Nominal Complements: Subjective and Objective Complements
... As the examples below show, the subjective complement may be a noun or an adjective, though for verbs with the sense ‘turn into, metamorphose into’, only a noun would be pragmatically appropriate. There are several variants with verbs and subjective complements. The simplest form is VERB+COMPLEMENT. ...
... As the examples below show, the subjective complement may be a noun or an adjective, though for verbs with the sense ‘turn into, metamorphose into’, only a noun would be pragmatically appropriate. There are several variants with verbs and subjective complements. The simplest form is VERB+COMPLEMENT. ...
Embedded Clauses in TAG
... clauses. When it comes after a verb, it is optional: – Sam said Sue saw him. – That he left is a problem. – *He left is a problem. • “That” is only optional after a verb. ...
... clauses. When it comes after a verb, it is optional: – Sam said Sue saw him. – That he left is a problem. – *He left is a problem. • “That” is only optional after a verb. ...
Spelling: Common Words that Sound Alike
... their = possessive adjective (possessive form of the pronoun they) : They bought their books. there = that place: My house is over there. This is a place word and thus contains the word here. they're = contraction for they are: They're making dinner. to, too, two to = preposition, or first part of t ...
... their = possessive adjective (possessive form of the pronoun they) : They bought their books. there = that place: My house is over there. This is a place word and thus contains the word here. they're = contraction for they are: They're making dinner. to, too, two to = preposition, or first part of t ...
LEL 1 - Linguistics and English Language
... Another way of describing this situation is to say that the subject moves from spec-VP to spec-IP, and that such movement leaves a trace which is identical to the moved element except for being silent. ...
... Another way of describing this situation is to say that the subject moves from spec-VP to spec-IP, and that such movement leaves a trace which is identical to the moved element except for being silent. ...
O > UE - Madame Thomas French
... You cannot create a sentence without a verb so knowing how they work is vital! You must know the important questions to ask yourself as you create verbs in French. We will look at the whole process in this presentation. ...
... You cannot create a sentence without a verb so knowing how they work is vital! You must know the important questions to ask yourself as you create verbs in French. We will look at the whole process in this presentation. ...
Accusative Case - David S. Danaher
... One of the most frequent uses of the accusative is as the direct object of a verb. Verbs that have direct objects are called transitive verbs, and we can think of a typical scenario in which someone (an agent or doer of an action) transfers the energy of the verb directly onto something else (the ob ...
... One of the most frequent uses of the accusative is as the direct object of a verb. Verbs that have direct objects are called transitive verbs, and we can think of a typical scenario in which someone (an agent or doer of an action) transfers the energy of the verb directly onto something else (the ob ...
Grammar Worksheets - SD43 Teacher Sites
... The demonstrative pronoun is used to point out -- this, that, these, those. e.g. That is red. ...
... The demonstrative pronoun is used to point out -- this, that, these, those. e.g. That is red. ...
Some technical terms for sentences
... Compound:- contains two or more independent clauses. Two simple sentences combined by an appropriate link word. (e.g. George bought a new car, and crowds of his students stood and stared.) Complex: contains one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. (e.g. When he had enough money, Geo ...
... Compound:- contains two or more independent clauses. Two simple sentences combined by an appropriate link word. (e.g. George bought a new car, and crowds of his students stood and stared.) Complex: contains one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. (e.g. When he had enough money, Geo ...
Document
... • but there are still language-universal patterns in the types of color schemes available to languages. • As linguists, we want to know what competent speakers of a language need to know in order to produce meaningful utterances in that language. • = the semantic features of a language • There are l ...
... • but there are still language-universal patterns in the types of color schemes available to languages. • As linguists, we want to know what competent speakers of a language need to know in order to produce meaningful utterances in that language. • = the semantic features of a language • There are l ...
没有幻灯片标题
... New items are constantly being added to the open class, as new ideas, inventions, etc, appear. Nouns, verbs, adjective and adverbs are open-class items. New items are not regularly added to the closed class as they are in the case of open-class items. Pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles, ...
... New items are constantly being added to the open class, as new ideas, inventions, etc, appear. Nouns, verbs, adjective and adverbs are open-class items. New items are not regularly added to the closed class as they are in the case of open-class items. Pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles, ...
Lesson 7 Grammar Lesson: Pronouns - Vocab10-2CHS
... antecedent. Intensive pronouns are identical in form to reflexive pronouns. ...
... antecedent. Intensive pronouns are identical in form to reflexive pronouns. ...
1 On some ways to test Tagalog nominalism from a
... subjects/topics can be extracted in this language, from the fact that NPs (unlike VPs) are often islands to extraction in languages of the world. This is an intriguing, somewhat radical, and potentially elegant proposal. As Kaufman himself points out, it falls squarely within a broader class of prop ...
... subjects/topics can be extracted in this language, from the fact that NPs (unlike VPs) are often islands to extraction in languages of the world. This is an intriguing, somewhat radical, and potentially elegant proposal. As Kaufman himself points out, it falls squarely within a broader class of prop ...
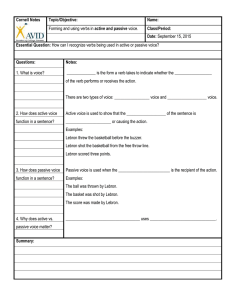
Active and Passive Voice Cornell Notes
... For example, a politician might say, “The mistake was made by someone” to hide the blame. -When intentionally trying to ______________________ the ______________ of the subject. For example, a cheating boyfriend might say, “Cheating was committed by me.” -When passive voice better __________________ ...
... For example, a politician might say, “The mistake was made by someone” to hide the blame. -When intentionally trying to ______________________ the ______________ of the subject. For example, a cheating boyfriend might say, “Cheating was committed by me.” -When passive voice better __________________ ...
Parts of Speech, Phrases, and Clauses
... This noun clause is working as the subject of the entire independent clause: That Raul kicks the ball pleases his coach. (3) adjective clause—a group of words containing a subject and a predicate working together to modify some noun or pronoun. It answers the question what kind of? (person, place, t ...
... This noun clause is working as the subject of the entire independent clause: That Raul kicks the ball pleases his coach. (3) adjective clause—a group of words containing a subject and a predicate working together to modify some noun or pronoun. It answers the question what kind of? (person, place, t ...
Dear Students,
... If it answers how? or when? or where? or why? or under what conditions? or to what degree? it is an adverb prepositional phrase. In the sentence above, “at the goalie” is answering the question where? (does he kick the ball). It is modifying the verb kicks so that it is an adverb prepositional phra ...
... If it answers how? or when? or where? or why? or under what conditions? or to what degree? it is an adverb prepositional phrase. In the sentence above, “at the goalie” is answering the question where? (does he kick the ball). It is modifying the verb kicks so that it is an adverb prepositional phra ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... o To jog in the early morning is an activity I enjoy. (infinitive phrase as subject) When any phrase with a verb form opens a sentence, the subject of the verb must correspond to the subject of the sentence. It also requires a comma. Jogging in the early morning, a car almost ran me down. (danglin ...
... o To jog in the early morning is an activity I enjoy. (infinitive phrase as subject) When any phrase with a verb form opens a sentence, the subject of the verb must correspond to the subject of the sentence. It also requires a comma. Jogging in the early morning, a car almost ran me down. (danglin ...
Clauses Phrases Pronouns Antecedents
... Relate a noun to another word in a sentence. A preposition and its object (and its object’s modifiers) create a prepositional phrase, that acts as a modifier. E.g., above, across, against, as, at, in, to, on, under. ...
... Relate a noun to another word in a sentence. A preposition and its object (and its object’s modifiers) create a prepositional phrase, that acts as a modifier. E.g., above, across, against, as, at, in, to, on, under. ...
Clause
... Relate a noun to another word in a sentence. A preposition and its object (and its object’s modifiers) create a prepositional phrase, that acts as a modifier. E.g., above, across, against, as, at, in, to, on, under. ...
... Relate a noun to another word in a sentence. A preposition and its object (and its object’s modifiers) create a prepositional phrase, that acts as a modifier. E.g., above, across, against, as, at, in, to, on, under. ...
CCR+1+Language+Grade+Level+Progression
... • Use verb tense to convey various times, sequences, states, and conditions. • Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb tense.* • Use correlative conjunctions (e.g., either/or, neither/nor). Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or sp ...
... • Use verb tense to convey various times, sequences, states, and conditions. • Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb tense.* • Use correlative conjunctions (e.g., either/or, neither/nor). Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or sp ...
Definitions of key terms from the English curriculum
... make a negative; no other auxiliary is present] Will you come with me or not? [modal verb will used to make a question about the other person’s willingness] It was raining. [single-clause sentence] It was raining but we were indoors. [two finite clauses] If you are coming to the party, please let us ...
... make a negative; no other auxiliary is present] Will you come with me or not? [modal verb will used to make a question about the other person’s willingness] It was raining. [single-clause sentence] It was raining but we were indoors. [two finite clauses] If you are coming to the party, please let us ...
Lecture 7 - Linguistics and English Language
... active verbs, they must have deficient Case-properties; they are not able to assign Accusative to the subject of their non-finite complement, like an Exceptional Case Marking verb can. (Nor can the subject of a non-finite sentence get Nominative, because finite inflection is needed to assign that). ...
... active verbs, they must have deficient Case-properties; they are not able to assign Accusative to the subject of their non-finite complement, like an Exceptional Case Marking verb can. (Nor can the subject of a non-finite sentence get Nominative, because finite inflection is needed to assign that). ...
English_Glossary National Curriculum
... A word’s etymology is its history: its origins in earlier forms of English or other languages, and how its form and meaning have changed. Many words in English have come from Greek, Latin or French. ...
... A word’s etymology is its history: its origins in earlier forms of English or other languages, and how its form and meaning have changed. Many words in English have come from Greek, Latin or French. ...
Communication Strategies: Commonly Confused Words
... that has gone by or the time before the present. Past as a preposition means beyond in time or after. Past as an adverb would mean so as to pass something. Passed, the verb, means to proceed or move forward. “In the past, twenty Easter parades have passed down this street.” Real, Really: The adjecti ...
... that has gone by or the time before the present. Past as a preposition means beyond in time or after. Past as an adverb would mean so as to pass something. Passed, the verb, means to proceed or move forward. “In the past, twenty Easter parades have passed down this street.” Real, Really: The adjecti ...