
Chapter 7:
... group 1A, it is not a member of any group because it has properties of both metals and nonmetals. It behaves as a metal when it loses its electron. It behaves as a nonmetal when it gains an electron. The universe contains more than 90% hydrogen by mass. Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen in the p ...
... group 1A, it is not a member of any group because it has properties of both metals and nonmetals. It behaves as a metal when it loses its electron. It behaves as a nonmetal when it gains an electron. The universe contains more than 90% hydrogen by mass. Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen in the p ...
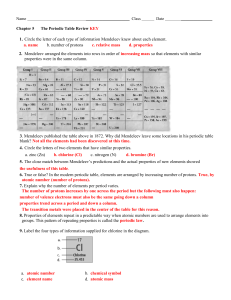
ORGANIZATION OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
... Group 2 = Alkaline Earth Metals 2 valence electrons Groups 3-12 =Transition Metals # electrons varies Groups 13-16 = BCNO group 3-6 valence electrons Group 17 = Halogens (combine to form salts) 7 valence electrons Group 18 = Nobel Gases (least reactive) 8 valence electrons Lanthanides & ...
... Group 2 = Alkaline Earth Metals 2 valence electrons Groups 3-12 =Transition Metals # electrons varies Groups 13-16 = BCNO group 3-6 valence electrons Group 17 = Halogens (combine to form salts) 7 valence electrons Group 18 = Nobel Gases (least reactive) 8 valence electrons Lanthanides & ...
Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table
... •The electron configuration of an atom’s highest occupied energy level generally governs the atom’s chemical properties (the highest occupied level of the noble gases contain stable octets – outer s and p orbitals are completely filled with 8 electrons. •The exception is helium (2 electrons in highe ...
... •The electron configuration of an atom’s highest occupied energy level generally governs the atom’s chemical properties (the highest occupied level of the noble gases contain stable octets – outer s and p orbitals are completely filled with 8 electrons. •The exception is helium (2 electrons in highe ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... 10. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about a carbon-12 atom. a. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. b. Scientists assigned a mass of 6 atomic mass units to the carbon-12 atom. c. It is used as a standard for comparing the masses of atoms. d. An atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth ...
... 10. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about a carbon-12 atom. a. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. b. Scientists assigned a mass of 6 atomic mass units to the carbon-12 atom. c. It is used as a standard for comparing the masses of atoms. d. An atomic mass unit is defined as one twelfth ...
Pre-Test Atomic Structure
... 5. An atom is usually neutrally charged. This means the number of protons must equal the number of ______________. 6. The atomic number of an atom equals the number of ____________ 7. All atoms of the same element will have the same number of ________________ 8. The periodic table is arranged in ord ...
... 5. An atom is usually neutrally charged. This means the number of protons must equal the number of ______________. 6. The atomic number of an atom equals the number of ____________ 7. All atoms of the same element will have the same number of ________________ 8. The periodic table is arranged in ord ...
A Level Chemistry B (Salters) Lesson Element Teachers` Instructions
... The halogens are to be found in this part of the periodic table. (1-5) ...
... The halogens are to be found in this part of the periodic table. (1-5) ...
Section 5.2 The Modern Periodic Table
... a. Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electric current. b. Many nonmetals are gases at room temperature. c. Some nonmetals are extremely reactive and others hardly react at all. d. Nonmetals that are solids tend to be malleable. ...
... a. Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electric current. b. Many nonmetals are gases at room temperature. c. Some nonmetals are extremely reactive and others hardly react at all. d. Nonmetals that are solids tend to be malleable. ...
Reactivity of Atoms Based on Their Placement in The Periodic Table
... numbers are used to arrange elements into groups. The elements in a group have similar electron configurations. An element's electron configuration determines it's chemical properties ...
... numbers are used to arrange elements into groups. The elements in a group have similar electron configurations. An element's electron configuration determines it's chemical properties ...
Atoms and Periodic Table Unit Plan IS
... Course: Integrated II Unit Number and Title: Atoms & the Periodic Table ...
... Course: Integrated II Unit Number and Title: Atoms & the Periodic Table ...
Y10 Chem SLOs 2016 File
... 5. I can draw an orbital diagram and write electron configurations for atoms 1-20. (given their atomic number). 6. I know that the periodic table is a way of classifying elements according to their atomic number and identify an elements position on the periodic table 7. I know what an ion is and how ...
... 5. I can draw an orbital diagram and write electron configurations for atoms 1-20. (given their atomic number). 6. I know that the periodic table is a way of classifying elements according to their atomic number and identify an elements position on the periodic table 7. I know what an ion is and how ...
Chapter 6
... -gases or brittle solids, dull surfaces, used as insulators -have 5 or more electrons in outer energy level ...
... -gases or brittle solids, dull surfaces, used as insulators -have 5 or more electrons in outer energy level ...
Chapter 15 – The Periodic Table
... elements in order of increasing atomic weights. Proposed the Law of Octaves. Meyer (1869) Compiled a periodic table with elements arranged by atomic weight. Elements with similar properties arranged in columns. Mendeleev (1869) Created a periodic with elements arranged by atomic weight. Elements ...
... elements in order of increasing atomic weights. Proposed the Law of Octaves. Meyer (1869) Compiled a periodic table with elements arranged by atomic weight. Elements with similar properties arranged in columns. Mendeleev (1869) Created a periodic with elements arranged by atomic weight. Elements ...
Section 15.1
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
Periodic Table[1]
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. ...
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. ...
Development of the Periodic Table
... called periods (organized by increasing atomic number) The vertical columns are called groups or families (organized by chemical properties) Periodic Law: when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties ...
... called periods (organized by increasing atomic number) The vertical columns are called groups or families (organized by chemical properties) Periodic Law: when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties ...
Unit 4: Periodic Table - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 5. Why did Mendeleyev arrange the elements the way he did? because of similarities in the chemical properties of various “families” of elements 6. What does the name periodic table refer to? the fact that as we increase the atomic number, every so often an element occurs that has properties similar ...
... 5. Why did Mendeleyev arrange the elements the way he did? because of similarities in the chemical properties of various “families” of elements 6. What does the name periodic table refer to? the fact that as we increase the atomic number, every so often an element occurs that has properties similar ...
File
... 16. Which of the following factorscontributesto the decreasein ionization energywithin a groupin the periodic table asthe atomic numberincreases? a. increasein atomic size b. increasein sizeofthe nucleus c. increasein numberofprotons d. fewer electronsin the highestoccupiedenergylevel 17. Which of t ...
... 16. Which of the following factorscontributesto the decreasein ionization energywithin a groupin the periodic table asthe atomic numberincreases? a. increasein atomic size b. increasein sizeofthe nucleus c. increasein numberofprotons d. fewer electronsin the highestoccupiedenergylevel 17. Which of t ...
1. Elements in the same family have similar chemical properties
... its own box in the table containing that element’s symbol, atomic number, atomic mass. The boxes are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called periods and these are numbered beginning at the top from 1 down to 7. Each vertical column i ...
... its own box in the table containing that element’s symbol, atomic number, atomic mass. The boxes are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called periods and these are numbered beginning at the top from 1 down to 7. Each vertical column i ...














![Periodic Table[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003104404_1-7138f0e5d3dcc06b9019743402d7e0ca-300x300.png)






