8 Grade Science Curriculum Motion and Forces
... 3. A combination of constructive and destructive geological processes formed Earth’s surface. 4. Evidence of the dynamic changes of Earth’s surface through time is found in the geologic record. ...
... 3. A combination of constructive and destructive geological processes formed Earth’s surface. 4. Evidence of the dynamic changes of Earth’s surface through time is found in the geologic record. ...
Study guide 3
... Unit 3: Evolution, Biodiversity and Ecology (Chapters 13-20) Below are a list of the major topics that we focused on. Other topics from the text and videos we saw could appear on the exam, but the majority of questions will focus on these topics: Micro-Evolution: -Darwin’s ideas of descent with modi ...
... Unit 3: Evolution, Biodiversity and Ecology (Chapters 13-20) Below are a list of the major topics that we focused on. Other topics from the text and videos we saw could appear on the exam, but the majority of questions will focus on these topics: Micro-Evolution: -Darwin’s ideas of descent with modi ...
Macroevolution - CPBiologyClass
... barrier can lead to speciation – We can apply microevolution (genetic drift and Natural Selection) to the evolution of the new species – Ex. Darwin’s finches ...
... barrier can lead to speciation – We can apply microevolution (genetic drift and Natural Selection) to the evolution of the new species – Ex. Darwin’s finches ...
4 Ecology - Kerboodle
... Abiotic factors the non-living physical and chemical attributes of a system, for example light or temperature in an environment. Autotroph an organism that uses solar energy or chemical energy to manufacture the organic compounds it needs as nutrients from simple inorganic compounds obtained from it ...
... Abiotic factors the non-living physical and chemical attributes of a system, for example light or temperature in an environment. Autotroph an organism that uses solar energy or chemical energy to manufacture the organic compounds it needs as nutrients from simple inorganic compounds obtained from it ...
Theory of Evolution
... WHAT IS EVOLUTION? Evolution is the gradual change in a species over time. A species is a group of similar organisms that can mate with each other and produce fertile offspring. Theory of Evolution: What is the difference between a theory, hypothesis, and a law? ...
... WHAT IS EVOLUTION? Evolution is the gradual change in a species over time. A species is a group of similar organisms that can mate with each other and produce fertile offspring. Theory of Evolution: What is the difference between a theory, hypothesis, and a law? ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... theory of evolution by natural selection? • It provided the first, and only explanation of the existence of adaptations in nature. • It got proven and accepted after Mendel’s statistical analysis of ...
... theory of evolution by natural selection? • It provided the first, and only explanation of the existence of adaptations in nature. • It got proven and accepted after Mendel’s statistical analysis of ...
Chapter 48 - Community Ecology
... 3. Explain the Competitive Exclusion Principle and how it relates to the concept of the ecological niche. 4. According to the principle of competitive exclusion, what outcome is expected when two species (or business’) with identical niches compete for a resource? Why? 5. Describe what is meant by a ...
... 3. Explain the Competitive Exclusion Principle and how it relates to the concept of the ecological niche. 4. According to the principle of competitive exclusion, what outcome is expected when two species (or business’) with identical niches compete for a resource? Why? 5. Describe what is meant by a ...
Ecosystem: Stability and Change
... Replacement of Organisms Ecological Succession- the natural replacement of one community in particular area with a different, and usually more complex community, over a period of time ...
... Replacement of Organisms Ecological Succession- the natural replacement of one community in particular area with a different, and usually more complex community, over a period of time ...
The fossil record, biostratigraphy and diversity of life
... • Evolution never goes in reverse, from complex to simple forms ...
... • Evolution never goes in reverse, from complex to simple forms ...
Document
... 14. Describe the Snowshoe Hare / Canadian Lynx relationship. 15. This will be an extra credit question – What is the paradox of enrichment? 16. Define alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) diversity. How are they related to one another? 17. What is species richness? What is Biodiversity? 18. Create a fl ...
... 14. Describe the Snowshoe Hare / Canadian Lynx relationship. 15. This will be an extra credit question – What is the paradox of enrichment? 16. Define alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) diversity. How are they related to one another? 17. What is species richness? What is Biodiversity? 18. Create a fl ...
Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology - the study of the interactions
... • How do diving whales select their feeding areas? • What processes recycle vital chemical elements, such as nitrogen, in a savanna ecosystem • What factors influence the diversity of tree species that make up a particular forest ...
... • How do diving whales select their feeding areas? • What processes recycle vital chemical elements, such as nitrogen, in a savanna ecosystem • What factors influence the diversity of tree species that make up a particular forest ...
Ch. 4 Ecosystems study guide. Change the underlined word in each
... 4. Animals that consume dead organisms, like worms, are herbivores. 5. Producers eat other organisms for food. 6. The carrying capacity of a population is anything that restricts the number of individuals. 7. A community consists of all the living organisms in one species in an area. 8. The biospher ...
... 4. Animals that consume dead organisms, like worms, are herbivores. 5. Producers eat other organisms for food. 6. The carrying capacity of a population is anything that restricts the number of individuals. 7. A community consists of all the living organisms in one species in an area. 8. The biospher ...
Population Ecology - Verona Public Schools
... Species: Genetically similar organisms that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring Members of a species may not all live in the same place. Field mice in Maine will not interact with field mice in Texas. However, each organism lives as part of a population. Populations are groups of organisms o ...
... Species: Genetically similar organisms that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring Members of a species may not all live in the same place. Field mice in Maine will not interact with field mice in Texas. However, each organism lives as part of a population. Populations are groups of organisms o ...
Ch 5 Evolution of Biodiversity Content
... Look at the photograph below or see page 142 and answer the following questions. ...
... Look at the photograph below or see page 142 and answer the following questions. ...
Ecological Networks - ChaosAndComplexity
... and their environment • Study of ecosystems – Ecosystem- web/network of relationships of organisms to each other and their environment ...
... and their environment • Study of ecosystems – Ecosystem- web/network of relationships of organisms to each other and their environment ...
What you Need to Know for the Ecology Test
... Know about Ecological Succession!! Watch the crash course ecological succession video ...
... Know about Ecological Succession!! Watch the crash course ecological succession video ...
Organismal ecology - Pine Plains Central School District
... and the physical factors with which they interact • A community is a group of populations of different species in an area • A population is a group of individuals of the same species living in an area • Organismal ecology studies how an organism’s structure, physiology, and (for animals) behavior me ...
... and the physical factors with which they interact • A community is a group of populations of different species in an area • A population is a group of individuals of the same species living in an area • Organismal ecology studies how an organism’s structure, physiology, and (for animals) behavior me ...
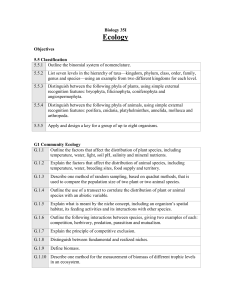
Biology 35I - Science-with
... G.1.1 Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species, including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients. G.1.2 ...
... G.1.1 Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species, including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients. G.1.2 ...
Ecosystem Notes - Alvin Independent School District
... life that is capable of growing, metabolizing nutrients, and usually reproducing. ...
... life that is capable of growing, metabolizing nutrients, and usually reproducing. ...
Exam 4 Review Part I
... b. Warm air has a greater ability to hold water c. Warm air cools as it rises d. Descending air absorbs moisture e. Atmospheric air holds more water than air near Earth 14. One species in a given space and time is called a ___. a. Population b. Community c. Ecosystem d. Biome e. Biosphere ...
... b. Warm air has a greater ability to hold water c. Warm air cools as it rises d. Descending air absorbs moisture e. Atmospheric air holds more water than air near Earth 14. One species in a given space and time is called a ___. a. Population b. Community c. Ecosystem d. Biome e. Biosphere ...
Chapter 2 Section 2
... weak individuals and often limit the size of the prey population. As populations of prey begin to decline, the predators either ...
... weak individuals and often limit the size of the prey population. As populations of prey begin to decline, the predators either ...
Biogeography

Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals.Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, geology, and physical geography.Modern biogeographic research combines information and ideas from many fields, from the physiological and ecological constraints on organismal dispersal to geological and climatological phenomena operating at global spatial scales and evolutionary time frames.The short-term interactions within a habitat and species of organisms describe the ecological application of biogeography. Historical biogeography describes the long-term, evolutionary periods of time for broader classifications of organisms. Early scientists, beginning with Carl Linnaeus, contributed theories to the contributions of the development of biogeography as a science. Beginning in the mid-18th century, Europeans explored the world and discovered the biodiversity of life. Linnaeus initiated the ways to classify organisms through his exploration of undiscovered territories.The scientific theory of biogeography grows out of the work of Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859), Hewett Cottrell Watson (1804–1881), Alphonse de Candolle (1806–1893), Alfred Russel Wallace (1823–1913), Philip Lutley Sclater (1829–1913) and other biologists and explorers.