slides - University of Surrey
... signals from 0Hz to its cut-off frequency − High Pass Filter – allows high frequency signals from its cut-off frequency − Band Pass Filter – allows signals within a frequency range between two points to pass through and blocks both the lower and higher frequencies on either side of this frequency ra ...
... signals from 0Hz to its cut-off frequency − High Pass Filter – allows high frequency signals from its cut-off frequency − Band Pass Filter – allows signals within a frequency range between two points to pass through and blocks both the lower and higher frequencies on either side of this frequency ra ...
Active Filters
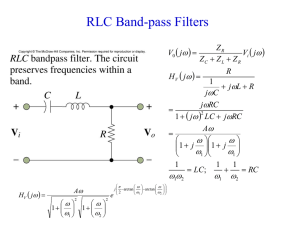
... inductors (RLC networks). To minimize distortion in the filter characteristic, it is desirable to use inductors with high quality factors (remember the model of a practical inductor includes a series resistance), however these are difficult to implement at frequencies below 1 kHz. ...
... inductors (RLC networks). To minimize distortion in the filter characteristic, it is desirable to use inductors with high quality factors (remember the model of a practical inductor includes a series resistance), however these are difficult to implement at frequencies below 1 kHz. ...
EEE 302 Lecture 23 - Arizona State University
... • Filters pass, reject, and attenuate signals at various frequencies • Common types of filters: Low-pass: pass low frequencies and reject high frequencies High-pass: pass high frequencies and reject low frequencies Band-pass: pass some particular range of frequencies, reject other frequencies outsid ...
... • Filters pass, reject, and attenuate signals at various frequencies • Common types of filters: Low-pass: pass low frequencies and reject high frequencies High-pass: pass high frequencies and reject low frequencies Band-pass: pass some particular range of frequencies, reject other frequencies outsid ...
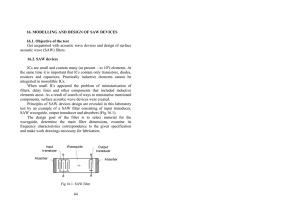
16. Modelling and design of SAW devices
... ICs are small and contain many (at present – to 108) elements. At the same time it is important that ICs contain only transistors, diodes, resistors and capacitors. Practically inductive elements cannot be integrated in monolithic ICs. When small ICs appeared the problem of miniaturisation of filter ...
... ICs are small and contain many (at present – to 108) elements. At the same time it is important that ICs contain only transistors, diodes, resistors and capacitors. Practically inductive elements cannot be integrated in monolithic ICs. When small ICs appeared the problem of miniaturisation of filter ...
Coulomb`s Law
... – More generally in this course, we are interested in voltage gain; since P ~ V2, voltage gain in dB= 20 log10 |Vout/Vin| Advantages of decibel measures: ...
... – More generally in this course, we are interested in voltage gain; since P ~ V2, voltage gain in dB= 20 log10 |Vout/Vin| Advantages of decibel measures: ...
DN169 - LTC1560-1: Tiny 1MHz Lowpass Filter Uses No Inductors
... other commercially available high frequency, continuoustime monolithic filters: • 5-pole 0.5MHz/1MHz elliptic in an SO-8 package • 70dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) measured at 0.07% THD • 75dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) measured at 0.5% THD • 60dB or more stopband attenuation • No external componen ...
... other commercially available high frequency, continuoustime monolithic filters: • 5-pole 0.5MHz/1MHz elliptic in an SO-8 package • 70dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) measured at 0.07% THD • 75dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) measured at 0.5% THD • 60dB or more stopband attenuation • No external componen ...
EMC Components and Filters
... Z0 should be as low as possible (a few Ω) Difficult with spaced round conductors ...
... Z0 should be as low as possible (a few Ω) Difficult with spaced round conductors ...
Millimeter Wave Corrugated Platelet Feeds
... compatible with available space and the desired circuit functionality. Between these two limiting cases, the use of delay lines and steps in impedance contrast between line sections can be used. The resonant sections formed by these circuit topologies for example can be cascaded and tailored to form ...
... compatible with available space and the desired circuit functionality. Between these two limiting cases, the use of delay lines and steps in impedance contrast between line sections can be used. The resonant sections formed by these circuit topologies for example can be cascaded and tailored to form ...
Log-domain low pass high pass first-order filter
... number of log-domain filters have been reported earlier1. The log-domain filters are externally linear but internally highly non-linear. The processing of the signals by transistors in exponentially manner has made log-domain filters attractive. In these filters, the input current signal is first ma ...
... number of log-domain filters have been reported earlier1. The log-domain filters are externally linear but internally highly non-linear. The processing of the signals by transistors in exponentially manner has made log-domain filters attractive. In these filters, the input current signal is first ma ...
Homework 15
... a) The gain of an RC filter (either hi-pass or lo-pass) at the cutoff frequency is _________________ . b) If an RC filter has an output of 7 V at its half-power point, the output voltage will be _______________ V at the cutoff frequency. c) If a device has a gain of 90, its gain in dB is ___________ ...
... a) The gain of an RC filter (either hi-pass or lo-pass) at the cutoff frequency is _________________ . b) If an RC filter has an output of 7 V at its half-power point, the output voltage will be _______________ V at the cutoff frequency. c) If a device has a gain of 90, its gain in dB is ___________ ...
Coulomb`s Law
... – More generally in this course, we are interested in voltage gain; since P ~ V2, voltage gain in dB= 20 log10 |Vout/Vin| Advantages of decibel measures: ...
... – More generally in this course, we are interested in voltage gain; since P ~ V2, voltage gain in dB= 20 log10 |Vout/Vin| Advantages of decibel measures: ...
Lab 7 - Electronic Filters (C and G Sections Only)
... 3dB drop of signal power from highest point on gain Signal power is half of original value Cutoff Frequency (in Hz) Frequency at -3dB Point ...
... 3dB drop of signal power from highest point on gain Signal power is half of original value Cutoff Frequency (in Hz) Frequency at -3dB Point ...
Active Filters - UniMAP Portal
... elliptic response will perform that function with the lowest-order filter.The elliptic function gives a sharp cutoff by adding notches in the stopband. These cause the transfer function to drop to zero at one or more frequencies in the stopband. Ripple is also introduced in the passband. An elliptic ...
... elliptic response will perform that function with the lowest-order filter.The elliptic function gives a sharp cutoff by adding notches in the stopband. These cause the transfer function to drop to zero at one or more frequencies in the stopband. Ripple is also introduced in the passband. An elliptic ...
Part 2 - UniMAP Portal
... Passive filters – combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors Active filters – incorporate operational amplifiers Important terms – roll-off (rate of transition where the magnitude ratio decreases relative to the frequency – dB/decade); phase shift (between input & output signal) ...
... Passive filters – combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors Active filters – incorporate operational amplifiers Important terms – roll-off (rate of transition where the magnitude ratio decreases relative to the frequency – dB/decade); phase shift (between input & output signal) ...
PENGENALAN FILTER AKTIF
... Filters are circuits that are capable of passing signals within a band of frequencies while rejecting or blocking signals of frequencies outside this band. This property of filters is also called “frequency selectivity”. Filter ...
... Filters are circuits that are capable of passing signals within a band of frequencies while rejecting or blocking signals of frequencies outside this band. This property of filters is also called “frequency selectivity”. Filter ...
Frequency response of feedback amplifiers
... • If we need to design a band-pass filter in which the lower cutoff frequency is much less than the upper cutoff frequency, we can cascade a low-pass filter with a high-pass filter. • The below band-pass filter uses the first stage as a low-pass filter which passes frequency less than 10KHz and the ...
... • If we need to design a band-pass filter in which the lower cutoff frequency is much less than the upper cutoff frequency, we can cascade a low-pass filter with a high-pass filter. • The below band-pass filter uses the first stage as a low-pass filter which passes frequency less than 10KHz and the ...
Lab 7
... 1. Design and construct the RC lowpass filter, assuming that it has a cutoff frequency of 1 kHz and a load of 5 k. 2. Test your low pass filter: Connect the filter (source side) to a 500 Hz sinusoidal function generator. Connect the filter (load side) to a 10 kΩ potentiometer set at 5 kΩ. Usi ...
... 1. Design and construct the RC lowpass filter, assuming that it has a cutoff frequency of 1 kHz and a load of 5 k. 2. Test your low pass filter: Connect the filter (source side) to a 500 Hz sinusoidal function generator. Connect the filter (load side) to a 10 kΩ potentiometer set at 5 kΩ. Usi ...
ee221_3
... output) are called active filters. Filters that contain only passive elements (elements that do not add energy to the system) are called passive filters. Active filters have the following advantages over passive filters: The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the ...
... output) are called active filters. Filters that contain only passive elements (elements that do not add energy to the system) are called passive filters. Active filters have the following advantages over passive filters: The gain of the filter is not limited between 0 and 1, and in most cases the ...
Wave, Filters
... • Learn about the different types of filters and their uses • Implement circuit elements to create different filters • Use your new knowledge to identify the filters based on the graphs created ...
... • Learn about the different types of filters and their uses • Implement circuit elements to create different filters • Use your new knowledge to identify the filters based on the graphs created ...
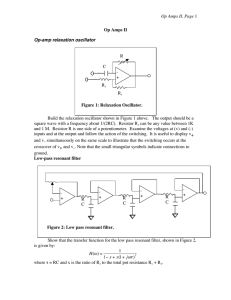
Op Amps II, Page R C -
... inputs and at the output and follow the action of the switching. It is useful to display v+ and v- simultaneously on the same scale to illustrate that the switching occurs at the crossover of v+ and v-. Note that the small triangular symbols indicate connections to ...
... inputs and at the output and follow the action of the switching. It is useful to display v+ and v- simultaneously on the same scale to illustrate that the switching occurs at the crossover of v+ and v-. Note that the small triangular symbols indicate connections to ...
10 GHZ TRANSVERTER
... quarter-wave resonator principle. The resonator longitude is less than quarter-wave. Shortening was done by a capacitor at the end of the resonator. This solution is very advantageous, because the physical longitude of a filter is shortened, as well as there is possibility to tune the filter on the ...
... quarter-wave resonator principle. The resonator longitude is less than quarter-wave. Shortening was done by a capacitor at the end of the resonator. This solution is very advantageous, because the physical longitude of a filter is shortened, as well as there is possibility to tune the filter on the ...
highpass filter - Jejaring Blog Unnes
... All materials are taken from “Fundamentals of electric circuits” ...
... All materials are taken from “Fundamentals of electric circuits” ...
Lecture 15: Wavelength-Division Multiplexing Components
... • Wavelengths for CWDM and frequencies for DWDM defined by International Telecommunication Union, a part of the United Nations located in Geneva • Central frequency is 193.1 THz, equivalent to 1552.52 nm • Frequencies for 50 GHz channel spacings are thus defined as 193.1 + 0.05n THz where n is a pos ...
... • Wavelengths for CWDM and frequencies for DWDM defined by International Telecommunication Union, a part of the United Nations located in Geneva • Central frequency is 193.1 THz, equivalent to 1552.52 nm • Frequencies for 50 GHz channel spacings are thus defined as 193.1 + 0.05n THz where n is a pos ...
Waveguide filter
A waveguide filter is an electronic filter that is constructed with waveguide technology. Waveguides are hollow metal tubes inside which an electromagnetic wave may be transmitted. Filters are devices used to allow signals at some frequencies to pass (the passband), while others are rejected (the stopband). Filters are a basic component of electronic engineering designs and have numerous applications. These include selection of signals and limitation of noise. Waveguide filters are most useful in the microwave band of frequencies, where they are a convenient size and have low loss. Examples of microwave filter use are found in satellite communications, telephone networks, and television broadcasting.Waveguide filters were developed during World War II to meet the needs of radar and electronic countermeasures, but afterwards soon found civilian applications such as use in microwave links. Much of post-war development was concerned with reducing the bulk and weight of these filters, first by using new analysis techniques that led to elimination of unnecessary components, then by innovations such as dual-mode cavities and novel materials such as ceramic resonators.A particular feature of waveguide filter design concerns the mode of transmission. Systems based on pairs of conducting wires and similar technologies have only one mode of transmission. In waveguide systems, any number of modes are possible. This can be both a disadvantage, as spurious modes frequently cause problems, and an advantage, as a dual-mode design can be much smaller than the equivalent waveguide single mode design. The chief advantages of waveguide filters over other technologies are their ability to handle high power and their low loss. The chief disadvantages are their bulk and cost when compared with technologies such as microstrip filters.There is a wide array of different types of waveguide filters. Many of them consist of a chain of coupled resonators of some kind that can be modelled as a ladder network of LC circuits. One of the most common types consists of a number of coupled resonant cavities. Even within this type, there are many subtypes, mostly differentiated by the means of coupling. These coupling types include apertures,[w] irises,[x] and posts. Other waveguide filter types include dielectric resonator filters, insert filters, finline filters, corrugated-waveguide filters, and stub filters. A number of waveguide components have filter theory applied to their design, but their purpose is something other than to filter signals. Such devices include impedance matching components, directional couplers, and diplexers. These devices frequently take on the form of a filter, at least in part.