Communicating
... A 1. Must exhibit 6 or more symptoms of inattention, persisting for minimum of 6 months: from list of 9 items, a through i. A 2. Must exhibit 6 or more symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity, persisting for minimum of 6 months, from list of 9 items, a through i. ...
... A 1. Must exhibit 6 or more symptoms of inattention, persisting for minimum of 6 months: from list of 9 items, a through i. A 2. Must exhibit 6 or more symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity, persisting for minimum of 6 months, from list of 9 items, a through i. ...
ADHD information
... excess of those required to impairment between “mild” make the diagnosis are and “severe” are present present, and symptoms result in no more than minor impairments in social or occupational functioning ...
... excess of those required to impairment between “mild” make the diagnosis are and “severe” are present present, and symptoms result in no more than minor impairments in social or occupational functioning ...
ADHD - SPED*NET Wilton
... • Some hyperactive-impulsive symptoms or inattentive symptoms that caused impairment were present before age 7. ...
... • Some hyperactive-impulsive symptoms or inattentive symptoms that caused impairment were present before age 7. ...
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Treatment
... symptoms of inattention and/or hyperactivity/impulsivity. The symptoms need to have persisted for at least six (6) months and caused impairment in at least two (2) settings, such as home and school. Symptoms are usually present before age seven (7), but other causes of the symptoms, such as Schizoph ...
... symptoms of inattention and/or hyperactivity/impulsivity. The symptoms need to have persisted for at least six (6) months and caused impairment in at least two (2) settings, such as home and school. Symptoms are usually present before age seven (7), but other causes of the symptoms, such as Schizoph ...
Schizophrenia - DSM-5
... Schizophrenia is characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech and behavior, and other symptoms that cause social or occupational dysfunction. For a diagnosis, symptoms must have been present for six months and include at least one month of active symptoms. DSM-5 raises the symptom ...
... Schizophrenia is characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech and behavior, and other symptoms that cause social or occupational dysfunction. For a diagnosis, symptoms must have been present for six months and include at least one month of active symptoms. DSM-5 raises the symptom ...
Word - University of Maine Farmington
... objective historical information about the educational impact of the ADHD from childhood to the present such as transcripts, report cards, teacher comments, tutoring evaluations, past psychoeducational testing, and other third party interviews. The individual’s history of using academic accommodatio ...
... objective historical information about the educational impact of the ADHD from childhood to the present such as transcripts, report cards, teacher comments, tutoring evaluations, past psychoeducational testing, and other third party interviews. The individual’s history of using academic accommodatio ...
Notes - ADHD Association of Greater Edmonton
... In adulthood: 56% inattentive type and 44% combined type. See comorbidity as child ages. 46% expelled, 35% drop out. Substance abuse: earlier onset and faster progression. Less likely to quit in adulthood. Absenteeism and productivity levels affected at work. 2 to 4 times as many motor accidents. ...
... In adulthood: 56% inattentive type and 44% combined type. See comorbidity as child ages. 46% expelled, 35% drop out. Substance abuse: earlier onset and faster progression. Less likely to quit in adulthood. Absenteeism and productivity levels affected at work. 2 to 4 times as many motor accidents. ...
powerpoint presentation for teaching
... • Lack of evidence of effectiveness on core ADHD symptoms • Evidence that they improve parenting and decrease childhood conduct problems • ADHD cases with comorbid ODD/CD and anxiety most likely to benefit • Larger effect size in non-medicated and pre-school age children • Worse outcomes with lowe ...
... • Lack of evidence of effectiveness on core ADHD symptoms • Evidence that they improve parenting and decrease childhood conduct problems • ADHD cases with comorbid ODD/CD and anxiety most likely to benefit • Larger effect size in non-medicated and pre-school age children • Worse outcomes with lowe ...
Assessment of ADHD - Tata Interactive Systems
... Depressive disorder/Bipolar disorder Substance use disorder ...
... Depressive disorder/Bipolar disorder Substance use disorder ...
Attention deficit
... Parents and teachers can miss the fact that children with symptoms of inattention have the disorder because they are often quiet and less likely to act out. They may sit quietly, seeming to work, but they are often not paying attention to what they are doing. They may get along well with other child ...
... Parents and teachers can miss the fact that children with symptoms of inattention have the disorder because they are often quiet and less likely to act out. They may sit quietly, seeming to work, but they are often not paying attention to what they are doing. They may get along well with other child ...
Adult ADHD: The Problems, the Tests, the Treatments, the Challenges
... 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
... 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
Adult ADHD: The Problems, the Tests, the Treatments, the
... 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
... 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
ADHD and the DSM 5 - ADHD Awareness Month
... ADHD and the DSM 5 What is ADHD? ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting both children and adults. It is described as a “persistent” or on-going pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that gets in the way of daily life or typical development. Individuals with ADHD may also h ...
... ADHD and the DSM 5 What is ADHD? ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting both children and adults. It is described as a “persistent” or on-going pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that gets in the way of daily life or typical development. Individuals with ADHD may also h ...
Attention Deficit Disorder and Attention Deficit
... Children with ADHD will experience an excess of these symptoms Clear evidence that the symptoms interfere with their functioning at school/work or impact ability to socialize ...
... Children with ADHD will experience an excess of these symptoms Clear evidence that the symptoms interfere with their functioning at school/work or impact ability to socialize ...
Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder ADHD) Is it ADHD?
... edition (DSM-5) is used by mental health professionals to help diagnose ADHD. It was released in May 2013 and replaces the previous version, the text revision of the fourth edition (DSM-IV-TR). This diagnostic standard helps ensure that people are appropriately diagnosed and treated for ADHD. Using ...
... edition (DSM-5) is used by mental health professionals to help diagnose ADHD. It was released in May 2013 and replaces the previous version, the text revision of the fourth edition (DSM-IV-TR). This diagnostic standard helps ensure that people are appropriately diagnosed and treated for ADHD. Using ...
SHIP conference July 31 2012 Linda Grossman M.D. Anna Maria Wilms Floet M.D.
... Description of new medications used in treatment of ADHD Describe information about co-occurring problems and long term outcomes and their implications for individuals with ADHD ...
... Description of new medications used in treatment of ADHD Describe information about co-occurring problems and long term outcomes and their implications for individuals with ADHD ...
Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder - DSM-5
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
Document
... and types of ADHD Basic interventions with ADHD ADHD and the typical comorbidity ...
... and types of ADHD Basic interventions with ADHD ADHD and the typical comorbidity ...
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
... ____ ____ often blurts out answers before question completed ____ ____ often has difficulty awaiting turn ____ ____ often interrupts or intrudes on others B. ____ ____ Some symptoms present before age 7 C. ____ ____ Some impairment present in 2 or more settings D. ____ ____ Symptoms do not occur exc ...
... ____ ____ often blurts out answers before question completed ____ ____ often has difficulty awaiting turn ____ ____ often interrupts or intrudes on others B. ____ ____ Some symptoms present before age 7 C. ____ ____ Some impairment present in 2 or more settings D. ____ ____ Symptoms do not occur exc ...
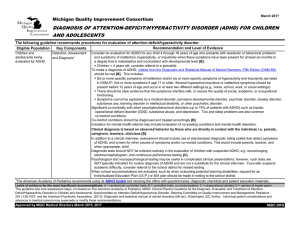
diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd)
... To make a diagnosis of ADHD, criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5®) should be met [B]. This includes: w Six or more specific symptoms of inattention and/or six or more specific symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity (as listed in DSM-5®; fi ...
... To make a diagnosis of ADHD, criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5®) should be met [B]. This includes: w Six or more specific symptoms of inattention and/or six or more specific symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity (as listed in DSM-5®; fi ...
ADHD (TDAH)
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
What Are the Symptoms
... Although it can often be challenging to raise kids with ADHD, it's important to remember they aren't "bad," "acting out," or being difficult on purpose. And children who are diagnosed with ADHD have difficulty controlling their behavior without medication or behavioral therapy. ...
... Although it can often be challenging to raise kids with ADHD, it's important to remember they aren't "bad," "acting out," or being difficult on purpose. And children who are diagnosed with ADHD have difficulty controlling their behavior without medication or behavioral therapy. ...