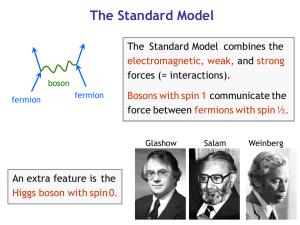
The Standard Model (SM) describes the fundamental particles of the
... Quarks – These are particles that are never found on their own and have fractional electric charges. Quarks come in six flavors: up, down, top, bottom, charm, and strange. Each quark has an associated anti-quark, typically indicated with a bar over the symbol. Quarks form two types of composite part ...
... Quarks – These are particles that are never found on their own and have fractional electric charges. Quarks come in six flavors: up, down, top, bottom, charm, and strange. Each quark has an associated anti-quark, typically indicated with a bar over the symbol. Quarks form two types of composite part ...
From ancient Greece to Nobel prize: a Higgs timeline
... United States propose that protons and neutrons well as invisible and indivisible particles called are comprised of quarks. atoms. 1974: The Standard Model of physics is devised: a theory that everything in the Universe is made up of 12 building-block particles governed by four fundamental forces. T ...
... United States propose that protons and neutrons well as invisible and indivisible particles called are comprised of quarks. atoms. 1974: The Standard Model of physics is devised: a theory that everything in the Universe is made up of 12 building-block particles governed by four fundamental forces. T ...
Bosons
... The anthropic principle The Standard Model does extremely well at predicting all kinds of measurements done by accelerators. But it is not able to calculate coupling constants. ...
... The anthropic principle The Standard Model does extremely well at predicting all kinds of measurements done by accelerators. But it is not able to calculate coupling constants. ...
GAUGE FIELD THEORY Examples
... where a ≈ α/2. (a) Investigate whether ψ is an eigenstate of Lz . (b) Find the expectation value of Lz and comment on the result. (c) Show that ψ is an eigenstate of Jz and find its eigenvalue. [ Don’t forget to normalize to one electron.] ...
... where a ≈ α/2. (a) Investigate whether ψ is an eigenstate of Lz . (b) Find the expectation value of Lz and comment on the result. (c) Show that ψ is an eigenstate of Jz and find its eigenvalue. [ Don’t forget to normalize to one electron.] ...
Higgs-part
... W and Z bosons (V) pick up mass from interaction with new scalar field Modifies V propagator from massless to effectively massive ...
... W and Z bosons (V) pick up mass from interaction with new scalar field Modifies V propagator from massless to effectively massive ...
Life in the Higgs condensate, where electrons have mass
... In 1963, Philip Anderson pointed out another important aspect: A would-be zero-mass Nambu-Goldstone boson in a superconductor is effectively eaten by the photon to become a finite-mass longitudinal mode, which appears as a plasmon in a nonrelativistic treatment. In 1964, realistic models with Lorent ...
... In 1963, Philip Anderson pointed out another important aspect: A would-be zero-mass Nambu-Goldstone boson in a superconductor is effectively eaten by the photon to become a finite-mass longitudinal mode, which appears as a plasmon in a nonrelativistic treatment. In 1964, realistic models with Lorent ...
Standard Model of Physics
... nature and the forces among them is in terms of gauge theories. These gauge theories are actually quantum field theories with a local symmetry under certain group transformations. To make the matters complicated, the local symmetry, and the coupling structure of matter and gauge fields, does not all ...
... nature and the forces among them is in terms of gauge theories. These gauge theories are actually quantum field theories with a local symmetry under certain group transformations. To make the matters complicated, the local symmetry, and the coupling structure of matter and gauge fields, does not all ...
Electroweak Theory - Florida State University
... must be two things, it must be gauge invariant and its must be renormalizable Gauge invariance requires that the boson which carries the force be massless, which is okay in E&M but the weak force is short range which would imply that its boson would have mass ...
... must be two things, it must be gauge invariant and its must be renormalizable Gauge invariance requires that the boson which carries the force be massless, which is okay in E&M but the weak force is short range which would imply that its boson would have mass ...
Rehearsal questions
... 1. What type of particles are described by the Klein-Gordon equation? Is there any such particle in the SM? 2. What type of particles are described by the Dirac equation? 3. How many Dirac matrices are there? 4. There are four solutions to the Dirac equations. What do they represent? 5. How many ind ...
... 1. What type of particles are described by the Klein-Gordon equation? Is there any such particle in the SM? 2. What type of particles are described by the Dirac equation? 3. How many Dirac matrices are there? 4. There are four solutions to the Dirac equations. What do they represent? 5. How many ind ...
Lecture 1 - Particle Physics Group
... An extra photon in the final state makes this a different process from the theoretical point of view, i.e. does not interfere with a). But may it be indistinguishable in practice, if so it has to be taken into account. ...
... An extra photon in the final state makes this a different process from the theoretical point of view, i.e. does not interfere with a). But may it be indistinguishable in practice, if so it has to be taken into account. ...