Lab 2 sample rubric
... Part 3 – section 2, , reflecting any changes in the actual steps performed Part 4 – Temperature (to tenths of a degree), density (to six sig figs) and citation (organization and URL) Part 4 – Data tables for all of the volume trials, all with the correct units and number of sig figs Part 4 – Data ta ...
... Part 3 – section 2, , reflecting any changes in the actual steps performed Part 4 – Temperature (to tenths of a degree), density (to six sig figs) and citation (organization and URL) Part 4 – Data tables for all of the volume trials, all with the correct units and number of sig figs Part 4 – Data ta ...
Properties of Matter - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... arrangement, motion, and interaction of these particles determine the three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas). Particles in all three states are in constant motion. In the solid state, tightly packed particles have a limited range of motion. In the liquid state, particles are loosely packed ...
... arrangement, motion, and interaction of these particles determine the three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas). Particles in all three states are in constant motion. In the solid state, tightly packed particles have a limited range of motion. In the liquid state, particles are loosely packed ...
Plasmonic Periodic Structures Composed by 2D Materials
... Abstract Two-dimensional (2D) media, such as Graphene, can give to the host material electromagnetic properties which are not found in nature. From these fascinating effective behaviors, the Epsilon-Near-Zero (ENZ) effect and accordingly the appearance of Dirac Point (DP) is the objective of this wo ...
... Abstract Two-dimensional (2D) media, such as Graphene, can give to the host material electromagnetic properties which are not found in nature. From these fascinating effective behaviors, the Epsilon-Near-Zero (ENZ) effect and accordingly the appearance of Dirac Point (DP) is the objective of this wo ...
Carrier Action: Motion, Recombination and Generation.
... charge passing through a unit area per unit time. Jx = (-q)(n0) in C/(s m2) or A/m2
= +(qn0mn)Ex for e-’s acting alone.
= sn Ex (defining e- conductivity)
If both electrons and holes are present:
...
... charge passing through a unit area per unit time. Jx = (-q)(n0)
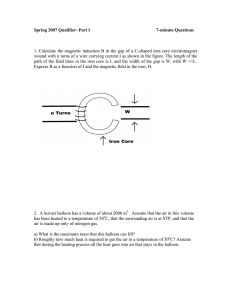
PHYS 2326 University Physics II
... 6. Two large parallel conducting plates are 8.0 cm apart and carry equal but opposite charges on their facing surfaces. The magnitude of the surface charge density on either of the facing surfaces is 2.0 nC/m2. Determine the magnitude of the electric potential difference between the plates. a. b. ...
... 6. Two large parallel conducting plates are 8.0 cm apart and carry equal but opposite charges on their facing surfaces. The magnitude of the surface charge density on either of the facing surfaces is 2.0 nC/m2. Determine the magnitude of the electric potential difference between the plates. a. b. ...
Minh Binh Nguyen Talk Announcement
... significantly broadening mankind's knowledge and experience on the quantum nano-world. However, in many cases, going toward low dimensionality requires to sacrifice a degree of freedom which is an intrinsic property of bulk 3D materials: interaction between sub-systems. Inspired by the way Nature pu ...
... significantly broadening mankind's knowledge and experience on the quantum nano-world. However, in many cases, going toward low dimensionality requires to sacrifice a degree of freedom which is an intrinsic property of bulk 3D materials: interaction between sub-systems. Inspired by the way Nature pu ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.