Elementary Results on the Fibonacci Numbers - IME-USP
... 2.3. Generating Functions and the Fibonacci Numbers. It is a fortunate case that many sequences may be “compactly” represented by a single, “simple” univariate function, whose Taylor-Maclaurin expansion (around 0) [5] has the i-th sequence number as the coefficient of the i-th power of the variable ...
... 2.3. Generating Functions and the Fibonacci Numbers. It is a fortunate case that many sequences may be “compactly” represented by a single, “simple” univariate function, whose Taylor-Maclaurin expansion (around 0) [5] has the i-th sequence number as the coefficient of the i-th power of the variable ...
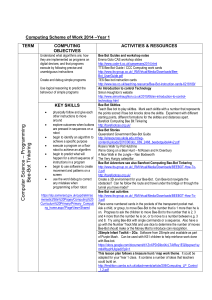
Computing Scheme of Work 2014 –Year 3
... A.L.E.X app and Cargo-Bot are used to meet new challenges. Children are encouraged to talk about the algorithm that will be required to meet the higher levels of challenge. NRICH Logo Resources First Forward Into Logo This series introduces Logo programming for beginners. These 12 challenges are wri ...
... A.L.E.X app and Cargo-Bot are used to meet new challenges. Children are encouraged to talk about the algorithm that will be required to meet the higher levels of challenge. NRICH Logo Resources First Forward Into Logo This series introduces Logo programming for beginners. These 12 challenges are wri ...
International Electrical Engineering Journal (IEEJ)
... Abstract- Economic load dispatch (ELD) in the operation of electric power system is an essential task, since it is required to determine the optimal output of electricity generating facilities, supplying the power to meet load demand at minimum cost while satisfying transmission and operational cons ...
... Abstract- Economic load dispatch (ELD) in the operation of electric power system is an essential task, since it is required to determine the optimal output of electricity generating facilities, supplying the power to meet load demand at minimum cost while satisfying transmission and operational cons ...
DECIMAL OPERATIONS EXPLORATION
... 5. Use fractional equivalents to explore division involving two decimals. Specifically, perform each of the following calculations in three ways: first, by changing the decimals to fractional form and then dividing (notice what’s happening!); second, by writing the division as a fraction and then mu ...
... 5. Use fractional equivalents to explore division involving two decimals. Specifically, perform each of the following calculations in three ways: first, by changing the decimals to fractional form and then dividing (notice what’s happening!); second, by writing the division as a fraction and then mu ...
Logarithmic Transformation-Based Gamma Random Number
... two illustrative algorithms for the special cases n = 2 and n = 4. In this article, we propose two algorithms to generate gamma random numbers using the ROU method. Both algorithms are based on logarithmic transformations of gamma random variables. One algorithm applies to all positive shape paramet ...
... two illustrative algorithms for the special cases n = 2 and n = 4. In this article, we propose two algorithms to generate gamma random numbers using the ROU method. Both algorithms are based on logarithmic transformations of gamma random variables. One algorithm applies to all positive shape paramet ...
Shortest Paths in Directed Planar Graphs with Negative Lengths: a
... All known planarity-exploiting algorithms for this problem, starting with that of Lipton, Rose, and Tarjan [1979], use planar separators, and use Bellman-Ford on a dense graph whose nodes are those comprising a planar separator. The algorithm of Henzinger et al. [1997] achieved an improvement by usi ...
... All known planarity-exploiting algorithms for this problem, starting with that of Lipton, Rose, and Tarjan [1979], use planar separators, and use Bellman-Ford on a dense graph whose nodes are those comprising a planar separator. The algorithm of Henzinger et al. [1997] achieved an improvement by usi ...
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm (/ˈælɡərɪðəm/ AL-gə-ri-dhəm) is a self-contained step-by-step set of operations to be performed. Algorithms exist that perform calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning.An algorithm is an effective method that can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time and in a well-defined formal language for calculating a function. Starting from an initial state and initial input (perhaps empty), the instructions describe a computation that, when executed, proceeds through a finite number of well-defined successive states, eventually producing ""output"" and terminating at a final ending state. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms, incorporate random input.The concept of algorithm has existed for centuries, however a partial formalization of what would become the modern algorithm began with attempts to solve the Entscheidungsproblem (the ""decision problem"") posed by David Hilbert in 1928. Subsequent formalizations were framed as attempts to define ""effective calculability"" or ""effective method""; those formalizations included the Gödel–Herbrand–Kleene recursive functions of 1930, 1934 and 1935, Alonzo Church's lambda calculus of 1936, Emil Post's ""Formulation 1"" of 1936, and Alan Turing's Turing machines of 1936–7 and 1939. Giving a formal definition of algorithms, corresponding to the intuitive notion, remains a challenging problem.