Example: Trend 2– Ionization Energy
... • Measures as distance from nucleus to the outermost electron • Unit commonly used is pm – picometer= 10-12m ...
... • Measures as distance from nucleus to the outermost electron • Unit commonly used is pm – picometer= 10-12m ...
Unit 2
... 45. The atomic radius generally increases with atomic number in a particular group of elements. The dominant factor that determines this variation is the _____ A. addition of energy levels. B. increase in the number of neutrons. C. formation of anew octet. D. increase in nuclear charge. 46. One-half ...
... 45. The atomic radius generally increases with atomic number in a particular group of elements. The dominant factor that determines this variation is the _____ A. addition of energy levels. B. increase in the number of neutrons. C. formation of anew octet. D. increase in nuclear charge. 46. One-half ...
Periodic table and the atom
... combine together in fixed ratios, so he developed a theory Results = Theory states: Each element has its own atoms which can rearrange/recombine with other atoms in chemical reactions. Idea of the atom = SOLID SPHERE ...
... combine together in fixed ratios, so he developed a theory Results = Theory states: Each element has its own atoms which can rearrange/recombine with other atoms in chemical reactions. Idea of the atom = SOLID SPHERE ...
atomic mass - ImlerBiology
... The number of protons and electrons in most atoms are equal giving the atom a net charge of zero. Periodic Table – the periodic table of elements is used to group elements according to their characteristics. Each element has a number and a symbol. ...
... The number of protons and electrons in most atoms are equal giving the atom a net charge of zero. Periodic Table – the periodic table of elements is used to group elements according to their characteristics. Each element has a number and a symbol. ...
Chapter 5
... • Example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 • Both have an atomic number of 6, but the mass numbers are different ...
... • Example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 • Both have an atomic number of 6, but the mass numbers are different ...
The Periodic Table
... toward NE corner of PT since these atoms have a great affinity (“love and happiness”) for e-. (Think of “Jumping for Joy”!) • What happens down a group? • Decreases; since the electrons are further from the nucleus, the atom has no desire to hang on to it’s electron, so it won’t release too much “Ha ...
... toward NE corner of PT since these atoms have a great affinity (“love and happiness”) for e-. (Think of “Jumping for Joy”!) • What happens down a group? • Decreases; since the electrons are further from the nucleus, the atom has no desire to hang on to it’s electron, so it won’t release too much “Ha ...
Atomic Theories
... • Performed the gold foil experiment to discover the positively charged nucleus • He shot a beam of alpha particles at a piece of gold foil, while most went through, there were some that got scattered in every direction • Pg. 104 ...
... • Performed the gold foil experiment to discover the positively charged nucleus • He shot a beam of alpha particles at a piece of gold foil, while most went through, there were some that got scattered in every direction • Pg. 104 ...
Name: Date: Period: Page # Evolution of Atomic Theory (Changed
... Atomic Theory Ancient Greeks were the first to think about the nature of _____________ Democritus proposed the idea of matter as small ____________ _________: the smallest particle of an element As more evidence was collected over time, the theory and models were ________ ...
... Atomic Theory Ancient Greeks were the first to think about the nature of _____________ Democritus proposed the idea of matter as small ____________ _________: the smallest particle of an element As more evidence was collected over time, the theory and models were ________ ...
AP Chapter 2 Outline 2014
... iii) Oxyanions: -ate vs. –ite; per vs. hypo iv) Hydrogen-containing polyatomics: add the word hydrogen (1) Older naming system: use the prefix biv) Further reading on acid nomenclature is available at this link vi) Naming binary molecular compounds (1) The name of the element farther to the left in ...
... iii) Oxyanions: -ate vs. –ite; per vs. hypo iv) Hydrogen-containing polyatomics: add the word hydrogen (1) Older naming system: use the prefix biv) Further reading on acid nomenclature is available at this link vi) Naming binary molecular compounds (1) The name of the element farther to the left in ...
Chapter 3, Section 1 Inside an Atom
... number of protons. The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in that element. The atomic number is a unique identifying characteristic. ...
... number of protons. The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in that element. The atomic number is a unique identifying characteristic. ...
Ch. 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) Teacher Relearn
... Balancing Equations: “Helpful Hints” a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound ________. last ...
... Balancing Equations: “Helpful Hints” a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound ________. last ...
Notetaking Workshee
... A. The Periodic Table. (Periodic means ______________________________. 1. In the 1800’s, Dmitri _________________________, a Russian chemist devised the first periodic table based on ___________ __________________________________. 2. In the ___________________________________, the elements are arran ...
... A. The Periodic Table. (Periodic means ______________________________. 1. In the 1800’s, Dmitri _________________________, a Russian chemist devised the first periodic table based on ___________ __________________________________. 2. In the ___________________________________, the elements are arran ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... Covalent compound – a compound formed between two or more non-metals with bonds that are formed by sharing electrons. Metallic compound – a compound formed between metals with bonds that consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. ...
... Covalent compound – a compound formed between two or more non-metals with bonds that are formed by sharing electrons. Metallic compound – a compound formed between metals with bonds that consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. ...
2. atom - New Hartford Central Schools
... -Atoms with the same atomic number, but different mass number -same bottom, different top -differ in the number of neutrons ...
... -Atoms with the same atomic number, but different mass number -same bottom, different top -differ in the number of neutrons ...
Electron Arrangement
... Atomic Number • Moseley, in an experiment called the X-ray tube experiment, determined that each element has a different and unique number of protons. • The number of protons is referred to as the element’s atomic number. • The atomic number can be used to identify the element. • Atomic Number = # ...
... Atomic Number • Moseley, in an experiment called the X-ray tube experiment, determined that each element has a different and unique number of protons. • The number of protons is referred to as the element’s atomic number. • The atomic number can be used to identify the element. • Atomic Number = # ...
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table - (Home) Collinsville Public
... energy - energy required to completely remove e- (from gaseous atom) energy required to remove only 1st ecalled first ionization energy. ...
... energy - energy required to completely remove e- (from gaseous atom) energy required to remove only 1st ecalled first ionization energy. ...
Atoms and elements Metals and non-metals
... 2. Work out which group the element is in and draw that number of electrons in the outer circle – with eight for Group 0 elements – except helium. 3. Fill the other circles with as many electrons as needed. Remember – two in the first circle, and eight in the second and third circles. 4. Finally, ch ...
... 2. Work out which group the element is in and draw that number of electrons in the outer circle – with eight for Group 0 elements – except helium. 3. Fill the other circles with as many electrons as needed. Remember – two in the first circle, and eight in the second and third circles. 4. Finally, ch ...
Measurement of the half-life of
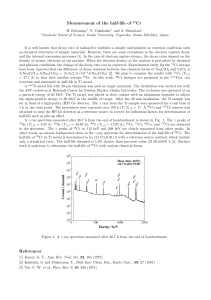
... the AVF cyclotron at Research Center for Nuclear Physics, Osaka University. The cyclotron was operated at an α-particle energy of 40 MeV. The Ti target was placed in close contact with an aluminium degrader to adjust the alpha-particle energy to 30 MeV in the middle of target. After the 30 min irrad ...
... the AVF cyclotron at Research Center for Nuclear Physics, Osaka University. The cyclotron was operated at an α-particle energy of 40 MeV. The Ti target was placed in close contact with an aluminium degrader to adjust the alpha-particle energy to 30 MeV in the middle of target. After the 30 min irrad ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...