- Dr.Divan Fard
... Thermochemistry is the study of heat change in chemical reactions. The system is the specific part of the universe that is of interest in the study. ...
... Thermochemistry is the study of heat change in chemical reactions. The system is the specific part of the universe that is of interest in the study. ...
Equilibrium Reactions
... We tend to think that all reactions go in only one direction. What is called the forward reaction. CaCO3 (aq) + HCl (aq) CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) In this reaction the reactants react to form products. It goes to completion, or until one of the reactants runs out But not reactions are like t ...
... We tend to think that all reactions go in only one direction. What is called the forward reaction. CaCO3 (aq) + HCl (aq) CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) In this reaction the reactants react to form products. It goes to completion, or until one of the reactants runs out But not reactions are like t ...
Which statement is false? A. Potential energy is associated with the
... A. Potential energy is associated with the position or composition of an object. B. Kinetic energy is associated with the motion of an of an object. ✓C. Chemical energy is created during a chemical reaction. D. Thermal energy is associated with molecular motion. ...
... A. Potential energy is associated with the position or composition of an object. B. Kinetic energy is associated with the motion of an of an object. ✓C. Chemical energy is created during a chemical reaction. D. Thermal energy is associated with molecular motion. ...
PHS 354 - The Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta
... concentrated in a small region called a nucleus at the center of the atom with electrons existing in orbits around it. Niels Bohr, coupling Rutherford's postulation with the quantum theory introduced by Max Planck, proposed that the atom consists of a dense nucleus of protons surrounded by electrons ...
... concentrated in a small region called a nucleus at the center of the atom with electrons existing in orbits around it. Niels Bohr, coupling Rutherford's postulation with the quantum theory introduced by Max Planck, proposed that the atom consists of a dense nucleus of protons surrounded by electrons ...
Part I Power generation in fuel cells
... become non-standard, and this must be taken into account when discussing the feasibility of the corrosion process. The iron half reaction coupled to a half reaction such as described above produces what is known as a corrosion cell, with the corrosion process being the cell reaction. Seeing corrosio ...
... become non-standard, and this must be taken into account when discussing the feasibility of the corrosion process. The iron half reaction coupled to a half reaction such as described above produces what is known as a corrosion cell, with the corrosion process being the cell reaction. Seeing corrosio ...
5.7 Quantity Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... reagent runs out before the other. The significance of this is that the reagent that runs out first defines or limits the amount of product made. We call the reagent that runs out first the limiting reagent. The one that does not run out is called the excess reagent. If the reagents are mixed in non ...
... reagent runs out before the other. The significance of this is that the reagent that runs out first defines or limits the amount of product made. We call the reagent that runs out first the limiting reagent. The one that does not run out is called the excess reagent. If the reagents are mixed in non ...
Chemistry Essentials Unit 2
... d) Two clear colorless liquids are mixed in a flask and the flask becomes cool to the ...
... d) Two clear colorless liquids are mixed in a flask and the flask becomes cool to the ...
Fusion Workbook - General Atomics Fusion Education
... called the nucleus and a number of light, negatively charged particles called electrons. The fast moving electrons whirl around the nucleus and form a cloud that completely surrounds the nucleus and electrically balances the atom. ...
... called the nucleus and a number of light, negatively charged particles called electrons. The fast moving electrons whirl around the nucleus and form a cloud that completely surrounds the nucleus and electrically balances the atom. ...
Chapter III: Matter - Norwell Public Schools
... As temperature and pressure change, substances change from one phase to another. ...
... As temperature and pressure change, substances change from one phase to another. ...
Is That a Fact!
... found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apart after a certain amount of time. As they do, they give ...
... found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apart after a certain amount of time. As they do, they give ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... 11) An atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. How many unpaired electrons does it have? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) 6 E) 2 or 4 12) The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 is heavier than nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains how many neutrons? A) 6 B) 7 C) 8 D) 12 E) 14 13 ...
... 11) An atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. How many unpaired electrons does it have? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) 6 E) 2 or 4 12) The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 is heavier than nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains how many neutrons? A) 6 B) 7 C) 8 D) 12 E) 14 13 ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... Part I of this test is designed to be taken with a Scantron® answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. Only this Scantron sheet is graded for a score on Part I. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the Scantron sheet should be made available to the student only during the exam ...
... Part I of this test is designed to be taken with a Scantron® answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. Only this Scantron sheet is graded for a score on Part I. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the Scantron sheet should be made available to the student only during the exam ...
Chapter 5 and 6 Notes
... Isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different masses. • Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons. ...
... Isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different masses. • Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons. ...
Unit 3 - High School Chemistry
... 2. The smallest unit of an Ionic Compound is called a “Unit Cell”. Because of the regular crystal structure of an ionic compound, they are not referred to as molecules. 3. Ionic solids are generally High Melting Points (typically 300°C to 1000°C). Since a strong force can only shatter the crystal bu ...
... 2. The smallest unit of an Ionic Compound is called a “Unit Cell”. Because of the regular crystal structure of an ionic compound, they are not referred to as molecules. 3. Ionic solids are generally High Melting Points (typically 300°C to 1000°C). Since a strong force can only shatter the crystal bu ...
Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions Balancing Equations Notes
... Single Replacement- a metal will _________________ a less active metal in an ionic compound OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds _________________ places. Combustion- an ____________________ compound containing carbon, hydrogen and some ...
... Single Replacement- a metal will _________________ a less active metal in an ionic compound OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds _________________ places. Combustion- an ____________________ compound containing carbon, hydrogen and some ...
Chemistry English
... writing electronic configurations are Pauli principle, Aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule. Pauli Principle: Each orbital may contain two electrons. It is possible for an orbital to contain no electrons or just one electron, but no more than two electrons. Aufbau Principle: Orbitals are filled by star ...
... writing electronic configurations are Pauli principle, Aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule. Pauli Principle: Each orbital may contain two electrons. It is possible for an orbital to contain no electrons or just one electron, but no more than two electrons. Aufbau Principle: Orbitals are filled by star ...
chemistry
... 29 Energy is released during the fission of Pu-239 atoms as a result of the (1) formation of covalent bonds (2) formation of ionic bonds (3) conversion of matter to energy (4) conversion of energy to matter ...
... 29 Energy is released during the fission of Pu-239 atoms as a result of the (1) formation of covalent bonds (2) formation of ionic bonds (3) conversion of matter to energy (4) conversion of energy to matter ...
study packet for chapter 5
... A) ice melting B) water freezing C) boiling soup D) Hydrochloric acid and barium hydroxide are mixed at 25 °C: the temperature increases. E) Both A and C 7) Which one of the following is an exothermic process? A) ice melting B) water evaporating C) boiling soup D) condensation of water vapor E) Ammo ...
... A) ice melting B) water freezing C) boiling soup D) Hydrochloric acid and barium hydroxide are mixed at 25 °C: the temperature increases. E) Both A and C 7) Which one of the following is an exothermic process? A) ice melting B) water evaporating C) boiling soup D) condensation of water vapor E) Ammo ...
n=1 l=0
... What is the wavelength of the light absorbed if a hydrogen atom in its ground state is excited into its n=4 state? How much energy is absorbed (what is the excitation energy)? ...
... What is the wavelength of the light absorbed if a hydrogen atom in its ground state is excited into its n=4 state? How much energy is absorbed (what is the excitation energy)? ...
Unit 2 - Solon City Schools
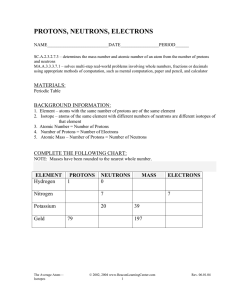
... 14)______________________ A positively charged particle. 15)______________________ Chemical compounds have the same elements in exactly the same ratios. 16)______________________ This English scientist is credited with discovering the neutron. 17)______________________ It represents the number of pr ...
... 14)______________________ A positively charged particle. 15)______________________ Chemical compounds have the same elements in exactly the same ratios. 16)______________________ This English scientist is credited with discovering the neutron. 17)______________________ It represents the number of pr ...