03_Worked_Examples
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
03_Worked_Examples
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
2 - cloudfront.net
... of moles of any two of the substances in a balanced chemical equation 1. Example: Write all possible mole ratios for: 2HgO (s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g) 2 mol HgO 2 mol HgO 2 mol Hg 1 mol O2 2 mol Hg 2 mol Hg 2 mol HgO 1 mol O2 1 mol O2 1 mol O2 2 mol HgO 2 mol Hg ...
... of moles of any two of the substances in a balanced chemical equation 1. Example: Write all possible mole ratios for: 2HgO (s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g) 2 mol HgO 2 mol HgO 2 mol Hg 1 mol O2 2 mol Hg 2 mol Hg 2 mol HgO 1 mol O2 1 mol O2 1 mol O2 2 mol HgO 2 mol Hg ...
A Dictionary of the New Chymical Nomenclature
... Salts formed by the combination of the lithic acid, or acid of the stone sometimes generated in the human bladder, with different bases. This genus of salts had no name in the ancient nomenclature, because it was not known before the time of Scheele. ...
... Salts formed by the combination of the lithic acid, or acid of the stone sometimes generated in the human bladder, with different bases. This genus of salts had no name in the ancient nomenclature, because it was not known before the time of Scheele. ...
Page 1.eps - TimeLine Theatre
... had been under German Occupation since April 9, 1940. While in Copenhagen, Heisenberg visited his former mentor and friend Niels Bohr. The dispute and uncertainty over exactly what was said during this visit, what Heisenberg’s intentions were, and the irresistible explanations for Heisenberg’s behav ...
... had been under German Occupation since April 9, 1940. While in Copenhagen, Heisenberg visited his former mentor and friend Niels Bohr. The dispute and uncertainty over exactly what was said during this visit, what Heisenberg’s intentions were, and the irresistible explanations for Heisenberg’s behav ...
Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe (CH2O)+ and Fe (CH2S)+ with Small
... dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisioninduced dissociation methods. Formaldehyde was chosen since it is the simplest hydrocarbon containing oxygen, and an und ...
... dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisioninduced dissociation methods. Formaldehyde was chosen since it is the simplest hydrocarbon containing oxygen, and an und ...
Advanced Higher - Hodder Education
... (c) (i) Using orbital box notation, write the electronic configuration for a phosphorus atom in its ground state. ...
... (c) (i) Using orbital box notation, write the electronic configuration for a phosphorus atom in its ground state. ...
Chapter 6 Quantities in Chemical Reactions
... In this paragraph from the Elements of Chemistry, Antoine Lavoisier (1743–94) is explaining an experiment in which he was trying to demonstrate that water is not an element but instead is composed of hydrogen (the gas “capable of being burnt”) and oxygen. This is a historical account of a groundbrea ...
... In this paragraph from the Elements of Chemistry, Antoine Lavoisier (1743–94) is explaining an experiment in which he was trying to demonstrate that water is not an element but instead is composed of hydrogen (the gas “capable of being burnt”) and oxygen. This is a historical account of a groundbrea ...
Stoichiometry
... 3. If necessary multiply the whole equation by a factor to clear the fractional coefficients 4. Verify that the equation is balanced and the coefficients are the smallest whole numbers 5. Specify physical states ...
... 3. If necessary multiply the whole equation by a factor to clear the fractional coefficients 4. Verify that the equation is balanced and the coefficients are the smallest whole numbers 5. Specify physical states ...
20.2 Oxidation Numbers
... were assigned to the atom of the more electronegative element. An increase in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates oxidation. A decrease in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates reduction. ...
... were assigned to the atom of the more electronegative element. An increase in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates oxidation. A decrease in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates reduction. ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical experiments depends.” --Antoine Lavoisier, 1789 ...
... “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical experiments depends.” --Antoine Lavoisier, 1789 ...
Preview Sample 1
... A. an atom contains 2 hydrogen molecules and 1 oxygen molecule. B. an atom contains 1 hydrogen atom and 2 oxygen molecules. C. a molecule contains 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom. D. a molecule contains 1 hydrogen atom and 2 oxygen atoms. E. a molecule contains 2 hydrogen atoms and no oxygen atom ...
... A. an atom contains 2 hydrogen molecules and 1 oxygen molecule. B. an atom contains 1 hydrogen atom and 2 oxygen molecules. C. a molecule contains 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom. D. a molecule contains 1 hydrogen atom and 2 oxygen atoms. E. a molecule contains 2 hydrogen atoms and no oxygen atom ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... 2 The relative importance of different elements From an academic point of view, all elements might be said to be equally important. The chemistry of each has to be understood in detail if the chemistry of matter as a whole is to be understood in detail. From the point of view of the world at large, ...
... 2 The relative importance of different elements From an academic point of view, all elements might be said to be equally important. The chemistry of each has to be understood in detail if the chemistry of matter as a whole is to be understood in detail. From the point of view of the world at large, ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... Which is the Limiting Reagent? Step 1: #moles CHCl3 = mass/GFM = 15.9 g/119.5 g/mol = 0.133 mol #moles Cl2 = mass/GFM = 12.6 g/71.0 g/mol = 0.177 mol Step 2: Use these equations: # mol reactant CHCl3 / coefficient CHCl3= 0.133/ 2 = 0.0665 # mol reactant Cl2 / coefficent Cl2 = 0.177/ 2 = 0.0885 Step ...
... Which is the Limiting Reagent? Step 1: #moles CHCl3 = mass/GFM = 15.9 g/119.5 g/mol = 0.133 mol #moles Cl2 = mass/GFM = 12.6 g/71.0 g/mol = 0.177 mol Step 2: Use these equations: # mol reactant CHCl3 / coefficient CHCl3= 0.133/ 2 = 0.0665 # mol reactant Cl2 / coefficent Cl2 = 0.177/ 2 = 0.0885 Step ...
CHAPTER 9 Notes
... theoretical yield: Amount of product one should get based on the chemical equation and the amount of reactants present -One generally calculates this in grams from info given Actual yield: Amount of produce one actually obtains -Generally smaller than the theoretical yield because of impurities and ...
... theoretical yield: Amount of product one should get based on the chemical equation and the amount of reactants present -One generally calculates this in grams from info given Actual yield: Amount of produce one actually obtains -Generally smaller than the theoretical yield because of impurities and ...
Ch 10 Practice Problems 1. Consider the process A(l) A(s). Which
... C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. q is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. H is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. E is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater th ...
... C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. q is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. H is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. E is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater th ...
expected output
... SYLLABUS: Quadratic functions and equations. Surds, logarithms and indices. Permutations and combinations. Series; finite, infinite, arithmetic, geometric and binomial(positive integral index only)including applications to compound interest, approximartions, growth and decay. Remainder theorem and i ...
... SYLLABUS: Quadratic functions and equations. Surds, logarithms and indices. Permutations and combinations. Series; finite, infinite, arithmetic, geometric and binomial(positive integral index only)including applications to compound interest, approximartions, growth and decay. Remainder theorem and i ...
Naming Compounds - Kowenscience.com
... • Chromium(IV) oxide. Cr is the symbol for chromium. O is the symbol for oxygen, but • take the first part of the element name (the root) and add –ide to get the name oxide. • Since chromium can have more than one charge, a Roman numeral must be used to identify that charge. • There are two oxygen i ...
... • Chromium(IV) oxide. Cr is the symbol for chromium. O is the symbol for oxygen, but • take the first part of the element name (the root) and add –ide to get the name oxide. • Since chromium can have more than one charge, a Roman numeral must be used to identify that charge. • There are two oxygen i ...
expected output
... SYLLABUS: Quadratic functions and equations. Surds, logarithms and indices. Permutations and combinations. Series; finite, infinite, arithmetic, geometric and binomial(positive integral index only)including applications to compound interest, approximartions, growth and decay. Remainder theorem and i ...
... SYLLABUS: Quadratic functions and equations. Surds, logarithms and indices. Permutations and combinations. Series; finite, infinite, arithmetic, geometric and binomial(positive integral index only)including applications to compound interest, approximartions, growth and decay. Remainder theorem and i ...
Oxidation of benzoin with anchored vanadyl and
... carried out in the absence of catalyst, was very slow and low yields of benzil were obtained even when the reaction was allowed to proceed for a longer time (up to 32 h). Experiments were carried out using (i) the organic polymer without ligand and metal complex and (ii) the organic polymer function ...
... carried out in the absence of catalyst, was very slow and low yields of benzil were obtained even when the reaction was allowed to proceed for a longer time (up to 32 h). Experiments were carried out using (i) the organic polymer without ligand and metal complex and (ii) the organic polymer function ...
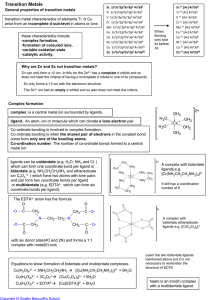
Transition Metals
... When transition metals in low oxidation states are in alkaline solution they are more easily oxidised than when in acidic solution ...
... When transition metals in low oxidation states are in alkaline solution they are more easily oxidised than when in acidic solution ...
Examiners` Report November 2012 GCSE Chemistry
... This was the second 5CH2H paper to be offered; the first being set in June 2012. This question paper assessed the specification items to be in Unit 2 Discovering Chemistry which forms part of the Additional Science course along with the corresponding biology and physics units, and also as part of th ...
... This was the second 5CH2H paper to be offered; the first being set in June 2012. This question paper assessed the specification items to be in Unit 2 Discovering Chemistry which forms part of the Additional Science course along with the corresponding biology and physics units, and also as part of th ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Analyze We are given a chemical formula, C12H22O11, and asked to calculate the percentage by mass of its component elements (C, H, and O). Plan We can use Equation 3.10, relying on a periodic table to obtain the atomic weight of each component element. The atomic weights are first used to determine ...
... Analyze We are given a chemical formula, C12H22O11, and asked to calculate the percentage by mass of its component elements (C, H, and O). Plan We can use Equation 3.10, relying on a periodic table to obtain the atomic weight of each component element. The atomic weights are first used to determine ...
19_Worked_Examples
... Plan We can answer part (a) by determining the sign of S for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we first calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction using data in Appendix C and then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG. Solve (a) The temperature dependence ...
... Plan We can answer part (a) by determining the sign of S for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we first calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction using data in Appendix C and then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG. Solve (a) The temperature dependence ...