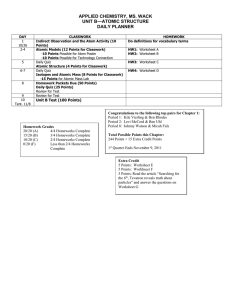
Lap 4: Atomic Structure Mead Chemistry Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the
... Def: Smallest particle of an element that still retains its identity in a chemical reaction Democritus’s Atomic Philosophy Greek philosopher 460 BC -370 BC First to suggest existence of atoms Believed atoms were indivisible and indestructable Ideas proved to be true, but not based on s ...
... Def: Smallest particle of an element that still retains its identity in a chemical reaction Democritus’s Atomic Philosophy Greek philosopher 460 BC -370 BC First to suggest existence of atoms Believed atoms were indivisible and indestructable Ideas proved to be true, but not based on s ...
History of the Atom Activity
... All matter is composed of tiny indivisible parts called atoms (they can be broken down further, although properties will not be retained) Atoms of the same element are exactly alike, atoms of different elements are different (not all atoms of the same element have the same mass – isotopes) Atoms can ...
... All matter is composed of tiny indivisible parts called atoms (they can be broken down further, although properties will not be retained) Atoms of the same element are exactly alike, atoms of different elements are different (not all atoms of the same element have the same mass – isotopes) Atoms can ...
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Bohr’s Model When an electron resides(居住) in the orbit designated by n = 1, it is said to be in the ground state(基态). This is the lowest possible energy level in which hydrogen’s electron can exist. If hydrogen’s electron is in a higher energy orbit, with n greater than 1, the atom is said to be in ...
... Bohr’s Model When an electron resides(居住) in the orbit designated by n = 1, it is said to be in the ground state(基态). This is the lowest possible energy level in which hydrogen’s electron can exist. If hydrogen’s electron is in a higher energy orbit, with n greater than 1, the atom is said to be in ...
1. Select the correct statement about subatomic particles. a
... e. No reaction takes place because silver is less reactive than potassium. 74. A double-replacement reaction takes place when aqueous cobalt(III) chloride reacts with aqueous lithium hydroxide. One of the products of this reaction would be ___. a. Co(OH)3 d. LiCl3 b. Co(OH)2 e. Cl3OH c. LiCo3 75. A ...
... e. No reaction takes place because silver is less reactive than potassium. 74. A double-replacement reaction takes place when aqueous cobalt(III) chloride reacts with aqueous lithium hydroxide. One of the products of this reaction would be ___. a. Co(OH)3 d. LiCl3 b. Co(OH)2 e. Cl3OH c. LiCo3 75. A ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... Definition: isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers Isotopes: element has same atomic number, same # protons, different # neutrons, different mass # Q: Why do isotopes have different mass numbers for the same element? A: Because they ...
... Definition: isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers Isotopes: element has same atomic number, same # protons, different # neutrons, different mass # Q: Why do isotopes have different mass numbers for the same element? A: Because they ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 4
... • Masses are additive; volumes are not • The total mass of a solution is the sum of the mass of the solute and the solvent • The total volume of a solution is not the sum of the volumes of the solute and solvent • Molarity as a conversion: Use: # moles = 1 Liter ...
... • Masses are additive; volumes are not • The total mass of a solution is the sum of the mass of the solute and the solvent • The total volume of a solution is not the sum of the volumes of the solute and solvent • Molarity as a conversion: Use: # moles = 1 Liter ...
(3.3 × 10!4) + (2.52 × 10!2) = (3.3 × 10!4) × (2.52 × 10!2)
... All Compounds are made up of molecules or ions. A molecule is the smallest unit of a compound that retains its chemical characteristics. Ionic compounds are described by a “formula unit”. Molecules are described by a “molecular formula”. ...
... All Compounds are made up of molecules or ions. A molecule is the smallest unit of a compound that retains its chemical characteristics. Ionic compounds are described by a “formula unit”. Molecules are described by a “molecular formula”. ...
review sheet
... 46. How many neutrons, protons and electrons does silicon have? 47. Why is the atomic mass not a whole number? 48. Draw orbital diagrams and electron configurations for Na and Al. ...
... 46. How many neutrons, protons and electrons does silicon have? 47. Why is the atomic mass not a whole number? 48. Draw orbital diagrams and electron configurations for Na and Al. ...
labeling electrons in atoms
... 3. Since nature likes being in the lowest energy state possible, the atom will return to the ground state. The electron will return to the n = 1 orbit and in the process emit a photon of energy. 4. Since only certain atomic energies are possible, only certain frequencies of electromagnetic radiation ...
... 3. Since nature likes being in the lowest energy state possible, the atom will return to the ground state. The electron will return to the n = 1 orbit and in the process emit a photon of energy. 4. Since only certain atomic energies are possible, only certain frequencies of electromagnetic radiation ...
Chemistry 2011-2012
... SC3 Students will use the modern atomic theory to explain the characteristics of atoms. SC3a. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, and position of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. SC3b. Use the orbital configuration of neutral atoms to explain its effect on the atom’s chemica ...
... SC3 Students will use the modern atomic theory to explain the characteristics of atoms. SC3a. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, and position of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. SC3b. Use the orbital configuration of neutral atoms to explain its effect on the atom’s chemica ...
Atoms and their structure
... elements to be considered that particular compound – Ex H2O or H2O2 two different ratios mean, two different compounds 4. TRUE b/c of Law of _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ ...
... elements to be considered that particular compound – Ex H2O or H2O2 two different ratios mean, two different compounds 4. TRUE b/c of Law of _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ ...
Atomic structure packets
... b. What does the word “atom” mean? c. What is the word origin for “atom?” ...
... b. What does the word “atom” mean? c. What is the word origin for “atom?” ...
Study Guide: Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Physical Properties
... Physical Properties: Can be observed or measured without chemically changing a substance. Can be used to identify an unknown substance (some are more useful for this purpose than others, such as: specific heat, density (mass/volume), melting point, boiling point) Are: malleability, solubility, densi ...
... Physical Properties: Can be observed or measured without chemically changing a substance. Can be used to identify an unknown substance (some are more useful for this purpose than others, such as: specific heat, density (mass/volume), melting point, boiling point) Are: malleability, solubility, densi ...
atoms - Alki Middle School
... that all matter is composed of small, fast moving particles called atoms. These atoms can join together to form molecules. This theory is really thousands of individual theories that provide evidence for the whole theory. ...
... that all matter is composed of small, fast moving particles called atoms. These atoms can join together to form molecules. This theory is really thousands of individual theories that provide evidence for the whole theory. ...
chaptyer 1 - drjepmaranan
... distribution of electrons in atom – the first three quantum numbers – the principal number, the angular momentum quantum number and the magnetic quantum number – describe the energy of the electron while the fourth quantum number – the spts quantum number describes the behavior of a specific electro ...
... distribution of electrons in atom – the first three quantum numbers – the principal number, the angular momentum quantum number and the magnetic quantum number – describe the energy of the electron while the fourth quantum number – the spts quantum number describes the behavior of a specific electro ...
EPSc 446 STABLE ISOTOPE GEOCHEMISTRY Instructor: Bob Criss
... Found that a few α particles were deflected through large angles- up to 180°. ...
... Found that a few α particles were deflected through large angles- up to 180°. ...
Intro to the atom - thsicp-23
... Matter The term matter describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, and so forth ...
... Matter The term matter describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, and so forth ...
Introduction to Atoms
... Electrons move around the nucleus, which contains the protons and neutrons. This area is called an electron cloud because electrons may move anywhere within it. Comparing Particle Masses: Although electrons occupy most of an atom’s volume, they don’t account for much of its mass. A proton and ...
... Electrons move around the nucleus, which contains the protons and neutrons. This area is called an electron cloud because electrons may move anywhere within it. Comparing Particle Masses: Although electrons occupy most of an atom’s volume, they don’t account for much of its mass. A proton and ...
P2 Topic 3
... The top diagram shows what happens during nuclear fission of uranium235. Fission occurs when a neutron hits a uranium nucleus. The nucleus splits into smaller nuclei (so they are different elements) and more neutrons. The neutrons hit more uranium nuclei causing them to split, producing smaller nucl ...
... The top diagram shows what happens during nuclear fission of uranium235. Fission occurs when a neutron hits a uranium nucleus. The nucleus splits into smaller nuclei (so they are different elements) and more neutrons. The neutrons hit more uranium nuclei causing them to split, producing smaller nucl ...
Ch 05 ElectronsInAtoms
... B. bonded atoms with one electron C. single atoms with more than one electron D. bonded atoms with more than one electron ____ 57. The quantum mechanical model of the atom A. defines the exact path of an electron around the nucleus. ...
... B. bonded atoms with one electron C. single atoms with more than one electron D. bonded atoms with more than one electron ____ 57. The quantum mechanical model of the atom A. defines the exact path of an electron around the nucleus. ...
P2 Knowledge Powerpoint – WIP Part 2
... The top diagram shows what happens during nuclear fission of uranium235. Fission occurs when a neutron hits a uranium nucleus. The nucleus splits into smaller nuclei (so they are different elements) and more neutrons. The neutrons hit more uranium nuclei causing them to split, producing smaller nucl ...
... The top diagram shows what happens during nuclear fission of uranium235. Fission occurs when a neutron hits a uranium nucleus. The nucleus splits into smaller nuclei (so they are different elements) and more neutrons. The neutrons hit more uranium nuclei causing them to split, producing smaller nucl ...
Review for Test
... Write the correct answer on the line. _____ 1. What was concluded about the structure of the atom as a result of the gold-foil experiment? a) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by positively charged particles b) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by mostly empty space c) A negatively ...
... Write the correct answer on the line. _____ 1. What was concluded about the structure of the atom as a result of the gold-foil experiment? a) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by positively charged particles b) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by mostly empty space c) A negatively ...
The Atom
... • Because Aristotle was so influential, his ideas were accepted and Democritus’s ideas about atoms were not studied again for more than 2,000 years. ...
... • Because Aristotle was so influential, his ideas were accepted and Democritus’s ideas about atoms were not studied again for more than 2,000 years. ...