Chapter 3
... The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table The periodic law is an organized "map" of the elements that relates their structure to their chemical and physical properties. The periodic table is the result of the periodic law, and provides the basis for prediction of such properties as relative atomic and ...
... The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table The periodic law is an organized "map" of the elements that relates their structure to their chemical and physical properties. The periodic table is the result of the periodic law, and provides the basis for prediction of such properties as relative atomic and ...
File
... Example: Barium forms the basic oxide BaO: Reacts with water: BaO (s) + H2O (ℓ) Ba2+ (aq) + 2 OH– (aq) Reacts with acid: BaO (s) + H+ (aq) Ba2+ (aq) + H2O (ℓ) Other examples of basic oxides: ...
... Example: Barium forms the basic oxide BaO: Reacts with water: BaO (s) + H2O (ℓ) Ba2+ (aq) + 2 OH– (aq) Reacts with acid: BaO (s) + H+ (aq) Ba2+ (aq) + H2O (ℓ) Other examples of basic oxides: ...
Periodic Trends - killingly.k12.ct.us
... a more complicated chemistry that does not generally follow any trends. Therefore, noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides do not have electronegativity values. • As for the transition metals, while they have values, there is little variance among them as you move across the period and up and down a ...
... a more complicated chemistry that does not generally follow any trends. Therefore, noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides do not have electronegativity values. • As for the transition metals, while they have values, there is little variance among them as you move across the period and up and down a ...
The physical characteristics of the atom of an element are called
... 14. Variation in Atomic Radius in Group: Within a family or vertical column of the periodic table, the atomic radius increases regularly with atomic number as). as we descend the groups, the principal quantum number (n) increases and the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. This happens b ...
... 14. Variation in Atomic Radius in Group: Within a family or vertical column of the periodic table, the atomic radius increases regularly with atomic number as). as we descend the groups, the principal quantum number (n) increases and the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. This happens b ...
Unit Packet 3: Periodic Properties
... periodic table. You should be able to explain why these properties change based primarily on the what the electrons are doing (their electronic configuration). Give the electron configurations and effective nuclear charges (on an outer electron) for the following atoms. This will illustrate how thes ...
... periodic table. You should be able to explain why these properties change based primarily on the what the electrons are doing (their electronic configuration). Give the electron configurations and effective nuclear charges (on an outer electron) for the following atoms. This will illustrate how thes ...
unit 3 ppt
... The d-Block Elements: Groups 3–12 For energy level n, there are n possible sublevels, so the d sublevel first appears when n=3. This 3d sublevel is slightly higher in energy than the 4s sublevel, so these are filled in the order 4s3d.This order of filling is also seen for higher values of n. Each d ...
... The d-Block Elements: Groups 3–12 For energy level n, there are n possible sublevels, so the d sublevel first appears when n=3. This 3d sublevel is slightly higher in energy than the 4s sublevel, so these are filled in the order 4s3d.This order of filling is also seen for higher values of n. Each d ...
Review
... given them up) because they are close to achieving the octet. The means it will require more energy to remove the outer most electron. Elements on the left of the chart would prefer to give up their electrons so it is easy to remove them, requiring less energy (low ionization energy). Group - ioniza ...
... given them up) because they are close to achieving the octet. The means it will require more energy to remove the outer most electron. Elements on the left of the chart would prefer to give up their electrons so it is easy to remove them, requiring less energy (low ionization energy). Group - ioniza ...
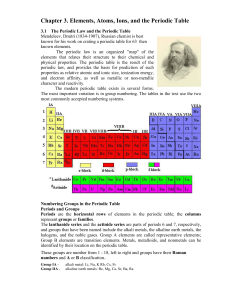
The Periodic Table
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, except for group 0. Tren ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, except for group 0. Tren ...
Lesson Plan
... Skill: students should be able to use the periodic table to determine various atomic properties such as atomic radius, ionic radius, effective nuclear charge, electron affinity, electronegativity, atomic mass and electron configuration using the periodic table. Students should also be able to descri ...
... Skill: students should be able to use the periodic table to determine various atomic properties such as atomic radius, ionic radius, effective nuclear charge, electron affinity, electronegativity, atomic mass and electron configuration using the periodic table. Students should also be able to descri ...
Worked solutions
... 4 C Germanium, it has properties of both a metal (e.g. forms alloys with other metals) and a non-metal (e.g. brittle). Calcium, manganese and magnesium are all metals. 5 B Graphite, as it has a network of delocalized electrons throughout its structure. 6 C Elements are arranged in the Perio ...
... 4 C Germanium, it has properties of both a metal (e.g. forms alloys with other metals) and a non-metal (e.g. brittle). Calcium, manganese and magnesium are all metals. 5 B Graphite, as it has a network of delocalized electrons throughout its structure. 6 C Elements are arranged in the Perio ...
Per.Table.Properties. Notes
... 1. Metals have a tendency to lose electrons; nonmetals tend to gain electrons. Nonmetals would be expected to have a high electron affinity. 2. As we move across the periodic table, we move from metals to nonmetals. The electron affinity should increase as we move from left to right. 3. Because of t ...
... 1. Metals have a tendency to lose electrons; nonmetals tend to gain electrons. Nonmetals would be expected to have a high electron affinity. 2. As we move across the periodic table, we move from metals to nonmetals. The electron affinity should increase as we move from left to right. 3. Because of t ...
CPO Science Link Teacher`s Guide
... alkali metals – elements in the first group of the periodic table atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The atomic number determines what element the atom represents. chemical properties – characteristics of matter that can be observed only when one substance changes into ...
... alkali metals – elements in the first group of the periodic table atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The atomic number determines what element the atom represents. chemical properties – characteristics of matter that can be observed only when one substance changes into ...
Metals and Nonmetals Metals and Nonmetals
... – Includes the noble (inert) gases as a special case ...
... – Includes the noble (inert) gases as a special case ...
120CH03 - Louisiana Tech University
... • How to tell metals from nonmetals: Be B Al Si Ge As Sb Te Po At ...
... • How to tell metals from nonmetals: Be B Al Si Ge As Sb Te Po At ...
1.1 elements and the periodic table
... modern periodic table. 12. Mendeleev placed sulfur and oxygen in the same family because of their similar chemical properties. For example, both oxygen and sulfur react with hydrogen according to the formula of H2R. 13. The discovery of noble gases supported Mendeleev’s periodic table in the sense t ...
... modern periodic table. 12. Mendeleev placed sulfur and oxygen in the same family because of their similar chemical properties. For example, both oxygen and sulfur react with hydrogen according to the formula of H2R. 13. The discovery of noble gases supported Mendeleev’s periodic table in the sense t ...
Chapter 6: Section 1 Searching for an Organizing Principle
... -includes some metals, some nonmetals, and some metalloids -most of them are solids, a few are gases, and only bromine is a liquid -the s and p sublevels of the highest occupied energy level are not filled ...
... -includes some metals, some nonmetals, and some metalloids -most of them are solids, a few are gases, and only bromine is a liquid -the s and p sublevels of the highest occupied energy level are not filled ...
Answer
... Electron gain enthalpy is the measure of the tendency of an isolated gaseous atom to accept an electron, whereas electronegativity is the measure of the tendency of an atom in a chemical compound to attract a shared pair of electrons. Question 3.23: How would you react to the statement that the elec ...
... Electron gain enthalpy is the measure of the tendency of an isolated gaseous atom to accept an electron, whereas electronegativity is the measure of the tendency of an atom in a chemical compound to attract a shared pair of electrons. Question 3.23: How would you react to the statement that the elec ...
1st semester Final Exam review material. Unit 1: Measurement and
... o most solutions are liquids but some can be solid (steel, bronze) and some are gases (air) o Phase describes any part of a sample with uniform composition and properties (solid, liquid, gas) o all homogeneous mixtures consist of a single phase Distinguishing Elements and Compounds A pure substanc ...
... o most solutions are liquids but some can be solid (steel, bronze) and some are gases (air) o Phase describes any part of a sample with uniform composition and properties (solid, liquid, gas) o all homogeneous mixtures consist of a single phase Distinguishing Elements and Compounds A pure substanc ...
Section 1 How Are Elements Organized
... • As the number of electrons in each element increases, stronger bonds between atoms can form. • As a result, more energy is needed for melting and boiling to occur. Near the middle of the d-block, the melting and boiling points reach a peak. As more electrons are added, they begin to form pairs wit ...
... • As the number of electrons in each element increases, stronger bonds between atoms can form. • As a result, more energy is needed for melting and boiling to occur. Near the middle of the d-block, the melting and boiling points reach a peak. As more electrons are added, they begin to form pairs wit ...
Periodic Table
... • Identify the four blocks of the periodic table based on their electron configuration. • Identify the two exceptions in normal orbital filling order in the period 4 transition metals. ...
... • Identify the four blocks of the periodic table based on their electron configuration. • Identify the two exceptions in normal orbital filling order in the period 4 transition metals. ...
Click_here
... When atoms have equal amount of protons and electrons, they are electrically neutral. But when enough energy is added, individual electrons can be removed from an atom. The neutral atom then becomes a positively charged ion. The ionization energy, or ionization potential, is the energy required to c ...
... When atoms have equal amount of protons and electrons, they are electrically neutral. But when enough energy is added, individual electrons can be removed from an atom. The neutral atom then becomes a positively charged ion. The ionization energy, or ionization potential, is the energy required to c ...
CHAPTER 8 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE ELEMENTS
... ionization energy. Thus, in the third period, sodium has the lowest and neon has the highest first ionization energy. ...
... ionization energy. Thus, in the third period, sodium has the lowest and neon has the highest first ionization energy. ...
Unit 1 Module 3 The Periodic Table
... What information is given by the atomic number of an element? Balance the equation: Na + Cl2 |l NaCl What is the formula of sulfuric acid? What gas is produced when magnesium reacts with an acid? ...
... What information is given by the atomic number of an element? Balance the equation: Na + Cl2 |l NaCl What is the formula of sulfuric acid? What gas is produced when magnesium reacts with an acid? ...
Summary 1 b - Uddingston Grammar School
... across periods and down groups in terms of atomic size, nuclear charge and the screening effect due to inner shell electrons. 14. Understand that atoms of different elements have different attractions for bonding electrons. 15. Define electronegativity as a measure of the attraction an atom involved ...
... across periods and down groups in terms of atomic size, nuclear charge and the screening effect due to inner shell electrons. 14. Understand that atoms of different elements have different attractions for bonding electrons. 15. Define electronegativity as a measure of the attraction an atom involved ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.