O - gearju.com
... At this stage of learning, you should realize that both representations are valid Lewis structures and you should be able to draw both types of structures. One helpful rule is that in trying to minimize formal charges by expanding the central atom’s octet, only add enough double bonds to make the fo ...
... At this stage of learning, you should realize that both representations are valid Lewis structures and you should be able to draw both types of structures. One helpful rule is that in trying to minimize formal charges by expanding the central atom’s octet, only add enough double bonds to make the fo ...
O - gearju.com
... At this stage of learning, you should realize that both representations are valid Lewis structures and you should be able to draw both types of structures. One helpful rule is that in trying to minimize formal charges by expanding the central atom’s octet, only add enough double bonds to make the fo ...
... At this stage of learning, you should realize that both representations are valid Lewis structures and you should be able to draw both types of structures. One helpful rule is that in trying to minimize formal charges by expanding the central atom’s octet, only add enough double bonds to make the fo ...
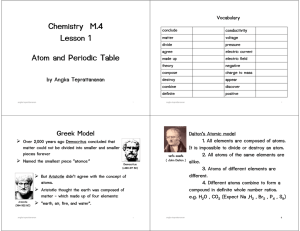
Chemistry M.4 Lesson 1 Atom and Periodic Table
... the exact location of an electron only predict where is could be based on how much energy it has. ...
... the exact location of an electron only predict where is could be based on how much energy it has. ...
Chapter 4 2013
... 2. NO3-, CH3COO- or C2H3O2- , ClO43. Cl-, Br- I- except those of Ag+, Pb2+, Cu+, and Hg22+. ...
... 2. NO3-, CH3COO- or C2H3O2- , ClO43. Cl-, Br- I- except those of Ag+, Pb2+, Cu+, and Hg22+. ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Base your answers to questions 74 through 76 on the passage below. Acid rain is a problem in industrialized countries around the world. Oxides of sulfur and nitrogen are formed when various fuels are burned. These oxides dissolve in atmospheric water droplets that fall to earth as acid rain or acid ...
... Base your answers to questions 74 through 76 on the passage below. Acid rain is a problem in industrialized countries around the world. Oxides of sulfur and nitrogen are formed when various fuels are burned. These oxides dissolve in atmospheric water droplets that fall to earth as acid rain or acid ...
B - Cloudfront.net
... This is the mass number of the atom. The mass number tells you which isotope of the element the atom belongs to. If the mass number is very close to the average atomic mass of the element, the atom probably isn’t radioactive. If the mass number of the atom is substantially different from the average ...
... This is the mass number of the atom. The mass number tells you which isotope of the element the atom belongs to. If the mass number is very close to the average atomic mass of the element, the atom probably isn’t radioactive. If the mass number of the atom is substantially different from the average ...
Chemical Reactions
... Burning butane in a cigarette lighter Burning gas in a gas hob Reacting an acid and alkali together Burning magnesium Rotting compost etc etc © Boardworks Ltd 2003 ...
... Burning butane in a cigarette lighter Burning gas in a gas hob Reacting an acid and alkali together Burning magnesium Rotting compost etc etc © Boardworks Ltd 2003 ...
Chemical Reactions
... in the direction that removes heat from the system (In the above reaction you would decrease the amount of ...
... in the direction that removes heat from the system (In the above reaction you would decrease the amount of ...
UNIT 3 - ATOMS 1 HISTORY OF ATOMIC THEORY NOTES I
... When we want to know how many atoms of a substance are in a sample of the substance that we can see, counting the atoms individually is not practical. First of all, atoms are so small that we cannot see them individually with our eyes. Second, we would be counting for a very, very, very long time. H ...
... When we want to know how many atoms of a substance are in a sample of the substance that we can see, counting the atoms individually is not practical. First of all, atoms are so small that we cannot see them individually with our eyes. Second, we would be counting for a very, very, very long time. H ...
The Bio-Organometallic Chemistry of Technetium and Rhenium
... Given its central position in the periodic table, it is not surprising that the chemistry of technetium, the most widely used element in diagnostic medicine, is so diverse. Compounds of technetium exist in oxidation states from -I to +VII consisting of ligands that are as simple as hydride (H-) to m ...
... Given its central position in the periodic table, it is not surprising that the chemistry of technetium, the most widely used element in diagnostic medicine, is so diverse. Compounds of technetium exist in oxidation states from -I to +VII consisting of ligands that are as simple as hydride (H-) to m ...
Chemistry(Class-IX)- Atoms and Molecules
... elements are taken from their Greek or Latin names. Symbol of some element which are derived from their Latin name ...
... elements are taken from their Greek or Latin names. Symbol of some element which are derived from their Latin name ...
lecture slides file
... color, density, taste/odor, melting/boiling point). Chemical properties describe the ability of the substance to form new substances, either by decomposition or reaction with other substances (corrosiveness, ...
... color, density, taste/odor, melting/boiling point). Chemical properties describe the ability of the substance to form new substances, either by decomposition or reaction with other substances (corrosiveness, ...
Ch 38 Powerpoint
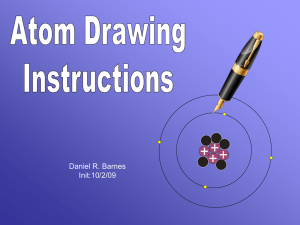
... This added electron makes the atom electrically neutral. The two electrons assume an orbit characteristic of helium. In a lithium atom, an additional proton pulls the electrons into an even closer orbit and holds a third electron in a second orbit. ...
... This added electron makes the atom electrically neutral. The two electrons assume an orbit characteristic of helium. In a lithium atom, an additional proton pulls the electrons into an even closer orbit and holds a third electron in a second orbit. ...
GCSE ADDITIONAL CHEMISTRY (C2) REVISION BOOKLET
... i) The first level is filled with electrons first and then the second and third ones. j) When atoms bond with other atoms, the number of electrons in their outermost energy level changes. 2 a) In ionic bonding, electrons from one atom are transferred/given to another. b) The charged particles formed ...
... i) The first level is filled with electrons first and then the second and third ones. j) When atoms bond with other atoms, the number of electrons in their outermost energy level changes. 2 a) In ionic bonding, electrons from one atom are transferred/given to another. b) The charged particles formed ...
Balancing and Predicting Chemical Reactions:
... metals are commonly referred to as the “coinage metals”. Why would these metals be chosen over more active metals for use in coins? Why do you think some more active metals, such as zinc or nickel, are sometimes used in coins? ...
... metals are commonly referred to as the “coinage metals”. Why would these metals be chosen over more active metals for use in coins? Why do you think some more active metals, such as zinc or nickel, are sometimes used in coins? ...
Lecture 1 - Алтайский государственный технический
... and 8 neutrons (8=14-6). This isotope is also known simply as "carbon 14". Carbon 12 is the most common form of carbon (~99% of all carbon). An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. Since all atoms are composed of protons, electrons and neutrons, all chemical and physical differences betw ...
... and 8 neutrons (8=14-6). This isotope is also known simply as "carbon 14". Carbon 12 is the most common form of carbon (~99% of all carbon). An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. Since all atoms are composed of protons, electrons and neutrons, all chemical and physical differences betw ...
No Slide Title
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
chemical reaction
... • How to Balance an Equation To balance an equation, you must use coefficients. A coefficient is a number that is placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula. • For an equation to be balanced, all atoms must be counted. So, you multiply the subscript of each element in a formula by the formula’s ...
... • How to Balance an Equation To balance an equation, you must use coefficients. A coefficient is a number that is placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula. • For an equation to be balanced, all atoms must be counted. So, you multiply the subscript of each element in a formula by the formula’s ...
6.1. Define and calculate kinetic and potential energy.
... • Work is defined as a force (which moves an object) x distance moved • w=Fxd • Pressure volume work is most common in chemical systems (PV work) • In a chemical reaction, if the number of moles of gas increases, ∆V >0 thus P∆V > 0 and work will w < 0 . Work is done by the system ...
... • Work is defined as a force (which moves an object) x distance moved • w=Fxd • Pressure volume work is most common in chemical systems (PV work) • In a chemical reaction, if the number of moles of gas increases, ∆V >0 thus P∆V > 0 and work will w < 0 . Work is done by the system ...
NCERT Solution - Mywayteaching
... forces in oxygen are weak van der Wall’s, which cause it to exist as gas. On the other ...
... forces in oxygen are weak van der Wall’s, which cause it to exist as gas. On the other ...
Chemistry Comes Alive
... As a rule, the atomic weight of an element is approximately equal to the mass number of its most abundant isotope. Chapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive ...
... As a rule, the atomic weight of an element is approximately equal to the mass number of its most abundant isotope. Chapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... 11) An atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. How many unpaired electrons does it have? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) 6 E) 2 or 4 12) The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 is heavier than nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains how many neutrons? A) 6 B) 7 C) 8 D) 12 E) 14 13 ...
... 11) An atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. How many unpaired electrons does it have? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) 6 E) 2 or 4 12) The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 is heavier than nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains how many neutrons? A) 6 B) 7 C) 8 D) 12 E) 14 13 ...
Atoms - Peoria Public Schools
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in si ...
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in si ...
Structure and Bonding
... Delocalization occurs in 1,3-butadiene where there are alternating single and double bonds. All four carbons in 1,3-butadiene are sp2 hybridized and so each of these carbons has a half-filled p orbital which can interact to give two π bonds. However, a certain amount of overlap is also possible be ...
... Delocalization occurs in 1,3-butadiene where there are alternating single and double bonds. All four carbons in 1,3-butadiene are sp2 hybridized and so each of these carbons has a half-filled p orbital which can interact to give two π bonds. However, a certain amount of overlap is also possible be ...