PeriodicTableA
... ANIONS are LARGER than the atoms from which they come. The electron/proton attraction has gone DOWN and so size INCREASES. Trends in ion sizes are the same as atom ...
... ANIONS are LARGER than the atoms from which they come. The electron/proton attraction has gone DOWN and so size INCREASES. Trends in ion sizes are the same as atom ...
Periodic Table - Red Deer Public
... ANIONS are LARGER than the atoms from which they come. The electron/proton attraction has gone DOWN and so size INCREASES. Trends in ion sizes are the same as atom ...
... ANIONS are LARGER than the atoms from which they come. The electron/proton attraction has gone DOWN and so size INCREASES. Trends in ion sizes are the same as atom ...
Trends in The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name
... All Halogens are very reactive because they only need 1 extra electron to fill their outer energy level. Trend: The reactivity of the Halogens increases going up the group. Reason: 1. The Halogens are the most electronegative of all elements. The values of their electronegativities increase go ...
... All Halogens are very reactive because they only need 1 extra electron to fill their outer energy level. Trend: The reactivity of the Halogens increases going up the group. Reason: 1. The Halogens are the most electronegative of all elements. The values of their electronegativities increase go ...
File
... (e) What common feature can be identified for all of the non-metals on the plot? (f) What accounts for the sharp increase in height of the blue lines that occurs at elements with atomic numbers 3, 11 and 19 respectively? (g) Make a prediction about the relative heights of the blue line and red line ...
... (e) What common feature can be identified for all of the non-metals on the plot? (f) What accounts for the sharp increase in height of the blue lines that occurs at elements with atomic numbers 3, 11 and 19 respectively? (g) Make a prediction about the relative heights of the blue line and red line ...
Chapter 6 - The Periodic Table
... High ionization energy: atoms want to hold on to electrons; likely to form ...
... High ionization energy: atoms want to hold on to electrons; likely to form ...
Review guide for Chemistry`s First Semester Exam Unit 1 Thinking
... Define: ion, cation, anion, oxidation number Match the items to the statement. Some items can be used more than once, and some statements have two correct answers. Fill in all answers that apply! 8. Has/have more electrons than protons. 9. Not an ion. 10. Cation(s) 11. Anion(s) 12. Has/have gained e ...
... Define: ion, cation, anion, oxidation number Match the items to the statement. Some items can be used more than once, and some statements have two correct answers. Fill in all answers that apply! 8. Has/have more electrons than protons. 9. Not an ion. 10. Cation(s) 11. Anion(s) 12. Has/have gained e ...
Electronegativity Periodic Trend
... Go to the Periodic Table Live! (http://www.chemeddl.org/resources/ptl/index.html) and click on the “Chart/Sort” button in the upper right corner. You will use this graphing feature to answer the questions below. A new tab will open. The page contains three windows: Periodic Table, Graph and Table. ...
... Go to the Periodic Table Live! (http://www.chemeddl.org/resources/ptl/index.html) and click on the “Chart/Sort” button in the upper right corner. You will use this graphing feature to answer the questions below. A new tab will open. The page contains three windows: Periodic Table, Graph and Table. ...
Lesson 7.8 Basic Properties of the Main Group Elements Suggested
... stored under water. In air it bursts into flame reacting with O2 to give the acidic oxides P4O6 and P4O10. Other allotropes, red and black phosphorus are much less reactive. Grey arsenic, the common form of the element, is a brittle solid with metallic luster. Yellow arsenic is an unstable, crystall ...
... stored under water. In air it bursts into flame reacting with O2 to give the acidic oxides P4O6 and P4O10. Other allotropes, red and black phosphorus are much less reactive. Grey arsenic, the common form of the element, is a brittle solid with metallic luster. Yellow arsenic is an unstable, crystall ...
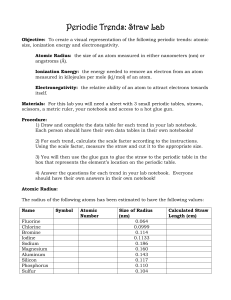
Periodic Trends: Straw Lab
... size, ionization energy and electronegativity. Atomic Radius: the size of an atom measured in either nanometers (nm) or angstroms (Ǻ). Ionization Energy: the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom measured in kilojoules per mole (kj/mol) of an atom. Electronegativity: the relative ability ...
... size, ionization energy and electronegativity. Atomic Radius: the size of an atom measured in either nanometers (nm) or angstroms (Ǻ). Ionization Energy: the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom measured in kilojoules per mole (kj/mol) of an atom. Electronegativity: the relative ability ...
The Periodic Table - Palisades High School
... – Tend to form salts with group 1 elements – Most reactive of the nonmetals – Have 7 valence electrons ...
... – Tend to form salts with group 1 elements – Most reactive of the nonmetals – Have 7 valence electrons ...
Atoms and Ions Practice Problems
... A) electrons located in the lowest energy level of an atom. B) the core electrons in an atom. C) electrons that do not participate in ion formation and bonding. D) the 8 highest energy electrons in the atom. E) the electrons in the highest energy level of an atom. ...
... A) electrons located in the lowest energy level of an atom. B) the core electrons in an atom. C) electrons that do not participate in ion formation and bonding. D) the 8 highest energy electrons in the atom. E) the electrons in the highest energy level of an atom. ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... trends or patterns found within the Periodic Table of Elements. The elements found within the Periodic Table are put in order in a very particular pattern, based on several common similarities or characteristics. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev produced a table of elements based on their atomic weights. P ...
... trends or patterns found within the Periodic Table of Elements. The elements found within the Periodic Table are put in order in a very particular pattern, based on several common similarities or characteristics. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev produced a table of elements based on their atomic weights. P ...
Chapter 1 - Study Guide Solutions
... Group 1 - ALKALI METALS (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr) Soft, low melting, shiny metals: conduct heat and electricity. They are stored in oil due to their high reactivity (also named oily metals). ...
... Group 1 - ALKALI METALS (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr) Soft, low melting, shiny metals: conduct heat and electricity. They are stored in oil due to their high reactivity (also named oily metals). ...
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table of the Elements The periodic table is
... disintegration of the nucleus of an unstable atom. Unstable isotopes of elements are referred to as radionuclides. The disintegration occurs in one of three ways, each emitting a kind of radiation: α alpha, β beta and γ gamma Each of these radiations is affected differently by electric fields. Alpha ...
... disintegration of the nucleus of an unstable atom. Unstable isotopes of elements are referred to as radionuclides. The disintegration occurs in one of three ways, each emitting a kind of radiation: α alpha, β beta and γ gamma Each of these radiations is affected differently by electric fields. Alpha ...
class notes packet - Social Circle City Schools
... the ____________ ___________ non-metals. They are never found free in nature. Halogen atoms only need to gain 1 electron to fill outermost level. They react with ______________ __________ to form _______________. Noble gases are ____________________ gases that are extremely _________________. One im ...
... the ____________ ___________ non-metals. They are never found free in nature. Halogen atoms only need to gain 1 electron to fill outermost level. They react with ______________ __________ to form _______________. Noble gases are ____________________ gases that are extremely _________________. One im ...
periodic table
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
the periodic law
... a. Tend to lose electrons, thus they have positive oxidation numbers 2. Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table a. Tend to gain electrons, thus they have negative oxidation numbers J. Electronegativity – a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons 1. ...
... a. Tend to lose electrons, thus they have positive oxidation numbers 2. Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table a. Tend to gain electrons, thus they have negative oxidation numbers J. Electronegativity – a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons 1. ...
Chemistry-notes-ch-5
... Periodic Table—an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column or group. The noble gases were not a part of the early periodic table. They were not yet discovered when Mendeleev published the first periodic table. Lanth ...
... Periodic Table—an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column or group. The noble gases were not a part of the early periodic table. They were not yet discovered when Mendeleev published the first periodic table. Lanth ...
Properties of Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
... Highly inert (unreactive) due to a full octet ...
... Highly inert (unreactive) due to a full octet ...
Classification of Matter
... protons does it have? No two elements have the same atomic number or the same number of protons. ...
... protons does it have? No two elements have the same atomic number or the same number of protons. ...
Untitled
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
Section 6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.