External Anatomy of Insects: The Exoskeleton, Head and Mouthparts
... A large, bulging compound eye is located dorsolaterally on each side of the head just posterior to the base of the antenna. Examine the surface of a compound eye and note that it is composed of an uncountable number of small light-receiving units known as ommatidia. The surface of the eye is a speci ...
... A large, bulging compound eye is located dorsolaterally on each side of the head just posterior to the base of the antenna. Examine the surface of a compound eye and note that it is composed of an uncountable number of small light-receiving units known as ommatidia. The surface of the eye is a speci ...
Phylum Arthopoda - Arthropods includes spiders, scorpions
... All have a pair of chelicerae, pair of pedipalps, four pairs of legs Chelicerae are first appendages, fangs with poison glands Pedipalps are next, similar to legs - rarely used for locomotion often used for catching and handling prey may also chew with basal portion may function as copulatory organs ...
... All have a pair of chelicerae, pair of pedipalps, four pairs of legs Chelicerae are first appendages, fangs with poison glands Pedipalps are next, similar to legs - rarely used for locomotion often used for catching and handling prey may also chew with basal portion may function as copulatory organs ...
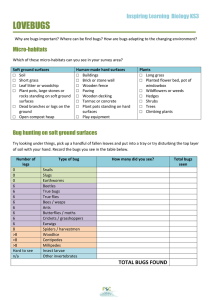
total bugs found
... Try looking on leaves and stems, flowers, and on trees and bushes by gently sweeping the plants with a dustpan to dislodge the bugs into your pan. Record the bugs you see in the table below. Number of legs ...
... Try looking on leaves and stems, flowers, and on trees and bushes by gently sweeping the plants with a dustpan to dislodge the bugs into your pan. Record the bugs you see in the table below. Number of legs ...
Phylum Arthopoda - Arthropods includes spiders, scorpions
... All have a pair of chelicerae, pair of pedipalps, four pairs of legs Chelicerae are first appendages, fangs with poison glands Pedipalps are next, similar to legs - rarely used for locomotion often used for catching and handling prey may also chew with basal portion may function as copulatory organs ...
... All have a pair of chelicerae, pair of pedipalps, four pairs of legs Chelicerae are first appendages, fangs with poison glands Pedipalps are next, similar to legs - rarely used for locomotion often used for catching and handling prey may also chew with basal portion may function as copulatory organs ...
Crustaceans Topics in Biodiversity
... Mystacocarida. These tiny crustaceans (less than 1 mm long) are well adapted to live in interstitial habitats between grains of sediment. There are only about a dozen known species. Like most interstitial organisms, they are not well studied, but are believed to scrape food from the surface of sand ...
... Mystacocarida. These tiny crustaceans (less than 1 mm long) are well adapted to live in interstitial habitats between grains of sediment. There are only about a dozen known species. Like most interstitial organisms, they are not well studied, but are believed to scrape food from the surface of sand ...
Zoology Ch. 14 Arthropods Arthropods and annelids are closely
... _____________ of the skin, eggs are deposited and ____________ of the mites irritate the skin, and ___________ occur. Ticks are ectoparasites during their __________ life. They may be up to _________ cm in length. Hooked mouthparts are used to attach to their hosts and to feed on ___________. Copula ...
... _____________ of the skin, eggs are deposited and ____________ of the mites irritate the skin, and ___________ occur. Ticks are ectoparasites during their __________ life. They may be up to _________ cm in length. Hooked mouthparts are used to attach to their hosts and to feed on ___________. Copula ...
Miller Harley Sample Chapter 15
... usually consists of small arthropods, earthworms, and snails; however, some centipedes feed on frogs and rodents. Poison claws (modified first-trunk appendages called maxillipeds) kill or immobilize prey. Maxillipeds, along with mouth appendages, hold the prey as mandibles chew and ingest the food. ...
... usually consists of small arthropods, earthworms, and snails; however, some centipedes feed on frogs and rodents. Poison claws (modified first-trunk appendages called maxillipeds) kill or immobilize prey. Maxillipeds, along with mouth appendages, hold the prey as mandibles chew and ingest the food. ...
Earthworm Dissection
... the worm ventral side up, as shown in the diagram below. What is the survival advantage of a darker dorsal side? ...
... the worm ventral side up, as shown in the diagram below. What is the survival advantage of a darker dorsal side? ...
Arthropods Again: The Crustacean
... The first type of arthropod that we will study is the crustacean. There are about 25,000 species in this class. They include: Barnacles Shrimp Lobster Crayfish Crab ...
... The first type of arthropod that we will study is the crustacean. There are about 25,000 species in this class. They include: Barnacles Shrimp Lobster Crayfish Crab ...
Unit 8: Invertebrates
... Each segment is similar and has the same organs. There are bristles between metameres that make easy the movement. They reproduce sexually and there are separate sexes species and hermaphrodite species. They have cross-fertilization. The phylum is divided into three classes: - Polychaetes (Bristle w ...
... Each segment is similar and has the same organs. There are bristles between metameres that make easy the movement. They reproduce sexually and there are separate sexes species and hermaphrodite species. They have cross-fertilization. The phylum is divided into three classes: - Polychaetes (Bristle w ...
i. 7 classes of vertebrates (1)
... Second loop takes O2 rich blood to body then takes O2 poor blood back to heart. Am phibian Types a. Salam anders i. Carnivores ii. Don't lose tail b. Frogs and Toads i. Toads can live in drier places that frogs. ...
... Second loop takes O2 rich blood to body then takes O2 poor blood back to heart. Am phibian Types a. Salam anders i. Carnivores ii. Don't lose tail b. Frogs and Toads i. Toads can live in drier places that frogs. ...
What Is an Amphibian? - Nashua School District
... begin a free-swimming, fishlike life. The larvae of most amphibians grow and eventually undergo metamorphosis. The larva of a frog or a toad is called a tadpole. Unlike tadpoles, the larvae of salamanders look like adults. Most salamander larvae undergo a metamorphosis in which they lose their gills ...
... begin a free-swimming, fishlike life. The larvae of most amphibians grow and eventually undergo metamorphosis. The larva of a frog or a toad is called a tadpole. Unlike tadpoles, the larvae of salamanders look like adults. Most salamander larvae undergo a metamorphosis in which they lose their gills ...
2007 Biology papers - Australian Science Innovations
... Q22 In a certain species of rat, fur colour is controlled by a single gene. There are two alleles for this gene, the black fur allele and the white fur allele. If these alleles were found to be incompletely dominant with respect to one another, then this species of rat would most likely have: A. onl ...
... Q22 In a certain species of rat, fur colour is controlled by a single gene. There are two alleles for this gene, the black fur allele and the white fur allele. If these alleles were found to be incompletely dominant with respect to one another, then this species of rat would most likely have: A. onl ...
Conor Porifera Quiz
... a. show how important crustaceans are in the aquatic food webs b. are never seen during daylight c. feed on seaweed and other aquatic plants d. cannot swim but draft instead 4. Crustaceans were once classified as molluscs because a. they live in a marine environment b. they secret a hard outer shell ...
... a. show how important crustaceans are in the aquatic food webs b. are never seen during daylight c. feed on seaweed and other aquatic plants d. cannot swim but draft instead 4. Crustaceans were once classified as molluscs because a. they live in a marine environment b. they secret a hard outer shell ...
Kingdom Animalia Outline
... Food is digested in a gut (gastrovascular cavity) and the resulting particles are absorbed by cells. This allows the animal to digest something larger than it’s own cells. c. Reproduction i. Separate sexes jellyfish but lower cnidarians like the hydra show asexual (budding) as well. Phylum Platyhelm ...
... Food is digested in a gut (gastrovascular cavity) and the resulting particles are absorbed by cells. This allows the animal to digest something larger than it’s own cells. c. Reproduction i. Separate sexes jellyfish but lower cnidarians like the hydra show asexual (budding) as well. Phylum Platyhelm ...
Kingdom Animalia
... particles are absorbed by cells. This allows the animal to digest something larger than it’s own cells. c. Reproduction i. Separate sexes jellyfish but lower cnidarians like the hydra show asexual (budding) as well. Phylum Platyhelminthes a. General i. Flatworms (e.g., planaria) ii. The bilateral sy ...
... particles are absorbed by cells. This allows the animal to digest something larger than it’s own cells. c. Reproduction i. Separate sexes jellyfish but lower cnidarians like the hydra show asexual (budding) as well. Phylum Platyhelminthes a. General i. Flatworms (e.g., planaria) ii. The bilateral sy ...
Chapter 17
... them a great delicacy and look forward to their breeding season. When the day arrives, they scoop them up in buckets and prepare a great feast, gorging themselves just as we do on thanksgiving day, knowing that there will not be another treat like it until exactly the same day of the next year. ...
... them a great delicacy and look forward to their breeding season. When the day arrives, they scoop them up in buckets and prepare a great feast, gorging themselves just as we do on thanksgiving day, knowing that there will not be another treat like it until exactly the same day of the next year. ...
Annelida
... from, seminal vesicles • Sperm from other worm stored in seminal receptacles • After separation, sperm from other worm used to fertilize eggs from the ovary ...
... from, seminal vesicles • Sperm from other worm stored in seminal receptacles • After separation, sperm from other worm used to fertilize eggs from the ovary ...
Chapter 17
... them a great delicacy and look forward to their breeding season. When the day arrives, they scoop them up in buckets and prepare a great feast, gorging themselves just as we do on thanksgiving day, knowing that there will not be another treat like it until exactly the same day of the next year." ...
... them a great delicacy and look forward to their breeding season. When the day arrives, they scoop them up in buckets and prepare a great feast, gorging themselves just as we do on thanksgiving day, knowing that there will not be another treat like it until exactly the same day of the next year." ...
lab 6 - natureboy
... • Use metanephridia for excretion, one in each segment • Use tracheal system with spiracles for respiration • Have hydrostatic skeleton, move like worms • Lay eggs (no larval stage) ...
... • Use metanephridia for excretion, one in each segment • Use tracheal system with spiracles for respiration • Have hydrostatic skeleton, move like worms • Lay eggs (no larval stage) ...
Invertebrates
... Platyhelminthes • Circulatory/Respiratory • no circulatory/respiratory organs • cells use diffusion to move dissolved oxygen/nutrients to all parts of their bodies • carbon dioxide/wastes are removed by diffusion • flame cells sweep water/waste into tubules to exit through pores ...
... Platyhelminthes • Circulatory/Respiratory • no circulatory/respiratory organs • cells use diffusion to move dissolved oxygen/nutrients to all parts of their bodies • carbon dioxide/wastes are removed by diffusion • flame cells sweep water/waste into tubules to exit through pores ...
Examples of Rarely Seen, Endemic, and Potentially Threatened
... occur in tropical Australia. These corals do not form large reefs in southern waters, but can grow as plates or heads (“bommies”) in some areas. Temperate corals extend their polyp tentacles at night to feed. They also make food during the day, with the aid of symbiotic zooxanthellae algae, which ph ...
... occur in tropical Australia. These corals do not form large reefs in southern waters, but can grow as plates or heads (“bommies”) in some areas. Temperate corals extend their polyp tentacles at night to feed. They also make food during the day, with the aid of symbiotic zooxanthellae algae, which ph ...
Segmented Worms cloze notes
... Annelids are worms with _________________ bodies. They have a true _____________ that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid The body of an annelid is divided into segments. Each segment is separated by ______________, which are internal walls between each segmen ...
... Annelids are worms with _________________ bodies. They have a true _____________ that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. Three Germ Layers of an Annelid The body of an annelid is divided into segments. Each segment is separated by ______________, which are internal walls between each segmen ...
Slide 1 - Images
... 39. The segments of an annelids body are separated by internal walls called septa. Most of these segments are the same but a few are modified to perform special functions such a ...
... 39. The segments of an annelids body are separated by internal walls called septa. Most of these segments are the same but a few are modified to perform special functions such a ...
Slide 1
... 39. The segments of an annelids body are separated by internal walls called septa. Most of these segments are the same but a few are modified to perform special functions such a ...
... 39. The segments of an annelids body are separated by internal walls called septa. Most of these segments are the same but a few are modified to perform special functions such a ...
Horse-fly

Horse-flies (for other names, see common names) are true flies in the family Tabanidae in the insect order Diptera. They are often large and agile in flight, and the females bite animals, including humans, in order to obtain blood. They prefer to fly in sunlight, avoiding dark and shady areas, and are inactive at night. They are found all over the world except for some islands and the polar regions.Adult horse-flies feed on nectar and plant exudates; the males have weak mouthparts and only the females bite animals to obtain enough protein from blood to produce eggs. The mouthparts of females are formed into a stout stabbing organ with two pairs of sharp cutting blades, and a spongelike part used to lap up the blood that flows from the wound. The larvae are predaceous and grow in semiaquatic habitats.Female horse-flies can transfer blood-borne diseases from one animal to another through their feeding habit. In areas where diseases occur, they have been known to carry equine infectious anaemia virus, some trypanosomes, the filarial worm Loa loa, anthrax among cattle and sheep, and tularemia. As well as making life outdoors uncomfortable for humans, they can reduce growth rates in cattle and lower the milk output of cows if suitable shelters are not provided.Horse-flies have appeared in literature since Aeschylus in Ancient Greece mentioned them driving people to madness through their persistent pursuit. Shakespeare uses the theme of the maddening gadfly in his plays King Lear and Antony and Cleopatra.