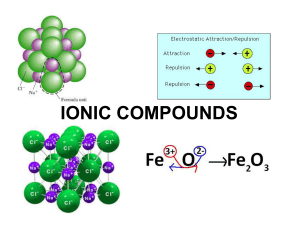
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... (written as a roman numeral in parentheses after the name of the cation). 5. If the compound contains a polyatomic ion, simply name the ion. ...
... (written as a roman numeral in parentheses after the name of the cation). 5. If the compound contains a polyatomic ion, simply name the ion. ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, MOLECULES AND IONS ULES AND IONS
... d) An individual atom cannot be considered to be a solid, liquid or gas 2) The weight of a container with some chemicals is 250 g. If the chemicals are burned in a closed container, which one of the following is true? a) Weight decrease less than 250 g change (250 g) ...
... d) An individual atom cannot be considered to be a solid, liquid or gas 2) The weight of a container with some chemicals is 250 g. If the chemicals are burned in a closed container, which one of the following is true? a) Weight decrease less than 250 g change (250 g) ...
CH 3 power point atomic structure
... ends exactly with a d4 it is an exception to the rule. Thus, Cr should be [Ar] 4s1 3d5. Procedure: Find the closest s orbital. Steal one electron from it, and add it to the d. ...
... ends exactly with a d4 it is an exception to the rule. Thus, Cr should be [Ar] 4s1 3d5. Procedure: Find the closest s orbital. Steal one electron from it, and add it to the d. ...
Atomic Structure and Types of Atoms
... is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most common isotope of carbon has a mass number of 12 (6 protons + 6 neutrons) and may be written as “carbon-12.” Two other isotopes are carbon-13 and carbon-14. As shown in Figure 3, a symbol with the mass number above and the at ...
... is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most common isotope of carbon has a mass number of 12 (6 protons + 6 neutrons) and may be written as “carbon-12.” Two other isotopes are carbon-13 and carbon-14. As shown in Figure 3, a symbol with the mass number above and the at ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
Unit 5 Practice Problems (with answers at end) - H
... 2. When a bond is formed between two atoms, what generally happens to the electron configurations of the atoms? 3. Show the electron dot diagrams for the following covalent compounds or ions: a. PH3 b. H2S c. SiCl4 d. HBr e. SF2 f. ClOBond Energies 4. Use bond energy values found in your text book t ...
... 2. When a bond is formed between two atoms, what generally happens to the electron configurations of the atoms? 3. Show the electron dot diagrams for the following covalent compounds or ions: a. PH3 b. H2S c. SiCl4 d. HBr e. SF2 f. ClOBond Energies 4. Use bond energy values found in your text book t ...
Pre-AP Chemistry - Simple Rules for Electron Exchange Simple
... Simple rules for assigning oxidation numbers Tracking electron gain and loss for simple reactions like metals becoming ionized is easy. But in most chemical reactions, it is impossible to simply look at the reactants and products and track the electron exchange. In those cases, we must do some elect ...
... Simple rules for assigning oxidation numbers Tracking electron gain and loss for simple reactions like metals becoming ionized is easy. But in most chemical reactions, it is impossible to simply look at the reactants and products and track the electron exchange. In those cases, we must do some elect ...
Activity series
... metals in reverse order of reactivity by filling in Table 2b. What criteria did you use for your rankings? ...
... metals in reverse order of reactivity by filling in Table 2b. What criteria did you use for your rankings? ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... new studies are done. Even though no one has ever seen an atom up close we are still able to make new discoveries – just like we have made new discoveries about dinosaurs. ...
... new studies are done. Even though no one has ever seen an atom up close we are still able to make new discoveries – just like we have made new discoveries about dinosaurs. ...
Webquest: Atomic Theories and Models
... couldn't) ultimately you would see individual atoms - objects that could not be divided further (that was the definition of atom). ...
... couldn't) ultimately you would see individual atoms - objects that could not be divided further (that was the definition of atom). ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... new studies are done. Even though no one has ever seen an atom up close we are still able to make new discoveries – just like we have made new discoveries about dinosaurs. ...
... new studies are done. Even though no one has ever seen an atom up close we are still able to make new discoveries – just like we have made new discoveries about dinosaurs. ...
Atomic Structure PP
... Electrons have a mass of almost zero, which means that the mass of each atom results almost entirely from the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is the mass number. It is the larger of the two numbers shown in most periodic tables. ...
... Electrons have a mass of almost zero, which means that the mass of each atom results almost entirely from the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is the mass number. It is the larger of the two numbers shown in most periodic tables. ...
Unit 2: Structure of Matter Content Outline: History of the Atomic
... charge is greater than the smaller negative charges and pulls them in toward the nucleus. ii. More electrons than protons = radii increases (getting larger) because the electrons are farther away from the positive nucleus. iii. The Natural state of atoms has protons = electrons; so atomic radii are ...
... charge is greater than the smaller negative charges and pulls them in toward the nucleus. ii. More electrons than protons = radii increases (getting larger) because the electrons are farther away from the positive nucleus. iii. The Natural state of atoms has protons = electrons; so atomic radii are ...
Exam Review
... c) polyatomic ion d) b or c 24. The most active __ have the highest electronegativities. a) nonmetals b) metalloids c) metals d) noble gases 25. __ compounds have high melting points, conduct electricity in the molten phase, and tend to be soluble in water. a) hydrogen b) metallic c) covalent d) ion ...
... c) polyatomic ion d) b or c 24. The most active __ have the highest electronegativities. a) nonmetals b) metalloids c) metals d) noble gases 25. __ compounds have high melting points, conduct electricity in the molten phase, and tend to be soluble in water. a) hydrogen b) metallic c) covalent d) ion ...
Reactions of Metals and Their Compounds
... I will give you the answer, you have to write the question! For example: Answer = Ms. Lee Question? Who is the most awesome teacher in the world, with beautiful long hair and a wonderful personality. And she is very nice and funny too. ...
... I will give you the answer, you have to write the question! For example: Answer = Ms. Lee Question? Who is the most awesome teacher in the world, with beautiful long hair and a wonderful personality. And she is very nice and funny too. ...
Electron Shells - rlas
... - upwards, downwards, or sideways - electrons can do it. The atomic shell, also called an _________________, is the distance from the nucleus that the electron spins. If you are an electron in the first shell, you are always closer to the nucleus than the electrons in the second shell. Electrons can ...
... - upwards, downwards, or sideways - electrons can do it. The atomic shell, also called an _________________, is the distance from the nucleus that the electron spins. If you are an electron in the first shell, you are always closer to the nucleus than the electrons in the second shell. Electrons can ...
Compounds Power point
... Using the Periodic Table, we can predict an element’s oxidation number. “Oxidation Number” means the charge of an ion (can be + or -), a particle which has gained or lost electrons. A (-) charge = gained electrons A (+) charge = lost electrons ...
... Using the Periodic Table, we can predict an element’s oxidation number. “Oxidation Number” means the charge of an ion (can be + or -), a particle which has gained or lost electrons. A (-) charge = gained electrons A (+) charge = lost electrons ...
AP Chap 2
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, ...
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, ...
PPT
... ►An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of the element. ► Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge. ► Protons and neutrons are present in a dense, positively cha ...
... ►An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of the element. ► Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge. ► Protons and neutrons are present in a dense, positively cha ...
e) an atom is mostly empty space. e) e) 20 protons, 20 neutrons, and
... Ions are formed by changing the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. Ions are formed by removing electrons from a neutral atom. An ion has a positive or negative charge. ...
... Ions are formed by changing the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. Ions are formed by removing electrons from a neutral atom. An ion has a positive or negative charge. ...
8th Grade Post Physical Science Test Study Guide PS 1: The
... Neutrons = neutral charge (found in the nucleus) Electrons = negative charge (found in the electron cloud/orbit) ...
... Neutrons = neutral charge (found in the nucleus) Electrons = negative charge (found in the electron cloud/orbit) ...
-- Chap 11, Atomic Nature of Matter -
... Uncharged particles in the neutron, with mass ~ that of proton. The # of neutrons need not match # of protons in atom, eg. H typically has 1 proton and 0 neutrons, but some H atoms may have 1 neutron, but always 1 proton, (called “heavy hydrogen”) Isotopes = atoms of same element that contain differ ...
... Uncharged particles in the neutron, with mass ~ that of proton. The # of neutrons need not match # of protons in atom, eg. H typically has 1 proton and 0 neutrons, but some H atoms may have 1 neutron, but always 1 proton, (called “heavy hydrogen”) Isotopes = atoms of same element that contain differ ...