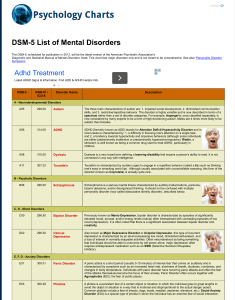
DSM-5 - KVCC Docs
... OCD stands for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and is characterized by uncontrollable thoughts (obsessions) that lead to repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at relieving the anxiety brought on by those thoughts. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, repeated checking, nervous rituals, ...
... OCD stands for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and is characterized by uncontrollable thoughts (obsessions) that lead to repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at relieving the anxiety brought on by those thoughts. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, repeated checking, nervous rituals, ...
Psychological Disorders
... to a child-like stage. Fantasies get confused with reality leading to hallucinations and delusions. The family with frequently critical attitudes towards a child could put the child at risk or cause someone to relapse. The Biological theorists believe it is a brain disorder Schizophrenics have small ...
... to a child-like stage. Fantasies get confused with reality leading to hallucinations and delusions. The family with frequently critical attitudes towards a child could put the child at risk or cause someone to relapse. The Biological theorists believe it is a brain disorder Schizophrenics have small ...
Chapter 18—Psychological Disorders
... patterns of inflexible traits that disrupt social life or work and/or distress the affected individual ...
... patterns of inflexible traits that disrupt social life or work and/or distress the affected individual ...
Conversion Disorder in Young People
... The symptom or deficit, after appropriate investigation, cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or as a culturally lt ll sanctioned ti d behavior b h i or experience. i The symptom or deficit causes clinically significant distress or impairment i ...
... The symptom or deficit, after appropriate investigation, cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or as a culturally lt ll sanctioned ti d behavior b h i or experience. i The symptom or deficit causes clinically significant distress or impairment i ...
chapter 13
... b. humanistic-existential (include the concepts of self-image and existential anxiety) c. behavioral (include the terms “self-defeating,” “paradox,” “avoidance learning,” and “anxiety reduction hypothesis”) d. cognitive 20. Define what is meant by the term “psychosis.” 21. Define “delusion.” 22. Def ...
... b. humanistic-existential (include the concepts of self-image and existential anxiety) c. behavioral (include the terms “self-defeating,” “paradox,” “avoidance learning,” and “anxiety reduction hypothesis”) d. cognitive 20. Define what is meant by the term “psychosis.” 21. Define “delusion.” 22. Def ...
View Presentation
... Clinical onset of panic disorder is later. The role of heredity appears to be greater in panic disorder. The ratio of women to men is greater in panic disorder. Alcoholism is more common in people suffering from panic disorder. Depression is more common in panic disorder. ...
... Clinical onset of panic disorder is later. The role of heredity appears to be greater in panic disorder. The ratio of women to men is greater in panic disorder. Alcoholism is more common in people suffering from panic disorder. Depression is more common in panic disorder. ...
Functional disorders: a neurologist`s account
... Figure 1 A simple cognitive model of physical symptoms. From Price and Leaver (2002). Reproduced with permission from BMJ Publishing. ...
... Figure 1 A simple cognitive model of physical symptoms. From Price and Leaver (2002). Reproduced with permission from BMJ Publishing. ...
Psych B – Module 27
... Classifying Disorders: DSM-IV-TR • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
... Classifying Disorders: DSM-IV-TR • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Fourth Edition • The text of the DSM-IV was recently revised, hence “TR” at the end • Published by the American Psychiatric ...
Psych B
... • In ancient times, mental illness was usually explained through a supernatural model; the person was possessed or a sinner • During the Middle Ages treatment methods were inhumane and cruel ...
... • In ancient times, mental illness was usually explained through a supernatural model; the person was possessed or a sinner • During the Middle Ages treatment methods were inhumane and cruel ...
psychological disorders - Bremerton School District
... 3. Inability to identify or avoid the cause of certain feelings. Two-thirds of the people with generalized anxiety disorder are women. The cause of the anxiety cannot be identified. It is often accompanied by depression. ...
... 3. Inability to identify or avoid the cause of certain feelings. Two-thirds of the people with generalized anxiety disorder are women. The cause of the anxiety cannot be identified. It is often accompanied by depression. ...
Mental & Physical Health Slides
... the floor on the axis of a crucifix. The victim's body is then brushed with a bouquet of fresh herbs, while the curandero and other participants recite prayers. Depending on local custom, the curandero may also jump over the victim's body - this is thought by some to exhort the frightened soul back ...
... the floor on the axis of a crucifix. The victim's body is then brushed with a bouquet of fresh herbs, while the curandero and other participants recite prayers. Depending on local custom, the curandero may also jump over the victim's body - this is thought by some to exhort the frightened soul back ...























