Psychological Disorders - Ed W. Clark High School
... To be considered a disorder, a behavior must be: Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional ...
... To be considered a disorder, a behavior must be: Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional ...
Module 27
... Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
... Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
Module 27
... Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
... Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
Somatoform Disorders - Mrs. Dillon`s History Site
... emotions (i.e. rejection), then they are expressed symbolically in physical symptoms. ...
... emotions (i.e. rejection), then they are expressed symbolically in physical symptoms. ...
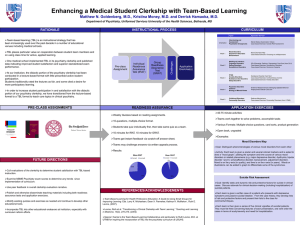
Enhancing a Medical Student Clerkship with Team
... Team-based learning (TBL) is an instructional strategy that has been increasingly used over the past decade in a number of educational venues including medical schools. ...
... Team-based learning (TBL) is an instructional strategy that has been increasingly used over the past decade in a number of educational venues including medical schools. ...
Module 27 - Cobb Learning
... Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
... Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
Psych B – Module 27
... Early Views of Mental Illness • In ancient times, mental illness was usually explained through a supernatural model; the person was possessed or a sinner • During the Middle Ages treatment methods were inhumane and cruel ...
... Early Views of Mental Illness • In ancient times, mental illness was usually explained through a supernatural model; the person was possessed or a sinner • During the Middle Ages treatment methods were inhumane and cruel ...
Psych B
... • A behavior which does normal, acceptable not have a rational basis behaviors • Destructive to oneself or others Atypical ...
... • A behavior which does normal, acceptable not have a rational basis behaviors • Destructive to oneself or others Atypical ...
Anxiety, Somatoform, Dissociative Disorders and Stress
... Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by repetitive, irrational thoughts and irresistible impulses such as washing hands. – The lifetime prevalence of OCD is about 2.5 percent and the rate is higher among women. ...
... Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by repetitive, irrational thoughts and irresistible impulses such as washing hands. – The lifetime prevalence of OCD is about 2.5 percent and the rate is higher among women. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • Affects children, teenagers, and adults • Occurs across all social and economic levels • 80% of all cases, it involves washing rituals linked to contamination fears ...
... • Affects children, teenagers, and adults • Occurs across all social and economic levels • 80% of all cases, it involves washing rituals linked to contamination fears ...
Personality Disorders
... • The brain of those with schizophrenia operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
... • The brain of those with schizophrenia operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
Psychological Disorders
... Freud did not have any good explanation for schizophrenia In terms of genetic factors, one stands a 13% chance of developing schizophrenia if one of his or her parents is schizophrenic, and a 45- 50% chance if his or her identical twin suffers from the disorder If heredity was the sole factor, it wo ...
... Freud did not have any good explanation for schizophrenia In terms of genetic factors, one stands a 13% chance of developing schizophrenia if one of his or her parents is schizophrenic, and a 45- 50% chance if his or her identical twin suffers from the disorder If heredity was the sole factor, it wo ...
Abnormal Psychology - Rutgers Psychology
... Course Objectives This course will introduce you to the fascinating study of abnormal behavior. We will examine such factors as: cultural norms, situational circumstances, cognitive, biological, social variables and how they interact to produce aberrant behavior. .We will compare various current the ...
... Course Objectives This course will introduce you to the fascinating study of abnormal behavior. We will examine such factors as: cultural norms, situational circumstances, cognitive, biological, social variables and how they interact to produce aberrant behavior. .We will compare various current the ...
Teacher Ratings of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms
... Typical factor extraction methods use a matrix of Pearson product–moment correlations; however, this method assumes that variables are at least at the interval level. For ordinal data, such as responses on behavior rating scales, it is more appropriate to use polychoric correlations (Joreskog & Sorb ...
... Typical factor extraction methods use a matrix of Pearson product–moment correlations; however, this method assumes that variables are at least at the interval level. For ordinal data, such as responses on behavior rating scales, it is more appropriate to use polychoric correlations (Joreskog & Sorb ...
Conditioning - WordPress.com
... Classical Conditioning Classical conditioning occurs gradually. The more frequently the tuning fork was paired with food the stronger the salivation response was. ...
... Classical Conditioning Classical conditioning occurs gradually. The more frequently the tuning fork was paired with food the stronger the salivation response was. ...
Unit 1 Notes: Psychological Disorders Dysfunctional Behavior
... – cognitive model: dysfunctional behavior is the result of irrational or distorted thinking that leads to emotional problems and maladaptive behaviors – psychoanalytic model: dysfunctional behavior is the result o ...
... – cognitive model: dysfunctional behavior is the result of irrational or distorted thinking that leads to emotional problems and maladaptive behaviors – psychoanalytic model: dysfunctional behavior is the result o ...
Personality Disorders in Long Term Care
... – Fear of rejection leads to “nursing home depression” • Planted in their room • Attempts by facility to socialize increase anxiety and depressed mood ...
... – Fear of rejection leads to “nursing home depression” • Planted in their room • Attempts by facility to socialize increase anxiety and depressed mood ...
Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormal Behavior
... – A mood disorder characterized by extreme mood swings that include one or more episodes of mania (an overexcited, unrealistically optimistic state) – Person may experience depression and mania ...
... – A mood disorder characterized by extreme mood swings that include one or more episodes of mania (an overexcited, unrealistically optimistic state) – Person may experience depression and mania ...
Psychological Disorder - MrKs
... o Persistent depressed mood for most of the day o Loss of interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, activities o Significant weight loss or gain due to changes in appetite o Sleeping more or less than usual o Speeding up or slowing down of physical and emotional o o o o ...
... o Persistent depressed mood for most of the day o Loss of interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, activities o Significant weight loss or gain due to changes in appetite o Sleeping more or less than usual o Speeding up or slowing down of physical and emotional o o o o ...
Chapter 10 Powerpoint Handout
... Mode of learning in which the frequency of responding is influenced by the consequences that are contingent upon a response bar-pressing in rats, reinforced by food smiling in a child, reinforced by parental approval ...
... Mode of learning in which the frequency of responding is influenced by the consequences that are contingent upon a response bar-pressing in rats, reinforced by food smiling in a child, reinforced by parental approval ...
Unit 1 Notes: Psychological Disorders
... – cognitive model: dysfunctional behavior is the result of irrational or distorted thinking that leads to emotional problems and maladaptive behaviors – psychoanalytic model: dysfunctional behavior is the result of internal, unconscious conflicts and motives stemming from childhood Reasons for Class ...
... – cognitive model: dysfunctional behavior is the result of irrational or distorted thinking that leads to emotional problems and maladaptive behaviors – psychoanalytic model: dysfunctional behavior is the result of internal, unconscious conflicts and motives stemming from childhood Reasons for Class ...
Personality Disorders
... Require constant attention and admiration Lack of empathy, strong feelings of arrogance, entitlement • Take advantage of others ...
... Require constant attention and admiration Lack of empathy, strong feelings of arrogance, entitlement • Take advantage of others ...
Impulsivity
Impulsivity (or impulsiveness) is a multifactorial construct that involves a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically ""poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation that often result in undesirable consequences,"" which imperil long-term goals and strategies for success. A functional variety of impulsivity has also been suggested, which involves action without much forethought in appropriate situations that can and does result in desirable consequences. ""When such actions have positive outcomes, they tend not to be seen as signs of impulsivity, but as indicators of boldness, quickness, spontaneity, courageousness, or unconventionality"" Thus, the construct of impulsivity includes at least the two independent components of, first: acting without an appropriate amount of deliberation, which may or may not be functional; and, second: choosing short-term gains over long-term ones.Impulsivity is both a facet of personality as well as a major component of various disorders, including ADHD, substance use disorders, bipolar disorder, antisocial personality disorder, and borderline personality disorder. Impulsiveness may also be a factor in procrastination. Abnormal patterns of impulsivity have also been noted instances of acquired brain injury and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiological findings suggest that there are specific brain regions involved in impulsive behavior, although different brain networks may contribute to different manifestations of impulsivity, and that genetics may play a role.Many actions contain both impulsive and compulsive features, but impulsivity and compulsivity are functionally distinct. Impulsivity and compulsivity are interrelated in that each exhibits a tendency to act prematurely or without considered thought and often include negative outcomes. Compulsivity may be on a continuum with compulsivity on one end and impulsivity on the other, but research has been contradictory on this point. Compulsivity occurs in response to a perceived risk or threat, impulsivity occurs in response to a perceived immediate gain or benefit, and, whereas compulsivity involves repetitive actions, impulsivity involves unplanned reactions.