. A less ...
... radioisotopes were used in what is now called nuclear medicine. The most common, stable form of iodine has an atomic number of 53 (protons) and an atomic weight of 127 (53 protons plus 74 neutrons). Because its nucleus has the "correct" number of neutrons, it is stable and is not radioactive. A less ...
Topic 2 Part 1 Slides - Coral Gables Senior High
... to Democritus’ model, the atom would be a fundamental particle: the smallest particle of matter. Does Democritus’ model of the atom agree with our current understanding of the atom? ...
... to Democritus’ model, the atom would be a fundamental particle: the smallest particle of matter. Does Democritus’ model of the atom agree with our current understanding of the atom? ...
electron
... was underpinned by false reasoning. – Mendeleev believed, incorrectly, that chemical properties were determined by atomic weight. ...
... was underpinned by false reasoning. – Mendeleev believed, incorrectly, that chemical properties were determined by atomic weight. ...
Final Exam - W09
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... transforms, one set of chemicals into another by changing the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds. ...
... transforms, one set of chemicals into another by changing the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds. ...
Interactive Notebook 2 for 2011-2012
... All atoms of any given element have the same numbers of protons (atomic number = Z) in their nucleus. Atoms are identified based on the number protons in the nucleus. The Periodic Table is organized in order of increasing atomic number. However, atoms of the same element may have different numbers o ...
... All atoms of any given element have the same numbers of protons (atomic number = Z) in their nucleus. Atoms are identified based on the number protons in the nucleus. The Periodic Table is organized in order of increasing atomic number. However, atoms of the same element may have different numbers o ...
atoms - Wylie ISD
... mass and properties. (This was later disproved by the discovery of isotopes). Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. (This was later disproved by the discovery of protons, neutrons and electrons). Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Atoms a ...
... mass and properties. (This was later disproved by the discovery of isotopes). Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. (This was later disproved by the discovery of protons, neutrons and electrons). Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Atoms a ...
Lab 5
... On the next page is a table of stellar spectra; each “row” represents the emissions from a particular star. The star’s abbreviated name is given to the left of its spectrum; for instance, the first star is “10 Lacerta”, which is the tenth brightest star in the constellation Lacerta. The star’s spec ...
... On the next page is a table of stellar spectra; each “row” represents the emissions from a particular star. The star’s abbreviated name is given to the left of its spectrum; for instance, the first star is “10 Lacerta”, which is the tenth brightest star in the constellation Lacerta. The star’s spec ...