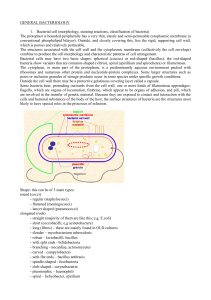
GENERAL BACTERIOLOGY 1. Bacterial cell
... at the bottom or a pellicle is seen at the top. In a solid medium (agar), a bacterial colony is formed. The result 109 cells/24 hours applies for stationary cultures, in which nutrients are consumed and metabolites accumulate. The speed of multiplication changes depending on time and the growth of t ...
... at the bottom or a pellicle is seen at the top. In a solid medium (agar), a bacterial colony is formed. The result 109 cells/24 hours applies for stationary cultures, in which nutrients are consumed and metabolites accumulate. The speed of multiplication changes depending on time and the growth of t ...
Microbial Metabolism
... For bacteria (e.g. E. coli ) that produces acids, causing the pH to drop below 4.4. When the pH indicator methyl red is added to this acidic broth it will be cherry red (a positive MR test). For bacteria (e.g. Klebsiella and Enterobacter) that produce more neutral products from glucose (e.g. ethyl a ...
... For bacteria (e.g. E. coli ) that produces acids, causing the pH to drop below 4.4. When the pH indicator methyl red is added to this acidic broth it will be cherry red (a positive MR test). For bacteria (e.g. Klebsiella and Enterobacter) that produce more neutral products from glucose (e.g. ethyl a ...
Special microbiology
... E. *Been treated with antibiotics. 14. Why tetanus is now a rare disease. Which factors below has been most important in preventing it? A. Vaccination of livestock, especially cattle, with a killed-organism vaccine B. Antibiotic treatment of contacts of patients with C. tetani infections. C. Eradica ...
... E. *Been treated with antibiotics. 14. Why tetanus is now a rare disease. Which factors below has been most important in preventing it? A. Vaccination of livestock, especially cattle, with a killed-organism vaccine B. Antibiotic treatment of contacts of patients with C. tetani infections. C. Eradica ...
The effect of histo-blood group antigen (HBGA)
... the estimated number of people that get infected with NoVs lies around 20 million in the USA and 15 million in Europe (CDC a, n.d.; WHO, 2015). The most common clinical symptoms include vomiting, non-bloody diarrhoea, abdominal cramps, nausea, fever and dehydration. NoV infections are mildly virulen ...
... the estimated number of people that get infected with NoVs lies around 20 million in the USA and 15 million in Europe (CDC a, n.d.; WHO, 2015). The most common clinical symptoms include vomiting, non-bloody diarrhoea, abdominal cramps, nausea, fever and dehydration. NoV infections are mildly virulen ...
ADVANCED OXIDATION TEST RESULTS 2000-2016
... become common as our litigious society has taught us to question things that significantly outperform existing methods or products. The RGF advanced oxidation technologies that produced the results found on the pages of this report certainly fall into the category of breakthrough technology. This is ...
... become common as our litigious society has taught us to question things that significantly outperform existing methods or products. The RGF advanced oxidation technologies that produced the results found on the pages of this report certainly fall into the category of breakthrough technology. This is ...
Bacteria Bafflement
... Part B: Identifying Bacteria Use the Dichotomous Key to help identify each bacterium pictured. What is its morphology? Read steps 1 and 1b. Choose the step that best describes the pictured bacterium. Do what the statement says to do. Continue until you arrive at the bacterium’s scientific name Writ ...
... Part B: Identifying Bacteria Use the Dichotomous Key to help identify each bacterium pictured. What is its morphology? Read steps 1 and 1b. Choose the step that best describes the pictured bacterium. Do what the statement says to do. Continue until you arrive at the bacterium’s scientific name Writ ...
Viruses - Red Wing Public Schools
... Is a Virus Alive?, continued Discovery of Viruses • Near the end of the nineteenth century, scientists were trying to find the cause of tobacco mosaic disease, which stunts the growth of tobacco plants. • In 1935, biologist Wendell Stanley of the Rockefeller Institute purified tobacco mosaic virus ( ...
... Is a Virus Alive?, continued Discovery of Viruses • Near the end of the nineteenth century, scientists were trying to find the cause of tobacco mosaic disease, which stunts the growth of tobacco plants. • In 1935, biologist Wendell Stanley of the Rockefeller Institute purified tobacco mosaic virus ( ...
Chapter 24-Bacteria
... can use, BUT they do NOT produces substances that are harmful either. Suggest a positive role you feel these bacteria might play. ...
... can use, BUT they do NOT produces substances that are harmful either. Suggest a positive role you feel these bacteria might play. ...
E-Coli - sohs
... high temperature of 41.5°C were examined on a genome wide scale for duplication/deletion events by using DNA high-density arrays. ...
... high temperature of 41.5°C were examined on a genome wide scale for duplication/deletion events by using DNA high-density arrays. ...
18.4 Bacteria and Archaea
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
VeryOldLabPractical
... and plated on blood agar as shown in the diagram above. What is the concentration of bacteria in the patient’s urine? a. 2800 bacteria/ml b. 2.8 x 10-3 bacteria/ml c. 2.8 x 104 bacteria/ml d. 2.8 x 105 bacteria/ml e. 2.8 x 103 bacteria/ml 14. What can you safely conclude about the patient above from ...
... and plated on blood agar as shown in the diagram above. What is the concentration of bacteria in the patient’s urine? a. 2800 bacteria/ml b. 2.8 x 10-3 bacteria/ml c. 2.8 x 104 bacteria/ml d. 2.8 x 105 bacteria/ml e. 2.8 x 103 bacteria/ml 14. What can you safely conclude about the patient above from ...
Document
... the smallest amount of preparation inhibiting the growth of a standard S. aureus strain. • One unit of activity (A.U.) corresponds to the activity of 0.6 micrograms (mg) of the chemically pure crystalline sodium salt of benzylpenicillin. ...
... the smallest amount of preparation inhibiting the growth of a standard S. aureus strain. • One unit of activity (A.U.) corresponds to the activity of 0.6 micrograms (mg) of the chemically pure crystalline sodium salt of benzylpenicillin. ...
Chp.5 Types of Bacteria
... There once lived a guy called Tyrone Cocci - He has a round shape -He likes to hang around singly or in groups -He is not very active -He is most comfortable when he is hanging out in the air or dirt ...
... There once lived a guy called Tyrone Cocci - He has a round shape -He likes to hang around singly or in groups -He is not very active -He is most comfortable when he is hanging out in the air or dirt ...
Chapter 25 Powerpoint Show
... One-third of missionaries are sick at any given time, largely due to impure water. ...
... One-third of missionaries are sick at any given time, largely due to impure water. ...
SWARTZ MICROBIOLOGY NOTES
... seed infusions and mutton gravy in flasks which were then sealed. He was able to see microorganisms some days later in the infusions. His infusions were obviously contaminated with microorganisms from the air. In 1769, Lazzaro Spallanzani (1729-1799) conducted experiments to disprove spontaneous gen ...
... seed infusions and mutton gravy in flasks which were then sealed. He was able to see microorganisms some days later in the infusions. His infusions were obviously contaminated with microorganisms from the air. In 1769, Lazzaro Spallanzani (1729-1799) conducted experiments to disprove spontaneous gen ...
Micro Chapter 18
... • strict human parasite, not able to culture it, was cultured in Armadillos so that it could be • studied and antigens harvested for evaluation and development of ?vaccine? • A. Not very virulent, slow progression • B. Tuberculoid form, minor skin damage, but can cause nerve damage • C. Lepromatous ...
... • strict human parasite, not able to culture it, was cultured in Armadillos so that it could be • studied and antigens harvested for evaluation and development of ?vaccine? • A. Not very virulent, slow progression • B. Tuberculoid form, minor skin damage, but can cause nerve damage • C. Lepromatous ...
Chapter 25 Powerpoint lecture
... Name the structures of the digestive system that contact food. ...
... Name the structures of the digestive system that contact food. ...
Obesity could be catching
... University of Wisconsin did research on a human virus that caused obesity in chickens. She believes it could also make humans fat. She also believes the virus exists in most countries around the world. Scientists have discussed the idea that a virus could lead to obesity for many years. Dr. Whigham ...
... University of Wisconsin did research on a human virus that caused obesity in chickens. She believes it could also make humans fat. She also believes the virus exists in most countries around the world. Scientists have discussed the idea that a virus could lead to obesity for many years. Dr. Whigham ...
A Guide to MANAGiNG RespiRAtoRy iNfectioNs
... In this booklet, you’ve learned that both viruses and bacteria can cause respiratory infections. Many times, the common cold, sore throat, sinus infections, and bronchitis are caused by viruses. With such infections, you will probably feel better within a week. You now know that antibiotics can’t ki ...
... In this booklet, you’ve learned that both viruses and bacteria can cause respiratory infections. Many times, the common cold, sore throat, sinus infections, and bronchitis are caused by viruses. With such infections, you will probably feel better within a week. You now know that antibiotics can’t ki ...
bacteria - MHS Biology Mrs. Gates
... b. A bacillus is an elongated or rod-shaped bacteria. c. Coccus bacteria are spherical (round). ...
... b. A bacillus is an elongated or rod-shaped bacteria. c. Coccus bacteria are spherical (round). ...
Medical Microbiology Core Competencies and Knowledge
... 1. Define, in detail, endogenous (i.e., normal flora) versus exogenous sources of infection. 2. Explain how normal flora on skin or mucosal membranes can cause disease when introduced into deeper tissues. 3. Explain how exogenous infections are a result of encounters with organisms in the environmen ...
... 1. Define, in detail, endogenous (i.e., normal flora) versus exogenous sources of infection. 2. Explain how normal flora on skin or mucosal membranes can cause disease when introduced into deeper tissues. 3. Explain how exogenous infections are a result of encounters with organisms in the environmen ...
Latin Root Word: archeo
... • Disease can also be caused by the immune response to the pathogen. • Pathogen-stimulated overproduction of cytokines can lead to symptoms of bacterial septic shock, and toxic shock syndrome. ...
... • Disease can also be caused by the immune response to the pathogen. • Pathogen-stimulated overproduction of cytokines can lead to symptoms of bacterial septic shock, and toxic shock syndrome. ...
Identifying Uropathogens
... Identifying different gram +ve bacteria: After gram stain, if the bacteria appear to be positive, the second step is to identify their shape. I.e. Cocci (spherical in shape) or Bacilli (rod-shaped). ...
... Identifying different gram +ve bacteria: After gram stain, if the bacteria appear to be positive, the second step is to identify their shape. I.e. Cocci (spherical in shape) or Bacilli (rod-shaped). ...
History of virology

The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Louis Pasteur and Edward Jenner developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitry Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a ""virus"" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology. By the 20th century many viruses were discovered.