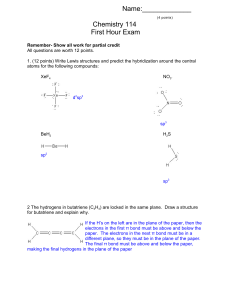
P2 Knowledge Powerpoint – WIP Part 2
... • Transform energy contained in nuclei of uranium and plutonium into thermal energy • Nuclear fission • Pellets of uranium inserted into hollow rods • Rods place in reactor core • Rate is kept constant but controlling the chain reaction • Number of free neutrons will not increase of decrease • Extra ...
... • Transform energy contained in nuclei of uranium and plutonium into thermal energy • Nuclear fission • Pellets of uranium inserted into hollow rods • Rods place in reactor core • Rate is kept constant but controlling the chain reaction • Number of free neutrons will not increase of decrease • Extra ...
Electrons
... one less proton than electron. One less proton means one less positive charge. This makes the total charge of the atom NEGATIVE. ...
... one less proton than electron. One less proton means one less positive charge. This makes the total charge of the atom NEGATIVE. ...
Chemistry Atoms Learning Objectives Atoms Essential knowledge
... The average atomic mass for each element is the weighted average of that element’s naturally occurring isotopes. The mass number of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. It is different for each element’s isotopes. An isotope is an atom that has the same number of protons as a ...
... The average atomic mass for each element is the weighted average of that element’s naturally occurring isotopes. The mass number of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. It is different for each element’s isotopes. An isotope is an atom that has the same number of protons as a ...
Classification of Matter slides
... □ Can only be observed when a substance is changed into another substance. • Flammability, corrosiveness, reactivity with acid, etc. ...
... □ Can only be observed when a substance is changed into another substance. • Flammability, corrosiveness, reactivity with acid, etc. ...
Atomic Theory
... Excited state – an energy level higher than the ground state for an electron; temporary condition ...
... Excited state – an energy level higher than the ground state for an electron; temporary condition ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... Glycine has an unusually high melting point for a small molecule. Suggest a reason for this. In its zwitterionic state, glycine has very strong electrostatic attractions (i.e. ionic bonds) between the NH3+ and CO2– groups giving it very high melting point. Do you expect glycine to be water soluble? ...
... Glycine has an unusually high melting point for a small molecule. Suggest a reason for this. In its zwitterionic state, glycine has very strong electrostatic attractions (i.e. ionic bonds) between the NH3+ and CO2– groups giving it very high melting point. Do you expect glycine to be water soluble? ...
Atom
... The atomic number of the element is shown centered above the symbol. Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number, from left to right and from top to bottom. Period - each horizontal row of the periodic table. Within a given period, the properties of the elements vary as you move across ...
... The atomic number of the element is shown centered above the symbol. Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number, from left to right and from top to bottom. Period - each horizontal row of the periodic table. Within a given period, the properties of the elements vary as you move across ...
Section 4.1 Studying Atoms Reading Strategy
... 7. What happened to the beam when Thomson placed a pair of charged metal plates on either side of the glass tube? 8. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) charge because they were attracted to a positive plate. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Thomson’s experim ...
... 7. What happened to the beam when Thomson placed a pair of charged metal plates on either side of the glass tube? 8. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) charge because they were attracted to a positive plate. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Thomson’s experim ...
4.1 Studying Atoms
... 7. What happened to the beam when Thomson placed a pair of charged metal plates on either side of the glass tube? 8. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) charge because they were attracted to a positive plate. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Thomson’s experim ...
... 7. What happened to the beam when Thomson placed a pair of charged metal plates on either side of the glass tube? 8. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) charge because they were attracted to a positive plate. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Thomson’s experim ...
File
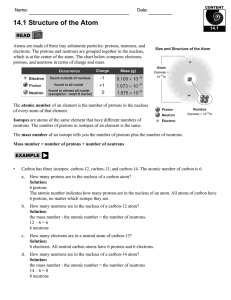
... 2. ______________________ and ____________________ are in the nucleus of the atom and when added together they give you the ___________________________ of the atom. 3. _________________ move quickly and constantly around the outside of the nucleus in the ____________ __________. 4. The number of ___ ...
... 2. ______________________ and ____________________ are in the nucleus of the atom and when added together they give you the ___________________________ of the atom. 3. _________________ move quickly and constantly around the outside of the nucleus in the ____________ __________. 4. The number of ___ ...
Printable Activities
... the sample. Constant proportionality is known as disintegration constant. Radioactive Disintegration Simulator. Remember that… An isotope is an atom belonging to the same chemical element; it has the same proton quantity, but a different number of neutrons. Learning Activity 1 The following activity ...
... the sample. Constant proportionality is known as disintegration constant. Radioactive Disintegration Simulator. Remember that… An isotope is an atom belonging to the same chemical element; it has the same proton quantity, but a different number of neutrons. Learning Activity 1 The following activity ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Calculate the average atomic mass. Avg. Mass = (0.9890*12) + (0.0110*13.003355) Avg. Mass = 12.0111 ...
... Calculate the average atomic mass. Avg. Mass = (0.9890*12) + (0.0110*13.003355) Avg. Mass = 12.0111 ...
electron configuration
... Electron Configuration: Notation used to describe the way an atom’s electrons are arranged into orbitals. Electrons are listed in order from lowest energy to highest. Aufbau Principle: Electrons will fill the lowest energy state available within an atom and only occupy a higher energy state if all l ...
... Electron Configuration: Notation used to describe the way an atom’s electrons are arranged into orbitals. Electrons are listed in order from lowest energy to highest. Aufbau Principle: Electrons will fill the lowest energy state available within an atom and only occupy a higher energy state if all l ...
The Structure of the Atom 1 Philosophers And Early Scientists
... 1 amu is approximately equal to the mass of a single proton or neutron ...
... 1 amu is approximately equal to the mass of a single proton or neutron ...
Unit 3 - Structure of the Atom
... has a mass of 62.930 amu and 69.17% abundance and copper-65 has a mass of 64.928 amu and 30.83% abundance, what is the average atomic mass of copper? 1. First, calculate the mass contribution of each isotope to the average atomic mass, being sure to convert each percent to a fractional ...
... has a mass of 62.930 amu and 69.17% abundance and copper-65 has a mass of 64.928 amu and 30.83% abundance, what is the average atomic mass of copper? 1. First, calculate the mass contribution of each isotope to the average atomic mass, being sure to convert each percent to a fractional ...
PowerPoint for Cornell Notes
... – Physical properties were those like mass, volume, density, melting point, boiling point, conductivity, malleability, state/phase of matter etc. • Changes within these properties can be undone and the properties of the substances are not altered. ...
... – Physical properties were those like mass, volume, density, melting point, boiling point, conductivity, malleability, state/phase of matter etc. • Changes within these properties can be undone and the properties of the substances are not altered. ...
14.1 Structure of the Atom
... chemical bonds are called valence electrons. Atoms can have up to eight valence electrons. These electrons exist in the outermost region of the electron cloud, often called the “valence shell.” The most stable atoms have eight valence electrons. When an atom has eight valence electrons, it is said t ...
... chemical bonds are called valence electrons. Atoms can have up to eight valence electrons. These electrons exist in the outermost region of the electron cloud, often called the “valence shell.” The most stable atoms have eight valence electrons. When an atom has eight valence electrons, it is said t ...
Democritus
... a specific element are different from other element 3. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed during Chemical reactions (law of conservation of mass as originally defined by Antoine Lavoisier in 1785) 4. In a chemical reaction atoms are separated, combined or rearranged And Lastly ...
... a specific element are different from other element 3. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed during Chemical reactions (law of conservation of mass as originally defined by Antoine Lavoisier in 1785) 4. In a chemical reaction atoms are separated, combined or rearranged And Lastly ...
Z eff
... Frequency (v) vs. Wavelength (l) Frequency ( v ) – number of waves (cycles) per second that pass a given point in space. ...
... Frequency (v) vs. Wavelength (l) Frequency ( v ) – number of waves (cycles) per second that pass a given point in space. ...
Sci7-Chapter3-Chemistry
... • You cannot use these three words. • 3 letter words – 1pt • 4 letter words – 2pts • 5 or more letter words – 4 points ...
... • You cannot use these three words. • 3 letter words – 1pt • 4 letter words – 2pts • 5 or more letter words – 4 points ...
Energy Levels of Helium
... All electrons within atoms are restricted by quantum theory to discrete energy levels as originally predicted by Bohr’s model of the atom. These energy levels (or orbitals) correspond, more accurately, to solutions of the Schrödinger wave equation for that atom. The first experiment to really demons ...
... All electrons within atoms are restricted by quantum theory to discrete energy levels as originally predicted by Bohr’s model of the atom. These energy levels (or orbitals) correspond, more accurately, to solutions of the Schrödinger wave equation for that atom. The first experiment to really demons ...
PP atoms - Lake County Schools
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical whereas atoms of different elements differ 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearr ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical whereas atoms of different elements differ 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearr ...