Law of Physics
... • Atomic number determines which element • Mass number determines the isotope-same atomic number, different mass because of amount of neutrons. • There is usually more than one type of isotope for all atoms ...
... • Atomic number determines which element • Mass number determines the isotope-same atomic number, different mass because of amount of neutrons. • There is usually more than one type of isotope for all atoms ...
Bohr model
... Shell model of the atom Bohr extended the model of Hydrogen to give an approximate model for heavier atoms. This gave a physical picture which reproduced many known atomic properties for the first time. Heavier atoms have more protons in the nucleus, and more electrons to cancel the charge. Bohr's i ...
... Shell model of the atom Bohr extended the model of Hydrogen to give an approximate model for heavier atoms. This gave a physical picture which reproduced many known atomic properties for the first time. Heavier atoms have more protons in the nucleus, and more electrons to cancel the charge. Bohr's i ...
Chapter 3
... is called the Balmer series. The energies of these emissions just happen to be in the visible range so we can see the colors. ...
... is called the Balmer series. The energies of these emissions just happen to be in the visible range so we can see the colors. ...
Word List
... 1.1 I can write the names and symbols of the elements in columns 1A – 4A on the periodic table. 1.5 I can write the names and symbols of the elements in columns 5A- 8A on the periodic table. 1.12 I can write the names and symbols of selected transition metals, lanthanides and actinides (1B12B) on th ...
... 1.1 I can write the names and symbols of the elements in columns 1A – 4A on the periodic table. 1.5 I can write the names and symbols of the elements in columns 5A- 8A on the periodic table. 1.12 I can write the names and symbols of selected transition metals, lanthanides and actinides (1B12B) on th ...
Electricity Principles
... An atom is the smallest unit of a natural element, or an element is a substance consisting of a large number of the same atom. Combinations of elements are known as Compounds and the smallest unit of a compound is called a Molecule. Water is an example of a liquid compound in which the Molecule ...
... An atom is the smallest unit of a natural element, or an element is a substance consisting of a large number of the same atom. Combinations of elements are known as Compounds and the smallest unit of a compound is called a Molecule. Water is an example of a liquid compound in which the Molecule ...
We cannot see an individual atom
... A given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process they were indivisible. A chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped together. ...
... A given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process they were indivisible. A chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped together. ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... NOTE: There are eleven more points/questions that are based on reaction rates Final Exam is six pages and has 60 question: 109 points possible = 100 points + 9 Extra Credit ...
... NOTE: There are eleven more points/questions that are based on reaction rates Final Exam is six pages and has 60 question: 109 points possible = 100 points + 9 Extra Credit ...
Measuring and Calculating
... Nonpolar covalent bond – very low electronegativity difference, results in a nearly equal sharing of the electron pair and thus no partial charge development, (often C-H) example: nonpolar covalent bonds are found in methane, CH 4, and nitrogen, N2. Polar covalent bond – larger electronegativity ...
... Nonpolar covalent bond – very low electronegativity difference, results in a nearly equal sharing of the electron pair and thus no partial charge development, (often C-H) example: nonpolar covalent bonds are found in methane, CH 4, and nitrogen, N2. Polar covalent bond – larger electronegativity ...
المرحلة الثانية / فيزياء المحاضرة الثامنة E
... uncuttable, or indivisible, something that cannot be divided further. The concept of an atom as an indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosophers. In the 17th and 18th centuries, chemists provided a physical basis for this idea by showing that certain subst ...
... uncuttable, or indivisible, something that cannot be divided further. The concept of an atom as an indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosophers. In the 17th and 18th centuries, chemists provided a physical basis for this idea by showing that certain subst ...
Review Unit - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ◘ The modern periodic table arranges the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ◘ Metals are separated from nonmetals by the “staircase line”. metals - shiny, malleable, ductile, conductors of heat and electricity. ◘ The columns are families (groups) of elements having similar chemical prope ...
... ◘ The modern periodic table arranges the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ◘ Metals are separated from nonmetals by the “staircase line”. metals - shiny, malleable, ductile, conductors of heat and electricity. ◘ The columns are families (groups) of elements having similar chemical prope ...
Chemistry: Nuclear Theory
... Uranium 234 is an isotope of Uranium ( 238U) that weighs 234 AMUs. It must have 92 protons to be Uranium, but it weighs about 4 AMUs less. This change in weight comes from having 4 fewer neutrons. Uranium usually has 146 neutrons, so 92234U must have 142 neutrons. Ions are atoms whose number of ...
... Uranium 234 is an isotope of Uranium ( 238U) that weighs 234 AMUs. It must have 92 protons to be Uranium, but it weighs about 4 AMUs less. This change in weight comes from having 4 fewer neutrons. Uranium usually has 146 neutrons, so 92234U must have 142 neutrons. Ions are atoms whose number of ...
Notes on Chemistry - Properties of Atoms
... • Differentiate average atomic mass of an element from the actual isotopic mass and mass number of specific isotopes. (Use example calculations to determine average atomic mass of atoms from relative abundance and actual isotopic mass to ...
... • Differentiate average atomic mass of an element from the actual isotopic mass and mass number of specific isotopes. (Use example calculations to determine average atomic mass of atoms from relative abundance and actual isotopic mass to ...
Histroy_of_the_Atom
... When you are done . . . Please place test and answer sheet in appropriate stacks at the front Get new Atomic Structure practice and use your periodic table to fill it out. Ms. Matte will call you to the front individually to see your test grade. ...
... When you are done . . . Please place test and answer sheet in appropriate stacks at the front Get new Atomic Structure practice and use your periodic table to fill it out. Ms. Matte will call you to the front individually to see your test grade. ...
Exam 2 Form N - TAMU Chemistry
... b) The number of electrons ejected from a metal surface irradiated with visible light does not depend on the color of the light as long as the light is above a certain, minimum energy . c) Electrons in atoms are found in s, p, d, or f orbitals. d) After an electron (in an atom) is excited to a highe ...
... b) The number of electrons ejected from a metal surface irradiated with visible light does not depend on the color of the light as long as the light is above a certain, minimum energy . c) Electrons in atoms are found in s, p, d, or f orbitals. d) After an electron (in an atom) is excited to a highe ...
1 An atom is the smallest particle of any element that still retains the
... Example: The element boron ( boro) consists of two isotopes, 10B and 11B. Their masses, based on the carbon scale, are 10,01 and 11,01 , respectively. The abundance of 10B is 20 %. What is the abundance of 11B. Solution: Since boron only has two isotopes, the abundance of one must be 100,0 - abundan ...
... Example: The element boron ( boro) consists of two isotopes, 10B and 11B. Their masses, based on the carbon scale, are 10,01 and 11,01 , respectively. The abundance of 10B is 20 %. What is the abundance of 11B. Solution: Since boron only has two isotopes, the abundance of one must be 100,0 - abundan ...
Structure of Atom
... The Maximum number of electrons that could be put in a particular shell (i.e., energy levels was given by Bohr and Bury. According to Bohr-Bury Scheme ...
... The Maximum number of electrons that could be put in a particular shell (i.e., energy levels was given by Bohr and Bury. According to Bohr-Bury Scheme ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
... Example…Cesium has three known isotopes: Cs – 133, Cs – 132, and Cs – 134. Their abundances in nature are 75%, 20%, and 5% respectively. What is the average atomic mass of cesium? Steps #1, #2 and #3 can be performed together: ...
... Example…Cesium has three known isotopes: Cs – 133, Cs – 132, and Cs – 134. Their abundances in nature are 75%, 20%, and 5% respectively. What is the average atomic mass of cesium? Steps #1, #2 and #3 can be performed together: ...
Block 1 and 2 The Nature of Matter
... Drawing an atom model… - Begin with the element and determine how many protons, neutrons, and electrons there are. Boron: Atomic Number 5 Atomic Mass 11 Protons: 5 Neutrons: 6 Electrons: 5 ...
... Drawing an atom model… - Begin with the element and determine how many protons, neutrons, and electrons there are. Boron: Atomic Number 5 Atomic Mass 11 Protons: 5 Neutrons: 6 Electrons: 5 ...
CH. 15 Notes
... Chemical ReactionsThe process by which 1 or more substances undergo change to produce 1 or more different substances Reactions occur when chemical bonds are broken. The atoms rearranged and form new bonds ...
... Chemical ReactionsThe process by which 1 or more substances undergo change to produce 1 or more different substances Reactions occur when chemical bonds are broken. The atoms rearranged and form new bonds ...
PDF(343KB)
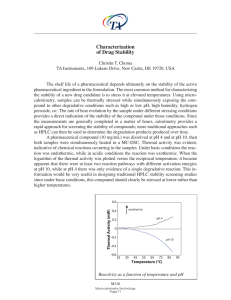
... the stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using microcalorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the compound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The rate of heat evoluti ...
... the stability of a new drug candidate is to stress it at elevated temperatures. Using microcalorimetry, samples can be thermally stressed while simultaneously exposing the compound to other degradative conditions such as high or low pH, high humidity, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The rate of heat evoluti ...
Electron orbitals imaginary
... call the “closing of the periods”—that is why the periods end, in the sense of achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme wou ...
... call the “closing of the periods”—that is why the periods end, in the sense of achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme wou ...
nuclear fission student handout ppf200.03.ho.01
... are all isotopes of the element Uranium. The left subscripts indicate the same atomic number, 92. However, the nucleus of these isotopes contains different neutron numbers, 141, 143, and 146, respectively. This makes their atomic mass numbers, A, different. Isotopes of the same element have identica ...
... are all isotopes of the element Uranium. The left subscripts indicate the same atomic number, 92. However, the nucleus of these isotopes contains different neutron numbers, 141, 143, and 146, respectively. This makes their atomic mass numbers, A, different. Isotopes of the same element have identica ...