maths_multiplication
... Joe has 14 sweets. Andy has 3 times as many as Joe. Fred has half as many as Andy. How many do they have altogether? ...
... Joe has 14 sweets. Andy has 3 times as many as Joe. Fred has half as many as Andy. How many do they have altogether? ...
Algebra 1 Name: Chapter 2: Properties of Real Numbers Big Ideas 1
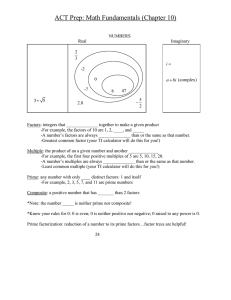
... ○ I can classify a number as an irrational number, rational number, an integer, and/or a whole number. (2.1) ○ I can order rational numbers from least to greatest. (2.1) ○ I can explain the difference between having a zero in the numerator and a zero in the denominator. (2.6) ...
... ○ I can classify a number as an irrational number, rational number, an integer, and/or a whole number. (2.1) ○ I can order rational numbers from least to greatest. (2.1) ○ I can explain the difference between having a zero in the numerator and a zero in the denominator. (2.6) ...
File - THANGARAJ MATH
... During stage 2 – two more branches grow During stage 3 – 4 more branches grow During stage 4 - ________ more branches grow During stage 5 - _____________ more branches grow ...
... During stage 2 – two more branches grow During stage 3 – 4 more branches grow During stage 4 - ________ more branches grow During stage 5 - _____________ more branches grow ...
Study notes for - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
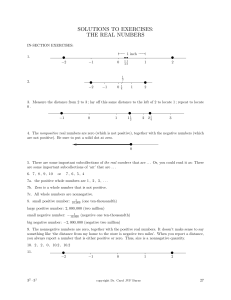
... EXAMPLE # 3: Graph the set of whole numbers greater than 2 but less than 6. ...
... EXAMPLE # 3: Graph the set of whole numbers greater than 2 but less than 6. ...
Big Maths Written Methods for Subtraction.
... right answer. This is used for subtracting 1d numbers from 2d numbers. This will then be extended to jumping back in tens. Subtracting bridging through 10. Using a number line, children will count back to the nearest multiple of 10 and then continue. This will involve partitioning the number being t ...
... right answer. This is used for subtracting 1d numbers from 2d numbers. This will then be extended to jumping back in tens. Subtracting bridging through 10. Using a number line, children will count back to the nearest multiple of 10 and then continue. This will involve partitioning the number being t ...
Activity overview - TI Education
... list L1. Examine L1 to determine the common ratio between the terms. Step 2: Multiply each of the terms in L1 by the common ratio. Arrow to the top of L2 and enter L2*(your common ratio). Notice the diagonals of the two columns have the same values. If you subtract the values that are the same, only ...
... list L1. Examine L1 to determine the common ratio between the terms. Step 2: Multiply each of the terms in L1 by the common ratio. Arrow to the top of L2 and enter L2*(your common ratio). Notice the diagonals of the two columns have the same values. If you subtract the values that are the same, only ...
NEWTON PREPARATORY TEST 2016 1. What is the largest prime
... 15. Mathilda has 4 sweaters (one yellow, one green, one blue, and one red) and 2 skirts (one cotton and one wool). If she randomly chooses a sweater and a skirt, what is the probability that she will choose the yellow sweater and the wool skirt? A) 1/6 ...
... 15. Mathilda has 4 sweaters (one yellow, one green, one blue, and one red) and 2 skirts (one cotton and one wool). If she randomly chooses a sweater and a skirt, what is the probability that she will choose the yellow sweater and the wool skirt? A) 1/6 ...
Representing Inequalities Inequalities Recall: Word Expression
... Used if the value is not included in the inequality. Used if the value is included in the inequality. The upper end of the inequality goes on forever in the positive direction. The lower end of the inequality goes on forever in the negative direction. Used to join two intervals together when there i ...
... Used if the value is not included in the inequality. Used if the value is included in the inequality. The upper end of the inequality goes on forever in the positive direction. The lower end of the inequality goes on forever in the negative direction. Used to join two intervals together when there i ...