Chapter 33: The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... consist of negatively charged electrons. Gamma rays are uncharged photons of light. A magnetic field will apply a force to a moving charged particle. Positively charged particles are accelerated in one direction and negative charged particles are accelerated in the opposite direction. Because gamma ...
... consist of negatively charged electrons. Gamma rays are uncharged photons of light. A magnetic field will apply a force to a moving charged particle. Positively charged particles are accelerated in one direction and negative charged particles are accelerated in the opposite direction. Because gamma ...
Modeling Radioactive and Stable Atoms
... An atom is made up of three subatomic particles -- protons, neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom, called the nucleus, is composed of protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged, neutrons have no charge at all and electrons are negatively charged. The proton-to-electron ratio is ge ...
... An atom is made up of three subatomic particles -- protons, neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom, called the nucleus, is composed of protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged, neutrons have no charge at all and electrons are negatively charged. The proton-to-electron ratio is ge ...
Document
... X is single complex doublet of fundamental scalars, predicting the existence of a new particle, the HIGGS BOSON. At the same time massive vector bosons are quantized without spoiling renormalizability and unitarity. ...
... X is single complex doublet of fundamental scalars, predicting the existence of a new particle, the HIGGS BOSON. At the same time massive vector bosons are quantized without spoiling renormalizability and unitarity. ...
Quark Gluon Plasma: the Hottest Matter on Earth
... • vn does not have significant beam energy dependence • Hydro dynamical behavior down to 39 GeV ...
... • vn does not have significant beam energy dependence • Hydro dynamical behavior down to 39 GeV ...
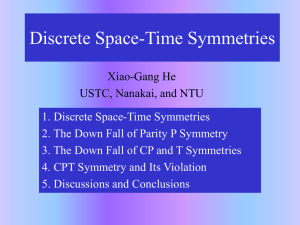
CHAPTER 14: Elementary Particles
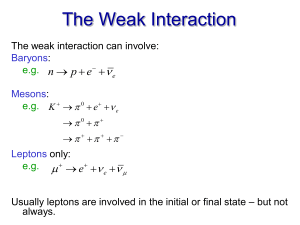
... act through the strong force. Two classes of hadrons: mesons and baryons. Mesons are particles with integral spin having masses greater than that of the muon (106 MeV/c2). (Mesons are made up of pairs of quarks—a quark and an anti-quark.) They’re unstable and rare. Baryons have masses at least as la ...
... act through the strong force. Two classes of hadrons: mesons and baryons. Mesons are particles with integral spin having masses greater than that of the muon (106 MeV/c2). (Mesons are made up of pairs of quarks—a quark and an anti-quark.) They’re unstable and rare. Baryons have masses at least as la ...
The Modification of Boundary Treatment in the Incompressible SPH
... are using pseudo Neumann condition and proposed MVMRG boundary treatment. This test was conducted to show the robustness of our modified boundary treatment. The tank was filled up with the water height of 0.2m and the particles size is 0.01m. Where, the point of pressure measurement is located in th ...
... are using pseudo Neumann condition and proposed MVMRG boundary treatment. This test was conducted to show the robustness of our modified boundary treatment. The tank was filled up with the water height of 0.2m and the particles size is 0.01m. Where, the point of pressure measurement is located in th ...
Document
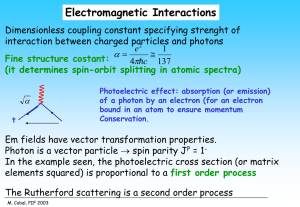
... • At low q2 (= larger distances) the coupling becomes large and the theory is not calculable. This large-distance behavior is linked with confinement of quarks and gluons inside hadrons. • Potential between two quarks often taken as: ...
... • At low q2 (= larger distances) the coupling becomes large and the theory is not calculable. This large-distance behavior is linked with confinement of quarks and gluons inside hadrons. • Potential between two quarks often taken as: ...
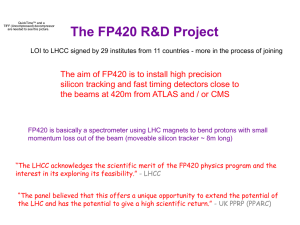
Understanding the Universe from Deep Underground
... •They only stop if they hit the nucleus of an atom or an electron head-on and can pass through a million billion kilometers of lead without stopping. They only feel the Weak Force. • Therefore they are very difficult to detect and their properties have been the least known among the basic particles. ...
... •They only stop if they hit the nucleus of an atom or an electron head-on and can pass through a million billion kilometers of lead without stopping. They only feel the Weak Force. • Therefore they are very difficult to detect and their properties have been the least known among the basic particles. ...
Pharmaceutical suspension
... Viscosity of suspensions is of great importance for stability and pourability of suspensions. As we know suspensions have least physical stability amongst all dosage forms due to sedimentation and cake formation. • So as the viscosity of the dispersion medium increases, the terminal settling velocit ...
... Viscosity of suspensions is of great importance for stability and pourability of suspensions. As we know suspensions have least physical stability amongst all dosage forms due to sedimentation and cake formation. • So as the viscosity of the dispersion medium increases, the terminal settling velocit ...
Linear Momentum
... external impulsive force on the ball and changes its momentum. The acceleration of the ball is greater because its mass is smaller. ...
... external impulsive force on the ball and changes its momentum. The acceleration of the ball is greater because its mass is smaller. ...
ATLAS experiment

ATLAS (A Toroidal LHC ApparatuS) is one of the seven particle detector experiments (ALICE, ATLAS, CMS, TOTEM, LHCb, LHCf and MoEDAL) constructed at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), a particle accelerator at CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research) in Switzerland. The experiment is designed to take advantage of the unprecedented energy available at the LHC and observe phenomena that involve highly massive particles which were not observable using earlier lower-energy accelerators. It is hoped that it will shed light on new theories of particle physics beyond the Standard Model.ATLAS is 46 metres long, 25 metres in diameter, and weighs about 7,000 tonnes; it contains some 3000 km of cable. The experiment is a collaboration involving roughly 3,000 physicists from over 175 institutions in 38 countries. The project was led for the first 15 years by Peter Jenni and between 2009 and 2013 was headed by Fabiola Gianotti. Since 2013 it has been headed by David Charlton. It was one of the two LHC experiments involved in the discovery of a particle consistent with the Higgs boson in July 2012.