Ecology Unit - OpenWetWare
... LO 4.11 The student is able to justify the selection of the kind of data needed to answer scientific questions about the interaction of populations within communities. LO 4.12 The student is able to apply mathematical routines to quantities that describe communities composed of populations of organi ...
... LO 4.11 The student is able to justify the selection of the kind of data needed to answer scientific questions about the interaction of populations within communities. LO 4.12 The student is able to apply mathematical routines to quantities that describe communities composed of populations of organi ...
Habitat (which is Latin for "it inhabits") is the place where a particular
... by) a species population. We use "species population" instead of "organism" here because, while it is possible to describe the habitat of a single black bear, we generally mean not any particular or individual bear, but the grouping of bears that comprise a breeding population and occupy a certain g ...
... by) a species population. We use "species population" instead of "organism" here because, while it is possible to describe the habitat of a single black bear, we generally mean not any particular or individual bear, but the grouping of bears that comprise a breeding population and occupy a certain g ...
What Is Conservation Biology? Michael E. Soulé BioScience
... weather. The unusually high populaThe fourth functional postulate is tion densities that often occur in na- that nature reserves are inherentlv ture reserves can also increase the rate diseqzrilibrial for large, rare orgaof disease transmission, frequently nisms. There are two reasons for this. lead ...
... weather. The unusually high populaThe fourth functional postulate is tion densities that often occur in na- that nature reserves are inherentlv ture reserves can also increase the rate diseqzrilibrial for large, rare orgaof disease transmission, frequently nisms. There are two reasons for this. lead ...
Niche-Based vs. Neutral Models of Ecological Communities
... treat the organisms of different species as ecological equivalents, each having an equal probability of survival and reproduction. Chase and Leibold do not acknowledge the above argument of Hubbell’s (2001). However, they do suggest one reason why it won’t work. Niche theory predicts that if two spe ...
... treat the organisms of different species as ecological equivalents, each having an equal probability of survival and reproduction. Chase and Leibold do not acknowledge the above argument of Hubbell’s (2001). However, they do suggest one reason why it won’t work. Niche theory predicts that if two spe ...
Energy Flow - SchoolRack
... on one another and their environments. – a. Demonstrate in a food web that matter is transferred from one organism to another and can recycle between organisms and their environments. – b. Explain in a food web that sunlight is the source of energy and that this energy moves from organism to organis ...
... on one another and their environments. – a. Demonstrate in a food web that matter is transferred from one organism to another and can recycle between organisms and their environments. – b. Explain in a food web that sunlight is the source of energy and that this energy moves from organism to organis ...
From DarwinPs Origin of Species toward a theory of natural history
... backbone of modern evolutionary theory. The later discovery of the laws of inheritance by Mendel and the rediscovery of Mendel in the early 20th century led to two reforms of Darwinism: NeoDarwinism and the Modern Synthesis (and subsequent refinements). If Darwin’s evolutionary thought required much ...
... backbone of modern evolutionary theory. The later discovery of the laws of inheritance by Mendel and the rediscovery of Mendel in the early 20th century led to two reforms of Darwinism: NeoDarwinism and the Modern Synthesis (and subsequent refinements). If Darwin’s evolutionary thought required much ...
The Fossil Record - modes of life
... What can these fossils tell us about the past? The study of the interaction of ancient organisms with their environment is called paleoecology. In large part, paleoecology depends on comparisons of ancient organisms with living organisms. We use modern analogs to help us interpret something about th ...
... What can these fossils tell us about the past? The study of the interaction of ancient organisms with their environment is called paleoecology. In large part, paleoecology depends on comparisons of ancient organisms with living organisms. We use modern analogs to help us interpret something about th ...
Fouling Community Studies in the Indian River
... The colonial ascidian Diplbsoma macdonaldi was common most of the year however the colonies reached greater size in the spring, often covering large areas of the plates. Some of the Botryllinae tunicates, Botryllus planus, Botrylloides nigrum and Symplegma viride were able to colonize areas on top o ...
... The colonial ascidian Diplbsoma macdonaldi was common most of the year however the colonies reached greater size in the spring, often covering large areas of the plates. Some of the Botryllinae tunicates, Botryllus planus, Botrylloides nigrum and Symplegma viride were able to colonize areas on top o ...
Patterns in Ecology
... Without bold, regular patterns in nature, ecologists do not have anything very interesting to explain. Patterns can exist at various scales in time and space, ranging from population abundances, through communities, ecosystems, biomes and the entire biosphere. Robert MacArthur understood this very c ...
... Without bold, regular patterns in nature, ecologists do not have anything very interesting to explain. Patterns can exist at various scales in time and space, ranging from population abundances, through communities, ecosystems, biomes and the entire biosphere. Robert MacArthur understood this very c ...
Biology Spring Semester Final Review Guide 2011
... 1. Test is about 75 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencil on the day of the test. 2. Topics that will be covered: History of Life (chapter 12), The theory of evolution (chapter 13), Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (chapter 5), Populations (chapter 15), Ecosystems (chapter 16), Biol ...
... 1. Test is about 75 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencil on the day of the test. 2. Topics that will be covered: History of Life (chapter 12), The theory of evolution (chapter 13), Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (chapter 5), Populations (chapter 15), Ecosystems (chapter 16), Biol ...
MARINE SCIENCE SEMESTER I REVIEW OCEAN EXPLORATION
... 37. What is thermal expansion? How does it relate to climate change? ...
... 37. What is thermal expansion? How does it relate to climate change? ...
Tenth Grade Science Indicators
... _____ 23 Describe how scientists continue to investigate and critically analyze aspects of evolutionary theory. (The intent of this indicator does not mandate the teaching or testing of intelligent design.) I Explain how natural selection and other evolutionary mechanisms account for the unity and d ...
... _____ 23 Describe how scientists continue to investigate and critically analyze aspects of evolutionary theory. (The intent of this indicator does not mandate the teaching or testing of intelligent design.) I Explain how natural selection and other evolutionary mechanisms account for the unity and d ...
Summer 2015 packet
... AP BIOLOGY 6. How does dispersal influence the distribution of individuals within a population? ...
... AP BIOLOGY 6. How does dispersal influence the distribution of individuals within a population? ...
Landscape Issues for Wildlife
... – Anthropogenic food available in these settings – Rate of predation on other birds’ nests is highest closest to such edges in our study area ...
... – Anthropogenic food available in these settings – Rate of predation on other birds’ nests is highest closest to such edges in our study area ...
An Ecological Perspective on the Biodiversity of Tropical Island
... area and species richness have been well studied for many terrestrial species, yet researchers know little about these species–area relations among fishes and aquatic invertebrates in insular lotic habitats (Haynes 1987, 1990, Donaldson 2002, Donaldson and Myers 2002, Bass 2003, Craig 2003). The num ...
... area and species richness have been well studied for many terrestrial species, yet researchers know little about these species–area relations among fishes and aquatic invertebrates in insular lotic habitats (Haynes 1987, 1990, Donaldson 2002, Donaldson and Myers 2002, Bass 2003, Craig 2003). The num ...
File - singhscience
... linking two of the following • there are variations within a species • some organisms have similar features / features that are common to more than one group / species / kingdom(1) • some closely related species can interbreed / breed with each other (1) • hybrids can be produced (1) ...
... linking two of the following • there are variations within a species • some organisms have similar features / features that are common to more than one group / species / kingdom(1) • some closely related species can interbreed / breed with each other (1) • hybrids can be produced (1) ...
biology 201 fall semester 2015 ecology and evolution
... (populations). Since all biological processes are ultimately part of evolution, ecology and evolution are intimately intertwined. The ecological interactions involving populations, species, communities and ecosystems all have evolutionary consequences. All environmental issues have an ecological bas ...
... (populations). Since all biological processes are ultimately part of evolution, ecology and evolution are intimately intertwined. The ecological interactions involving populations, species, communities and ecosystems all have evolutionary consequences. All environmental issues have an ecological bas ...
Competition It`s a struggle, a fight, two entities opposing each other
... boasts high species richness (diversity). The more generalist an organism is, the better chances it has to co-exist with its conspecifics (other members of the same species) and other taxa. Animals and plants that have specific life history requirements, like cavity-nesting birds, plants with ph-spe ...
... boasts high species richness (diversity). The more generalist an organism is, the better chances it has to co-exist with its conspecifics (other members of the same species) and other taxa. Animals and plants that have specific life history requirements, like cavity-nesting birds, plants with ph-spe ...
Terrestrial Biomes Self-Quiz
... sources. Can be categorized as oligotrophic, mesotrophic, or eutrophic depending on nutrients. i __________ 10. These areas can change dramatically from its source to its final destination. Organisms very dependent on oxygen levels and flow rates. n __________ 11. Very small plants with mat like gro ...
... sources. Can be categorized as oligotrophic, mesotrophic, or eutrophic depending on nutrients. i __________ 10. These areas can change dramatically from its source to its final destination. Organisms very dependent on oxygen levels and flow rates. n __________ 11. Very small plants with mat like gro ...
Insect Conservation and Diversity
... Earth is far from complete, and that the rate-limiting step remains the craft of collecting specimens in the field. Further, the inability of the scientific community to document species diversity, and hence its decline, is hugely detrimental to the credibility of the conservation movement (Mann, 19 ...
... Earth is far from complete, and that the rate-limiting step remains the craft of collecting specimens in the field. Further, the inability of the scientific community to document species diversity, and hence its decline, is hugely detrimental to the credibility of the conservation movement (Mann, 19 ...
Printing - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B
... One contribution of 16 to a Discussion Meeting Issue ‘Biological diversity in a changing world’. ...
... One contribution of 16 to a Discussion Meeting Issue ‘Biological diversity in a changing world’. ...
Species diversity
... • Top predators: species eaten by nothing else in the food web • Basal species: species that feed on nothing within the food web • Intermediate species: species that have both predators and prey within the food web • Trophic species: groups of organisms that have identical sets of predators and prey ...
... • Top predators: species eaten by nothing else in the food web • Basal species: species that feed on nothing within the food web • Intermediate species: species that have both predators and prey within the food web • Trophic species: groups of organisms that have identical sets of predators and prey ...
File
... The Niche Every species has its own tolerance, or a range of conditions under which it can grow and reproduce. A species’ tolerance determines its habitat, the place where it lives. A niche consists of all the physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtain ...
... The Niche Every species has its own tolerance, or a range of conditions under which it can grow and reproduce. A species’ tolerance determines its habitat, the place where it lives. A niche consists of all the physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtain ...
Final Exam objectives
... Know the structure and function of the structures you identified during the fetal pig dissection. Wisconsin State Science Standards C.12.2 Identify issues from an area of science study, write questions that could be investigated, review previous research on these questions, and design and conduc ...
... Know the structure and function of the structures you identified during the fetal pig dissection. Wisconsin State Science Standards C.12.2 Identify issues from an area of science study, write questions that could be investigated, review previous research on these questions, and design and conduc ...
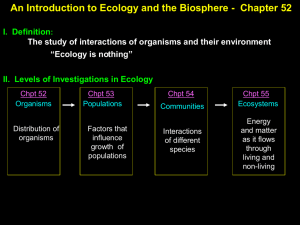
Biogeography

Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals.Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, geology, and physical geography.Modern biogeographic research combines information and ideas from many fields, from the physiological and ecological constraints on organismal dispersal to geological and climatological phenomena operating at global spatial scales and evolutionary time frames.The short-term interactions within a habitat and species of organisms describe the ecological application of biogeography. Historical biogeography describes the long-term, evolutionary periods of time for broader classifications of organisms. Early scientists, beginning with Carl Linnaeus, contributed theories to the contributions of the development of biogeography as a science. Beginning in the mid-18th century, Europeans explored the world and discovered the biodiversity of life. Linnaeus initiated the ways to classify organisms through his exploration of undiscovered territories.The scientific theory of biogeography grows out of the work of Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859), Hewett Cottrell Watson (1804–1881), Alphonse de Candolle (1806–1893), Alfred Russel Wallace (1823–1913), Philip Lutley Sclater (1829–1913) and other biologists and explorers.