1. Assume a plane wave in vacuum for which... and the amplitude of the electric field is E
... B1. Is the direction of S in the direction of k for a plane wave in vacuum? B2. Is the direction of S always in the direction of k for a plane wave in a metal? C. The answer to B2 has implications for the energy flow per unit second of an EM-wave in a metal, the momentum density of and EM-wave in a ...
... B1. Is the direction of S in the direction of k for a plane wave in vacuum? B2. Is the direction of S always in the direction of k for a plane wave in a metal? C. The answer to B2 has implications for the energy flow per unit second of an EM-wave in a metal, the momentum density of and EM-wave in a ...
Fluids and Viscosity Chapter 7 Particle Theory of Matter (PTM)
... - Density is the measure of the mass contained in a given volume. - Density also describes how tightly packed together particles are in a material. More dense materials have more particles packed closer together. - Mass – the amount of matter in a substance - Volume – the amount of space occupied by ...
... - Density is the measure of the mass contained in a given volume. - Density also describes how tightly packed together particles are in a material. More dense materials have more particles packed closer together. - Mass – the amount of matter in a substance - Volume – the amount of space occupied by ...
First Exam
... other person. Do all three problems, showing your method and working clearly (a correct answer alone is not necessarily sufficient). Include correct SI units in your answers where appropriate. The number of marks for each part is given in square brackets, [ ], to its right. 1. (a) A very long, thin, ...
... other person. Do all three problems, showing your method and working clearly (a correct answer alone is not necessarily sufficient). Include correct SI units in your answers where appropriate. The number of marks for each part is given in square brackets, [ ], to its right. 1. (a) A very long, thin, ...
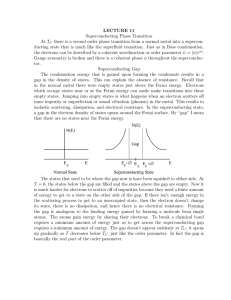
LECTURE 11 Superconducting Phase Transition At TC there is a
... exponentially because the thermal conductivity κ is proportional to the specific heat. (κ = 31 CV ve ℓ where ve is the electron drift velocity and ℓ is the electron mean free path, i.e., how far the electron gets before colliding with something.) In a metal it is primarily the electrons which are re ...
... exponentially because the thermal conductivity κ is proportional to the specific heat. (κ = 31 CV ve ℓ where ve is the electron drift velocity and ℓ is the electron mean free path, i.e., how far the electron gets before colliding with something.) In a metal it is primarily the electrons which are re ...
Two-Dimensional Quantum Effects and Structural Optimization of
... the current is suppressed compared to the classical one, due to the quantum-confinement effects. A comparison of the classical and QM electron density as seen for a cut through the Si channel is shown in Figure 12, and QM electron-density variations by changing Vg from 0.2 V to 0.6 V are shown in Fi ...
... the current is suppressed compared to the classical one, due to the quantum-confinement effects. A comparison of the classical and QM electron density as seen for a cut through the Si channel is shown in Figure 12, and QM electron-density variations by changing Vg from 0.2 V to 0.6 V are shown in Fi ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.