Grammar at a Glance Job Aid
... anyone, anybody, anything, each, each one, everyone, everybody, everything, someone, somebody, something, either, neither, no one, nobody, nothing, one, another ...
... anyone, anybody, anything, each, each one, everyone, everybody, everything, someone, somebody, something, either, neither, no one, nobody, nothing, one, another ...
Grammar at a Glance Job Aid
... anyone, anybody, anything, each, each one, everyone, everybody, everything, someone, somebody, something, either, neither, no one, nobody, nothing, one, another ...
... anyone, anybody, anything, each, each one, everyone, everybody, everything, someone, somebody, something, either, neither, no one, nobody, nothing, one, another ...
Instructions for Essay Corrections
... speech and correct. Example: We are asking for your support and to lend us your voice. (incorrect) prep. phrase infinitive phrase We are asking you to support us and lend us your voice. If the sentence lacks parallelism due to a misplaced correlative conjunction, circle both conjunctions and correct ...
... speech and correct. Example: We are asking for your support and to lend us your voice. (incorrect) prep. phrase infinitive phrase We are asking you to support us and lend us your voice. If the sentence lacks parallelism due to a misplaced correlative conjunction, circle both conjunctions and correct ...
Scope and Sequence -- Language Arts/English
... Review sentence structure, fragments, and run-ons. Focus on verb tense and consistency, adjectives, and adverbs Review sentence structure and use of various phrases including: noun, verb, prepositional, gerund, infinitive, and participial Review the parts of speech and how to ...
... Review sentence structure, fragments, and run-ons. Focus on verb tense and consistency, adjectives, and adverbs Review sentence structure and use of various phrases including: noun, verb, prepositional, gerund, infinitive, and participial Review the parts of speech and how to ...
English for Grade 9
... or clauses; Ex: The concert got off to a rough start because the musicians were nervous, but after intermission the performers played much better. 15. Declarative sentence: a sentence that makes a statement and ends in a period; Ex: My birthday is in December. 16. Dependent clauses: cannot stand alo ...
... or clauses; Ex: The concert got off to a rough start because the musicians were nervous, but after intermission the performers played much better. 15. Declarative sentence: a sentence that makes a statement and ends in a period; Ex: My birthday is in December. 16. Dependent clauses: cannot stand alo ...
Studies of particular languages
... best examined by using' free logic' - which relates to all possible universes (and hence to contexts of discourse) rather than to the ' real' universe of Peano and Russell. Such an approach harmonises the operations of natural languages with the laws of logic, making the languages appear less irregu ...
... best examined by using' free logic' - which relates to all possible universes (and hence to contexts of discourse) rather than to the ' real' universe of Peano and Russell. Such an approach harmonises the operations of natural languages with the laws of logic, making the languages appear less irregu ...
Grammar Notes - Holly High School
... of the preposition and includes any adjectives or articles that modify the object of the preposition. o Prepositional phrases can act as adjectives or adverbs. o Prepositional phrases often tell direction. o Look for phrases that begin with words such as: in, between, on, under, around, inside, etc. ...
... of the preposition and includes any adjectives or articles that modify the object of the preposition. o Prepositional phrases can act as adjectives or adverbs. o Prepositional phrases often tell direction. o Look for phrases that begin with words such as: in, between, on, under, around, inside, etc. ...
BCC 101 Grammar I
... contains two or more subjects, joined by and, or, or nor, which share the same verb: A debutante and a troll are squatting under the bridge. A compound predicate is two or more verbs that are joined by and, or, but, yet, or nor, and that belong to the same subject: We complied but spat on our captor ...
... contains two or more subjects, joined by and, or, or nor, which share the same verb: A debutante and a troll are squatting under the bridge. A compound predicate is two or more verbs that are joined by and, or, but, yet, or nor, and that belong to the same subject: We complied but spat on our captor ...
Grammar – Verbal Participial phrases When a participial phrase
... comma only if the information is not essential to the meaning of the sentence The school, destroyed by the scary monster, was never rebuilt (thankfully) If the participial phrase is essential to the meaning of the sentence no commas should be used The monster let loose inside the school was Mr ...
... comma only if the information is not essential to the meaning of the sentence The school, destroyed by the scary monster, was never rebuilt (thankfully) If the participial phrase is essential to the meaning of the sentence no commas should be used The monster let loose inside the school was Mr ...
This page doesn*t mean you don*t need the books
... 1. DO is used when talking about work, jobs or tasks. Note, they do not produce any physical object. Have you done your homework? 2. DO is used when we refer to activities in general without being specific. In these cases, we normally use words like thing, something, nothing, anything, everything et ...
... 1. DO is used when talking about work, jobs or tasks. Note, they do not produce any physical object. Have you done your homework? 2. DO is used when we refer to activities in general without being specific. In these cases, we normally use words like thing, something, nothing, anything, everything et ...
The Giver/Parts of Speech
... • As in any subject, it is important that writers understand the “nuts and bolts” English grammar. The most basic of these are the parts of speech. The 8 Basic Parts of Speech are: • Noun • Pronoun • Adjective • Verb • Adverb • Conjunction • Preposition ...
... • As in any subject, it is important that writers understand the “nuts and bolts” English grammar. The most basic of these are the parts of speech. The 8 Basic Parts of Speech are: • Noun • Pronoun • Adjective • Verb • Adverb • Conjunction • Preposition ...
Verbs: Lie-Lay Verbs: Lie-Lay, Sit-Set, Rise
... The verb lie (lie, lay, lain, lying) means to recline or rest. It never has a direct object. (Intransitive verb) Example: He lies on the couch. (Reclines) Lay (lay, laid, laid, laying) means to put; it always takes a direct object. (Transitive verb) Example: He lays the book on the desk. (Puts) Note ...
... The verb lie (lie, lay, lain, lying) means to recline or rest. It never has a direct object. (Intransitive verb) Example: He lies on the couch. (Reclines) Lay (lay, laid, laid, laying) means to put; it always takes a direct object. (Transitive verb) Example: He lays the book on the desk. (Puts) Note ...
Standards Test Rubric sb_test_rubric
... I can translate only a I can translate and use different Spanish few words from English to Spanish, words (nouns, and there are many pronouns, verbs, spelling errors (less phrases) than 70% are correct). VOCABULARY I can conjugate Spanish verbs to the appropriate tenses ...
... I can translate only a I can translate and use different Spanish few words from English to Spanish, words (nouns, and there are many pronouns, verbs, spelling errors (less phrases) than 70% are correct). VOCABULARY I can conjugate Spanish verbs to the appropriate tenses ...
Parts of Speech
... • The ending –self or –selves can be added to some personal pronouns to form reflexive and intensive pronouns. • A reflexive pronoun ends in –self or –selves and indicates that someone or something performs an action to, for, or upon itself. • Reflexive pronouns point back to a noun or pronoun earli ...
... • The ending –self or –selves can be added to some personal pronouns to form reflexive and intensive pronouns. • A reflexive pronoun ends in –self or –selves and indicates that someone or something performs an action to, for, or upon itself. • Reflexive pronouns point back to a noun or pronoun earli ...
Sentence Fragments In order to punctuate sentences correctly and
... sentence. A dependent clause is a fragment. Here are some examples of fragments. See if you can spot the phrases and the dependent clauses: On that morning, I sat in my usual spot. On the old wooden stool in the corner of my grandmother’s kitchen. Americans have come to fear the West Nile virus. Bec ...
... sentence. A dependent clause is a fragment. Here are some examples of fragments. See if you can spot the phrases and the dependent clauses: On that morning, I sat in my usual spot. On the old wooden stool in the corner of my grandmother’s kitchen. Americans have come to fear the West Nile virus. Bec ...
Tree Syntax of Natural Language
... The star notation used above is used to mark sentences which do not sound right to the native speaker, and which, though they may possibly be comprehensible, would not be used. Such sentences are ungrammatical in the language under discussion. Scientific and technical work on human language takes a ...
... The star notation used above is used to mark sentences which do not sound right to the native speaker, and which, though they may possibly be comprehensible, would not be used. Such sentences are ungrammatical in the language under discussion. Scientific and technical work on human language takes a ...
AN EFFICIENT TREATMENT OF JAPANESE VERB INFLECTION
... In this paper we focus on lexical entries for coping with Japanese verb inflection. The problem of treating verb inflection comes from the nature of written Japanese, in which word boundaries are not usually indicated explicitly. The morphological analyzer must therefore check for the existence of a ...
... In this paper we focus on lexical entries for coping with Japanese verb inflection. The problem of treating verb inflection comes from the nature of written Japanese, in which word boundaries are not usually indicated explicitly. The morphological analyzer must therefore check for the existence of a ...
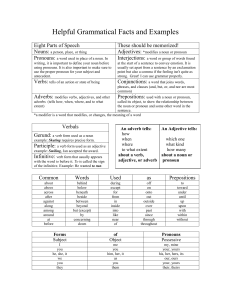
Helpful Grammatical Facts and Examples
... Stumbling and falling, the explorer found his way out of the forest. after an introductory word or phrase, to set it off from the main part of the sentence Ex. After dinner, Leo usually takes a walk. For example, this comma is needed to set off the introductory phrase. with an appositive (a word ...
... Stumbling and falling, the explorer found his way out of the forest. after an introductory word or phrase, to set it off from the main part of the sentence Ex. After dinner, Leo usually takes a walk. For example, this comma is needed to set off the introductory phrase. with an appositive (a word ...
part one - Lindfield Primary Academy
... A pronoun (I, me, he, she, herself, you, it, that, they, each, few, many, who, whoever, whose, someone, everybody, etc.) is a word that takes the place of a noun. Example: Joe saw Jill and he waved at her. The pronouns he and her take the place of Joe and Jill, respectively. ...
... A pronoun (I, me, he, she, herself, you, it, that, they, each, few, many, who, whoever, whose, someone, everybody, etc.) is a word that takes the place of a noun. Example: Joe saw Jill and he waved at her. The pronouns he and her take the place of Joe and Jill, respectively. ...
notes on subordination
... • Clause: a group of related words that functions as a single unit of speech and contains both a subject and a verb. • Independent (Main): a clause that can stand by itself as a complete sentence. Example: John often forgets to water his plants, but they thrive anyway. ...
... • Clause: a group of related words that functions as a single unit of speech and contains both a subject and a verb. • Independent (Main): a clause that can stand by itself as a complete sentence. Example: John often forgets to water his plants, but they thrive anyway. ...
A Guide to Grammar and Spelling
... country/countries ). In the singular, they can be preceded by a or an . Most nouns come into this category. A smaller number of nouns do not typically refer to things that can be counted and so they do not regularly have a plural form: these are known as uncountable nouns (or mass nouns). Examples ...
... country/countries ). In the singular, they can be preceded by a or an . Most nouns come into this category. A smaller number of nouns do not typically refer to things that can be counted and so they do not regularly have a plural form: these are known as uncountable nouns (or mass nouns). Examples ...
Teacher`s Glossary - Savile Park Primary School
... about what happens in a sentence by adding to the meaning of the verb. They can answer the questions ‘how?’ (‘happily’), ‘when?’ (‘always’) or ‘where?’ (‘here’). However, adverbs have many other functions. For instance, adverbs of degree, such as ‘very’ or ‘extremely’, answer the question ‘how much? ...
... about what happens in a sentence by adding to the meaning of the verb. They can answer the questions ‘how?’ (‘happily’), ‘when?’ (‘always’) or ‘where?’ (‘here’). However, adverbs have many other functions. For instance, adverbs of degree, such as ‘very’ or ‘extremely’, answer the question ‘how much? ...
Action and Linking Verbs
... There are no DOs in the following sentences. We arrived on time yesterday. You cannot arrive something so this verb is always intransitive. The audience applauded for three minutes. The audience applauded what? There is no answer to that question in this sentence. The verb APPLAUDED does not have a ...
... There are no DOs in the following sentences. We arrived on time yesterday. You cannot arrive something so this verb is always intransitive. The audience applauded for three minutes. The audience applauded what? There is no answer to that question in this sentence. The verb APPLAUDED does not have a ...