Topic 1 notes - A
... 1 unit of charge is 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs. A proton is given a charge of +1 and an electron a charge of -1. All charges are measured in these units. 1 unit of mass is 1.661 x 10-27 kg. This is also not a convenient number, so we use “atomic mass units”. Since the mass of protons and neutrons varies ...
... 1 unit of charge is 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs. A proton is given a charge of +1 and an electron a charge of -1. All charges are measured in these units. 1 unit of mass is 1.661 x 10-27 kg. This is also not a convenient number, so we use “atomic mass units”. Since the mass of protons and neutrons varies ...
Atoms, Molecules, Formula, and Subatomic Particles - Ars
... Subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons, Oh! My! All atoms are composed of at least 1 proton and one electron. Most atoms have at least one neutron. Evidence from the latter part of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th centuries indicated that the atom was not as indestructible ...
... Subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons, Oh! My! All atoms are composed of at least 1 proton and one electron. Most atoms have at least one neutron. Evidence from the latter part of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th centuries indicated that the atom was not as indestructible ...
Parts per million
... *Calculate the amount of substance in a solution of known concentration *Use chemical equations to calculate reacting masses *Use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases *Use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar ...
... *Calculate the amount of substance in a solution of known concentration *Use chemical equations to calculate reacting masses *Use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases *Use chemical equations to calculate volumes of gases and vice versa using the concepts of amount of substance and molar ...
Study Guide –Chapter 4 Atomic Theory and The Atom
... Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. ...
... Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. ...
Chapter 11
... configurations Titanium - 22 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d2 Vanadium - 23 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3 Chromium - 24 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4 is expected But this is wrong!! ...
... configurations Titanium - 22 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d2 Vanadium - 23 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3 Chromium - 24 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4 is expected But this is wrong!! ...
CHEMISTRY
... One element replaces a similar element in a compound Also called displacement Many are in aqueous solutions Less E required The more active element replaces the less active one Most active metals (group 1) react w/water and produce metal hydroxides ...
... One element replaces a similar element in a compound Also called displacement Many are in aqueous solutions Less E required The more active element replaces the less active one Most active metals (group 1) react w/water and produce metal hydroxides ...
08 PowerPoint
... hydrocarbon is hard to tell, but is usually a liquid after C=6 or higher. Most other covalent compounds are gases. Acids (chemicals starting with hydrogen) are always aqueous ...
... hydrocarbon is hard to tell, but is usually a liquid after C=6 or higher. Most other covalent compounds are gases. Acids (chemicals starting with hydrogen) are always aqueous ...
Chapter13
... the d orbitals are half filled so Cr and Cu move things around to make this happen. ...
... the d orbitals are half filled so Cr and Cu move things around to make this happen. ...
System International Base Units
... Ions – are formed from atoms that have lost electrons and become positively charged or atoms that have gained electrons becoming negatively charged Metals form cations (positively charged ions due to loss of their valence electrons) in reaction with nonmetals o For group A metals, their ion charge ...
... Ions – are formed from atoms that have lost electrons and become positively charged or atoms that have gained electrons becoming negatively charged Metals form cations (positively charged ions due to loss of their valence electrons) in reaction with nonmetals o For group A metals, their ion charge ...
Chem 110 Fall 2004 Exam I Key Information You May Need: 100 cm
... produce 6 moles of water and 6 moles of carbon dioxide ...
... produce 6 moles of water and 6 moles of carbon dioxide ...
Review 1
... The calculated density of the figurine is less than the value for silver. This does not conclusively prove the figurine is made of another metal. The figurine could be pure silver but hollow. It also might be an alloy of silver and another, less dense metal. ...
... The calculated density of the figurine is less than the value for silver. This does not conclusively prove the figurine is made of another metal. The figurine could be pure silver but hollow. It also might be an alloy of silver and another, less dense metal. ...
CHEMISTRY
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
CHEMISTRY
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
Chapter 4: Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... 1. For the atoms in a neutral species—an isolated atom, a molecule, or a formula unit—the sum of all the oxidation numbers is 0. 2. For the atoms in an ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge on the ion. 3. In compounds, the group 1A metals all have an oxidation number of + ...
... 1. For the atoms in a neutral species—an isolated atom, a molecule, or a formula unit—the sum of all the oxidation numbers is 0. 2. For the atoms in an ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge on the ion. 3. In compounds, the group 1A metals all have an oxidation number of + ...
Chapter 7
... 7.6 & 7.7: Quantum Numbers & Atomic Orbitals Quantum Numbers: - a series of number that describe the distribution of electrons in hydrogen and other atoms. They are derived from the mathematical solutions of the Schrödinger Wave Equation for the hydrogen atom. There are four sets of quantum numbers ...
... 7.6 & 7.7: Quantum Numbers & Atomic Orbitals Quantum Numbers: - a series of number that describe the distribution of electrons in hydrogen and other atoms. They are derived from the mathematical solutions of the Schrödinger Wave Equation for the hydrogen atom. There are four sets of quantum numbers ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 2
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be appro ...
Unit 13: Electrochemistry (Link to Prentice Hall Text: Chapters 22
... (a) To obtain pure metals Many metals are only found as compounds in nature. Electrolysis can lead to a deposit of the pure metal on the cathode. (b) To recharge a battery A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on t ...
... (a) To obtain pure metals Many metals are only found as compounds in nature. Electrolysis can lead to a deposit of the pure metal on the cathode. (b) To recharge a battery A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on t ...
Unit 1 - doctortang.com
... alchemists. Their purpose was to find a chemical recipe to make gold from other less valuable metals. (We now know that it is only possible now if we can change the number of protons in the nucleus). In 1808, a British scientist by the name of John Dalton published his theory of atoms that would hav ...
... alchemists. Their purpose was to find a chemical recipe to make gold from other less valuable metals. (We now know that it is only possible now if we can change the number of protons in the nucleus). In 1808, a British scientist by the name of John Dalton published his theory of atoms that would hav ...
Chapter 6 ppt
... The Parts of an Atom, continued • The charges of protons and electrons are opposite but equal, so the charges cancel out. If the numbers of electrons and protons become unequal, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ion. • The SI unit that is used to express the mass of a particle in an atom ...
... The Parts of an Atom, continued • The charges of protons and electrons are opposite but equal, so the charges cancel out. If the numbers of electrons and protons become unequal, the atom becomes a charged particle called an ion. • The SI unit that is used to express the mass of a particle in an atom ...
Atomic Mass - Warren County Schools
... • I can determine the atomic composition of atoms when I know the atomic mass and atomic #. • I can recognize that the periodic table is organized by an element’s atomic number. • I can divide the elements in the periodic table into periods and groups. • I can identify and distinguish between metals ...
... • I can determine the atomic composition of atoms when I know the atomic mass and atomic #. • I can recognize that the periodic table is organized by an element’s atomic number. • I can divide the elements in the periodic table into periods and groups. • I can identify and distinguish between metals ...
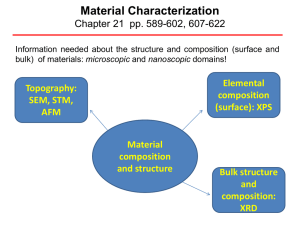
Material Characterization
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
Chapter 10 - Chemical Reactions
... However, you should be familiar with the rules which describe balanced chemical reactions. 1. Number of Atoms of each element conserved in reactants and products 2. Cannot change formula of reactants or products 3. Can only change coefficients to balance equation Hints to help in balancing equations ...
... However, you should be familiar with the rules which describe balanced chemical reactions. 1. Number of Atoms of each element conserved in reactants and products 2. Cannot change formula of reactants or products 3. Can only change coefficients to balance equation Hints to help in balancing equations ...
Document
... How Many Grams of N2(g) Can Be Made from 9.05 g of NH3 Reacting with 45.2 g of CuO? 2 NH3(g) + 3 CuO(s) → N2(g) + 3 Cu(s) + 3 H2O(l) If 4.61 g of N2 Are Made, What Is the Percent Yield? ...
... How Many Grams of N2(g) Can Be Made from 9.05 g of NH3 Reacting with 45.2 g of CuO? 2 NH3(g) + 3 CuO(s) → N2(g) + 3 Cu(s) + 3 H2O(l) If 4.61 g of N2 Are Made, What Is the Percent Yield? ...