Atoms and Elements
... atom, J.J. Thomson’s Plum Pudding model, Rutherford’s Nuclear model of the atom, the Bohr’s Quantum (orbit) model that mathematically only works for one electron systems and the Orbital Wave Mechanical model. The first three models are found in Chapter 4 while the last two are found in Chapters 9. Y ...
... atom, J.J. Thomson’s Plum Pudding model, Rutherford’s Nuclear model of the atom, the Bohr’s Quantum (orbit) model that mathematically only works for one electron systems and the Orbital Wave Mechanical model. The first three models are found in Chapter 4 while the last two are found in Chapters 9. Y ...
Unit 2 Notes Name - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... atomic number: the identity of an atom is based on the number of protons in its nucleus. (This works because the nucleus cannot be given to or shared with another atom.) The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. Each element has a unique atomic number. mass number: the mass of an at ...
... atomic number: the identity of an atom is based on the number of protons in its nucleus. (This works because the nucleus cannot be given to or shared with another atom.) The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. Each element has a unique atomic number. mass number: the mass of an at ...
Chapter 2. The Chemical Context of Life
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
Name the three parts of an atom and where they are located
... The mass of an atom; the # protons + # of neutrons What parts of the atom account for the atomic mass? protons & neutrons What is an isotope? An atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Are isotopes always the same element? Why? Yes, the # of protons determines an ...
... The mass of an atom; the # protons + # of neutrons What parts of the atom account for the atomic mass? protons & neutrons What is an isotope? An atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons Are isotopes always the same element? Why? Yes, the # of protons determines an ...
Atomic Model Power Point
... concluded that they were composed of positive particles. • These positive particles are called ...
... concluded that they were composed of positive particles. • These positive particles are called ...
Atoms & Mass Spectrometry
... emitted by nuclei with too many protons. Beta (): electrons are ejected (owing to neutron decay) from nuclei with too many neutrons. Gamma (): rays that are a high-energy form of electromagnetic ration. ...
... emitted by nuclei with too many protons. Beta (): electrons are ejected (owing to neutron decay) from nuclei with too many neutrons. Gamma (): rays that are a high-energy form of electromagnetic ration. ...
e - Humble ISD
... He fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. He found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit and bounced back. ...
... He fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. He found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit and bounced back. ...
bluevale collegiate institute
... Elements in the same horizontal row on the periodic table... A) are members of the same family. C) have the same number of electron shells B) have the same number of outer shell electrons. D) have similar chemical properties. ...
... Elements in the same horizontal row on the periodic table... A) are members of the same family. C) have the same number of electron shells B) have the same number of outer shell electrons. D) have similar chemical properties. ...
Definitions - Loreto Science
... The first ionisation energy of an atom • is the minimum energy required to completely remove the most loosely bound electron from a neutral gaseous atom in the ground state.****** ...
... The first ionisation energy of an atom • is the minimum energy required to completely remove the most loosely bound electron from a neutral gaseous atom in the ground state.****** ...
Atomic Theory: History - stpats-sch4u-sem1-2013
... Rules for drawing energy-level diagrams: 1. Start adding electrons into the lowest energy level and build up form the bottom until the limit on the number of electrons for the particle is reached. 2. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers; if an electron is in the same orbital with ...
... Rules for drawing energy-level diagrams: 1. Start adding electrons into the lowest energy level and build up form the bottom until the limit on the number of electrons for the particle is reached. 2. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers; if an electron is in the same orbital with ...
Name: Date: ______ Current Atomic Models Refining Nuclear
... • Electrons act like __________ (because they have a mass) and _________ (because they have certain frequencies corresponding to their energy levels) • Electrons are located in orbitals around the nucleus that correspond to specific energy levels • Electron clouds = orbitals that do not have sharp b ...
... • Electrons act like __________ (because they have a mass) and _________ (because they have certain frequencies corresponding to their energy levels) • Electrons are located in orbitals around the nucleus that correspond to specific energy levels • Electron clouds = orbitals that do not have sharp b ...
Bohr awarded Nobel prize for physics in 1922
... increased in intensity of reactions c. Conclusion >> Slow Neutrons are better at causing fissions d. This is because slow neutrons are unrepelled by the nucleus and spend greater time in vicinity of nucleus >> more chance of being captured 3. Lise Meitner and Frisch Strassman Identify Fission a. Mei ...
... increased in intensity of reactions c. Conclusion >> Slow Neutrons are better at causing fissions d. This is because slow neutrons are unrepelled by the nucleus and spend greater time in vicinity of nucleus >> more chance of being captured 3. Lise Meitner and Frisch Strassman Identify Fission a. Mei ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... Democritus (400 BC) first suggests the idea of the atom. Atom is a Greek word meaning “indivisible”. Aristotle, however, did not believe in atoms. He thought all matter was continuous. Democritus does not get credit for discovering the atom because he had no scientific evidence to back it up. ...
... Democritus (400 BC) first suggests the idea of the atom. Atom is a Greek word meaning “indivisible”. Aristotle, however, did not believe in atoms. He thought all matter was continuous. Democritus does not get credit for discovering the atom because he had no scientific evidence to back it up. ...
Date: ______ Current Atomic Models Refining Nuclear Models • In
... • Electrons act like __________ (because they have a mass) and _________ (because they have certain frequencies corresponding to their energy levels) • Electrons are located in orbitals around the nucleus that correspond to specific energy levels • Electron clouds = orbitals that do not have sharp b ...
... • Electrons act like __________ (because they have a mass) and _________ (because they have certain frequencies corresponding to their energy levels) • Electrons are located in orbitals around the nucleus that correspond to specific energy levels • Electron clouds = orbitals that do not have sharp b ...
Atomic Theory - St John Brebeuf
... scientists in specific ! Theories in science are proposed to explain the evidence available at the time. As new evidence is discovered, theories are adapted to explain new data. ...
... scientists in specific ! Theories in science are proposed to explain the evidence available at the time. As new evidence is discovered, theories are adapted to explain new data. ...
Interesting and Helpful Websites Early Models of the Atom
... Rutherford (1871 to 1937) Schrodinger (1887 to 1961) ...
... Rutherford (1871 to 1937) Schrodinger (1887 to 1961) ...
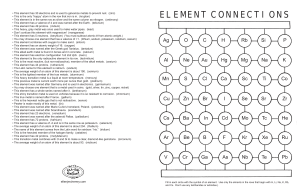
element connections
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... have the same number of protons, but have different numbers of neutrons. Radioisotopes – radioactive decay The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay is called its half-life. ...
... have the same number of protons, but have different numbers of neutrons. Radioisotopes – radioactive decay The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay is called its half-life. ...
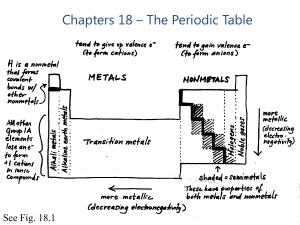
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... The head of "strike anywhere" matches contain an oxidizing agent such as potassium chlorate together with tetraphosphorus trisulfide (P4S3), glass and binder. The phosphorus sulfide is easily ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to bu ...
... The head of "strike anywhere" matches contain an oxidizing agent such as potassium chlorate together with tetraphosphorus trisulfide (P4S3), glass and binder. The phosphorus sulfide is easily ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to bu ...
View PDF
... b. collide with other electrons. c. move from higher to lower energy levels. d. collide with the nucleus. ...
... b. collide with other electrons. c. move from higher to lower energy levels. d. collide with the nucleus. ...
Chemistry I - Palisades High School
... element theory. • Antoine Lavoisier – 1770’s: His greatest contributions were the co-discovery of oxygen, gunpowder manufacture, and law of conservation of mass. • Sir Isaac Newton – 1642 – 1727: He freed science from “Godlessness” as it was thought of by the church. ...
... element theory. • Antoine Lavoisier – 1770’s: His greatest contributions were the co-discovery of oxygen, gunpowder manufacture, and law of conservation of mass. • Sir Isaac Newton – 1642 – 1727: He freed science from “Godlessness” as it was thought of by the church. ...
Unit 2 * Chapter 11 - Dr. Wall`s Science
... – Nucleus will DECAY over time – This is called radioactivity – Spontaneous – Gives off energy and particles ...
... – Nucleus will DECAY over time – This is called radioactivity – Spontaneous – Gives off energy and particles ...
Regents Chemistry Review Questions
... What is the chemical formula for ammonia? Is it an acid or a base? Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between carbonic acid and magnesium hydroxide. Name the salt that is produced in this reaction. Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization re ...
... What is the chemical formula for ammonia? Is it an acid or a base? Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between carbonic acid and magnesium hydroxide. Name the salt that is produced in this reaction. Write and balance the chemical equation for the neutralization re ...
Evolution of Atomic Models
... -Energy is lost and gained -Not always the same (depends on energy level -higher energy level = less distance between energy levels thus less energy is required to move from one level to the next -lower energy levels have greater distance between them = more energy to transfer between levels) ...
... -Energy is lost and gained -Not always the same (depends on energy level -higher energy level = less distance between energy levels thus less energy is required to move from one level to the next -lower energy levels have greater distance between them = more energy to transfer between levels) ...