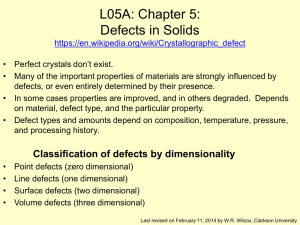
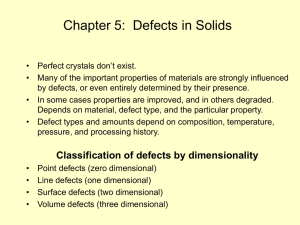
Spectral properties of Luttinger liquids: A comparative analysis of regular,... spiral Luttinger liquids
... On a spinoff from the LL theory, it has been shown in Refs. 37 and 38 that in the presence of a lattice of nuclear moments and of the hyperfine interaction, an exotic ordered phase emerges at low temperature in which the magnetic moments of the nuclei and the conduction electrons of a 1D conductor a ...
... On a spinoff from the LL theory, it has been shown in Refs. 37 and 38 that in the presence of a lattice of nuclear moments and of the hyperfine interaction, an exotic ordered phase emerges at low temperature in which the magnetic moments of the nuclei and the conduction electrons of a 1D conductor a ...
Lecture Notes in Statistical Mechanics and Mesoscopics Doron Cohen
... have a multi-component phase space with separatrix. The dynamics is not chaotic. One can define the oscillation frequency ω(E) as a function of energy. In the quantum case ω(E) corresponds to the level spacing at the vicinity of the energy E. Chaotic system:– The student is expected to be familiar w ...
... have a multi-component phase space with separatrix. The dynamics is not chaotic. One can define the oscillation frequency ω(E) as a function of energy. In the quantum case ω(E) corresponds to the level spacing at the vicinity of the energy E. Chaotic system:– The student is expected to be familiar w ...
... pressure related effects are similar to the previous curve. The 30 kbar plots require a closer look since at this pressure the system has undergone the Γ − X transition and the barrier height, both for the central and border barriers, has substantially decrease becoming a bulk-like structure. For ze ...
857_1.pdf
... Fokker-Planck) solutions are fundamentally different from the VDF associated with the solutions of 5 or 8moment hydrodynamic equations [19], or of any other set of hydrodynamic equations that proceed from the Grad or Chapman-Enskog expansion of the VDF. The Grad and Chapman-Enskog mathematical theor ...
... Fokker-Planck) solutions are fundamentally different from the VDF associated with the solutions of 5 or 8moment hydrodynamic equations [19], or of any other set of hydrodynamic equations that proceed from the Grad or Chapman-Enskog expansion of the VDF. The Grad and Chapman-Enskog mathematical theor ...
vertical component - H2 Physics Tuition
... Liquid flows through the horizontal tube T. By maintaining a constant liquid level in the reservoir, liquid flows through T at a constant rate. The rate of flow of the liquid is measured for different tubes T with the same length but of different radii r. The same liquid level is used in each experi ...
... Liquid flows through the horizontal tube T. By maintaining a constant liquid level in the reservoir, liquid flows through T at a constant rate. The rate of flow of the liquid is measured for different tubes T with the same length but of different radii r. The same liquid level is used in each experi ...
Optical spectroscopy of InGaAs quantum dots Arvid Larsson
... The work presented in this thesis deals with optical studies of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) in the InGaAs material system. It is shown that for selfassembled InAs QDs, the interaction with the surrounding GaAs barrier and the InAs wetting layer (WL) in particular, has a very large impact on the ...
... The work presented in this thesis deals with optical studies of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) in the InGaAs material system. It is shown that for selfassembled InAs QDs, the interaction with the surrounding GaAs barrier and the InAs wetting layer (WL) in particular, has a very large impact on the ...
Spin filling of valley-orbit states in a silicon quantum dot
... observed, before concluding in section 6. 2. Low-disorder silicon MOS quantum dot The triple-layer gate stack in our structure (Figure 1a and 1b) provides excellent flexibility for tuning the barrier transparency and the energy levels of the dot independently, see Supplementary Information for fabri ...
... observed, before concluding in section 6. 2. Low-disorder silicon MOS quantum dot The triple-layer gate stack in our structure (Figure 1a and 1b) provides excellent flexibility for tuning the barrier transparency and the energy levels of the dot independently, see Supplementary Information for fabri ...
Chapter 4 Above threshold ionization in atomic systems
... for 800 nm, 120 fs pulses at the intensities given in TW/cm2 in the figure (10Up = 39 eV). From Nandor et al. [2]. ing because of the large excursion amplitudes of free-electron motion in highintensity low-frequency fields and therefore necessitates a large spatial grid. The progress achieved in rec ...
... for 800 nm, 120 fs pulses at the intensities given in TW/cm2 in the figure (10Up = 39 eV). From Nandor et al. [2]. ing because of the large excursion amplitudes of free-electron motion in highintensity low-frequency fields and therefore necessitates a large spatial grid. The progress achieved in rec ...
637_diffusion
... of marked particles emitted from a source. Although the basic equations describing turbulent diffusion are available, there does not exist a single mathematical model that can be used as a practical means of computing atmospheric concentrations over all ranges of conditions. • The deciding factor in ...
... of marked particles emitted from a source. Although the basic equations describing turbulent diffusion are available, there does not exist a single mathematical model that can be used as a practical means of computing atmospheric concentrations over all ranges of conditions. • The deciding factor in ...
full-wave vlf modes in a cylindrically symmetric enhancement of
... half gyrofrequency, that is, with Y slightly greater than 2, the situation is more complicated. As k is decreased in the search procedure, it is evident from Fig. 1 that the two roots of equation (16) get very close. It was found that modes can exist for which l&l is not close to unity, indicating a ...
... half gyrofrequency, that is, with Y slightly greater than 2, the situation is more complicated. As k is decreased in the search procedure, it is evident from Fig. 1 that the two roots of equation (16) get very close. It was found that modes can exist for which l&l is not close to unity, indicating a ...
Calculation of the Cherenkov Light Yield for High
... energy of a cascade inducing particle. The light yield itself is described by the well-known Frank-Tamm formula which is a measure for the number of photons per unit path length and unit frequency of light of a single track. However, the theory behind the Frank-Tamm formula uses an infinite track ap ...
... energy of a cascade inducing particle. The light yield itself is described by the well-known Frank-Tamm formula which is a measure for the number of photons per unit path length and unit frequency of light of a single track. However, the theory behind the Frank-Tamm formula uses an infinite track ap ...
Atomic properties of superheavy elements No, Lr, and Rf
... shells with many valence electrons and strong correlations between them and between valence electrons and electrons in the core. Therefore, it is particulary important to establish the benchmark values for superheavy systems that have one to four valence electrons which can be treated by the most hi ...
... shells with many valence electrons and strong correlations between them and between valence electrons and electrons in the core. Therefore, it is particulary important to establish the benchmark values for superheavy systems that have one to four valence electrons which can be treated by the most hi ...
29 Electronic Response to External Perturbations
... in Chapters 24 and 25 without taking the interaction between electrons into account, although its role may be important in some cases. In this chapter we will study the response of the interacting electron system to external perturbations, to an applied electromagnetic field. We will consider first th ...
... in Chapters 24 and 25 without taking the interaction between electrons into account, although its role may be important in some cases. In this chapter we will study the response of the interacting electron system to external perturbations, to an applied electromagnetic field. We will consider first th ...
Thermalization of photoexcited carriers in bismuth investigated by
... material for the investigation of lattice dynamics in out-ofequilibrium conditions. The photoexcitation of this material generates coherent phonons which have various point group symmetries.3,4 Time-resolved reflectivity and time-resolved x-ray diffraction show that the frequency of the totally symm ...
... material for the investigation of lattice dynamics in out-ofequilibrium conditions. The photoexcitation of this material generates coherent phonons which have various point group symmetries.3,4 Time-resolved reflectivity and time-resolved x-ray diffraction show that the frequency of the totally symm ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.