Parts of Speech
... very, now, then, there, up, down, certainly, however, etc.) *Adverbs usually answer the questions: how? When? Where? To what extent? And many adverbs are formed by adding –ly to an adjective (e.g. Quickly) ...
... very, now, then, there, up, down, certainly, however, etc.) *Adverbs usually answer the questions: how? When? Where? To what extent? And many adverbs are formed by adding –ly to an adjective (e.g. Quickly) ...
GMAS Crash Couse
... Indirect object – noun or pronoun for whom or to whom something was done. I read the class the entire book. Object of a preposition – answers the question whom or what after the preposition. ...
... Indirect object – noun or pronoun for whom or to whom something was done. I read the class the entire book. Object of a preposition – answers the question whom or what after the preposition. ...
Parts of Speech - Northampton Community College
... Nouns: A noun is a person (librarian), a place (home), a thing (book), or an idea (justice). Proper Nouns are capitalized and name particular people (Steve), places (the Poconos), or things (the Eiffel Tower). Pronouns: A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. There are several types of pronouns ...
... Nouns: A noun is a person (librarian), a place (home), a thing (book), or an idea (justice). Proper Nouns are capitalized and name particular people (Steve), places (the Poconos), or things (the Eiffel Tower). Pronouns: A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. There are several types of pronouns ...
Parts of Speech
... The words that make up sentences can be classified into nine grammatical categories or word classes. The function of a word in a sentence determines what part of speech it is. The word rock, for example, can belong to any one of three categories, depending on its context. We stopped to rest in the s ...
... The words that make up sentences can be classified into nine grammatical categories or word classes. The function of a word in a sentence determines what part of speech it is. The word rock, for example, can belong to any one of three categories, depending on its context. We stopped to rest in the s ...
notes as word document
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
English Grammar - HCC Learning Web
... object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
... object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
GaPS Definitions - Priory Junior School
... Subjunctive form Usually only used in very formal language to express intention or proposal about the future. It also appears in commands, wishes, and requests. ...
... Subjunctive form Usually only used in very formal language to express intention or proposal about the future. It also appears in commands, wishes, and requests. ...
Verbals
... The choir tried to sing together. (“to sing” is a noun and the object of “tried”) Shelly needs someone to advise her. (“to advise” is an adjective modifying “someone”) Greg is afraid to talk to Jessica (“to talk” is an adverb modifying “afraid”) ...
... The choir tried to sing together. (“to sing” is a noun and the object of “tried”) Shelly needs someone to advise her. (“to advise” is an adjective modifying “someone”) Greg is afraid to talk to Jessica (“to talk” is an adverb modifying “afraid”) ...
Multi Sensory Grammar
... • A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with either a noun or pronoun. The preposition is underlined in green and the entire prepositional phrase is circled in green. ...
... • A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with either a noun or pronoun. The preposition is underlined in green and the entire prepositional phrase is circled in green. ...
English Grammar
... preposition introduces is its object. They received a postcard from Bobby telling about his trip to Canada. ...
... preposition introduces is its object. They received a postcard from Bobby telling about his trip to Canada. ...
Parts of speech
... • Modal verbs give extra meaning to a sentence. Can, must, may, might, could, should, and would are modal verbs. ...
... • Modal verbs give extra meaning to a sentence. Can, must, may, might, could, should, and would are modal verbs. ...
Parts of Speech - Capital Community College
... object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
... object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
Parts of Speech - Capital Community College
... object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
... object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
Parts of Speech
... Answer the questions: What kind?, How many?, Which ones? Come before the noun or pronoun they modify (tell you about) – the small dog Include comparison words like tougher or more wonderful The articles (a, an, the) are adjectives – because they tell how many ADVERB: modify verbs, adjectives ...
... Answer the questions: What kind?, How many?, Which ones? Come before the noun or pronoun they modify (tell you about) – the small dog Include comparison words like tougher or more wonderful The articles (a, an, the) are adjectives – because they tell how many ADVERB: modify verbs, adjectives ...
Parts of Speech - Net Start Class
... A PRONOUN takes the place of a NOUN. It refers to a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... A PRONOUN takes the place of a NOUN. It refers to a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
Parts of Speech
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
GLOSARIO DE INGLÉS (Educación Media) Adjective: A word that
... Guess: To give an answer to a particular question without all the facts and so cannot be certain if it is correct. Infinitive: The basic form of a verb, without an inflection binding it to a particular subject or tense. It usually follows to. Label: To describe someone or something using a particula ...
... Guess: To give an answer to a particular question without all the facts and so cannot be certain if it is correct. Infinitive: The basic form of a verb, without an inflection binding it to a particular subject or tense. It usually follows to. Label: To describe someone or something using a particula ...
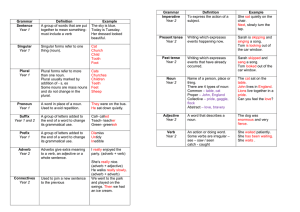
Grammar Definition Example Sentence Year 1 A group of words that
... Writing which expresses events that have already occurred. ...
... Writing which expresses events that have already occurred. ...
Noun Study Guide
... Comparative & Superlative Adjectives A comparative adjective compares two things (nouns). Uses –er or more A superlative adjective compares three or more things (nouns). Uses –est or most There are irregulars like: good, well, better, best, bad, worse, worst * NEVER use both –er and more or –e ...
... Comparative & Superlative Adjectives A comparative adjective compares two things (nouns). Uses –er or more A superlative adjective compares three or more things (nouns). Uses –est or most There are irregulars like: good, well, better, best, bad, worse, worst * NEVER use both –er and more or –e ...