Texts in Computational Complexity - The Faculty of Mathematics and
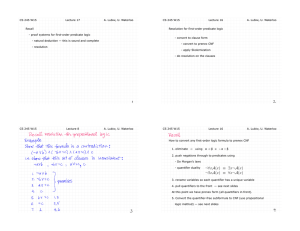
... 1. The type of failure is a qualitative notion. One aspect of this type is whether, in case of failure, the algorithm produces a wrong answer or merely an indication that it failed to nd a correct answer. Another aspect is whether failure may occur on all instances or merely on certain types of in ...
... 1. The type of failure is a qualitative notion. One aspect of this type is whether, in case of failure, the algorithm produces a wrong answer or merely an indication that it failed to nd a correct answer. Another aspect is whether failure may occur on all instances or merely on certain types of in ...
1 Integer Division
... we want to know how many times b goes into a, we can always write a in terms of b like so: a = qb + r, where 0 ≤ r < b This is known as the division algorithm and it tells us that b goes into a q times with r left over. So, to be formal: Theorem 1 (The Division Algorithm) If a, b ∈ Z, with b > 0 the ...
... we want to know how many times b goes into a, we can always write a in terms of b like so: a = qb + r, where 0 ≤ r < b This is known as the division algorithm and it tells us that b goes into a q times with r left over. So, to be formal: Theorem 1 (The Division Algorithm) If a, b ∈ Z, with b > 0 the ...
An Algorithm for Solving Scaled Total Least Squares Problems
... where (v22 we know, computing the SVD is expensive. In this paper, we present an algorithm for solving the STLS problem using a rank revealing decomposition. This algorithm is more efficient than the SVD method and it is particularly efficient for the STLS problems with same coefficient matrix A but ...
... where (v22 we know, computing the SVD is expensive. In this paper, we present an algorithm for solving the STLS problem using a rank revealing decomposition. This algorithm is more efficient than the SVD method and it is particularly efficient for the STLS problems with same coefficient matrix A but ...
Process optimization of pointing of the onboard weapon
... Sometimes the customer completely supervises all development process, and sometimes on such inspection it hasn't enough time, and, occasionally, and profound knowledge of the theory of the hardware and program creation of robotics complexes. In that case, cost of a robotics complex can appear much u ...
... Sometimes the customer completely supervises all development process, and sometimes on such inspection it hasn't enough time, and, occasionally, and profound knowledge of the theory of the hardware and program creation of robotics complexes. In that case, cost of a robotics complex can appear much u ...
An Improved Ant Colony Optimisation Algorithm for the 2D HP
... Protein Folding Problem incorporates a local search phase. In this work, we modified the local search mechanism from our previous ACO algorithm by using a new type of long range move, selective local search, and improving ants that perform probabilistic iterative improvement on the best conformation ...
... Protein Folding Problem incorporates a local search phase. In this work, we modified the local search mechanism from our previous ACO algorithm by using a new type of long range move, selective local search, and improving ants that perform probabilistic iterative improvement on the best conformation ...
Optimal Resource Allocation for MIMO Ad Hoc Cognitive Radio
... that impinge upon the receiver of link ), and thus possesses improved scalability and robustness properties. Remark 2: There are avenues to further reduce the feedback overhead in practice. First, the feedback information may be transmitted only when it has changed significantly. Since the channels ...
... that impinge upon the receiver of link ), and thus possesses improved scalability and robustness properties. Remark 2: There are avenues to further reduce the feedback overhead in practice. First, the feedback information may be transmitted only when it has changed significantly. Since the channels ...
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm (/ˈælɡərɪðəm/ AL-gə-ri-dhəm) is a self-contained step-by-step set of operations to be performed. Algorithms exist that perform calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning.An algorithm is an effective method that can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time and in a well-defined formal language for calculating a function. Starting from an initial state and initial input (perhaps empty), the instructions describe a computation that, when executed, proceeds through a finite number of well-defined successive states, eventually producing ""output"" and terminating at a final ending state. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms, incorporate random input.The concept of algorithm has existed for centuries, however a partial formalization of what would become the modern algorithm began with attempts to solve the Entscheidungsproblem (the ""decision problem"") posed by David Hilbert in 1928. Subsequent formalizations were framed as attempts to define ""effective calculability"" or ""effective method""; those formalizations included the Gödel–Herbrand–Kleene recursive functions of 1930, 1934 and 1935, Alonzo Church's lambda calculus of 1936, Emil Post's ""Formulation 1"" of 1936, and Alan Turing's Turing machines of 1936–7 and 1939. Giving a formal definition of algorithms, corresponding to the intuitive notion, remains a challenging problem.