The Brain The brain is responsible for everything we think, feel and
... Parietal Lobe: receives and processes sensory information from the body and other sensory areas in the brain; also involved in spatial perception and memory. The parietal lobe allows us to process and perceive the sensations of touch, temperature, pressure and pain. These sensations are processed in ...
... Parietal Lobe: receives and processes sensory information from the body and other sensory areas in the brain; also involved in spatial perception and memory. The parietal lobe allows us to process and perceive the sensations of touch, temperature, pressure and pain. These sensations are processed in ...
lecture9
... 5 months: hand does not orient to object until contact 9 months: hand orients prior to contact (note visual information about orientation is available at 2 months). Pre-shape for object size. Still adjusting grip force by 7-8 years (grip force larger for larger objects). Use palmar grasp until about ...
... 5 months: hand does not orient to object until contact 9 months: hand orients prior to contact (note visual information about orientation is available at 2 months). Pre-shape for object size. Still adjusting grip force by 7-8 years (grip force larger for larger objects). Use palmar grasp until about ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 46.2 Two drawings that were made by a patient with spatial neglect. The patient was asked to copy the two models (clock, house). In each case, the copies exclude important elements that appeared on the left side of the model, indicating that the patient was unable to process information abou ...
... FIGURE 46.2 Two drawings that were made by a patient with spatial neglect. The patient was asked to copy the two models (clock, house). In each case, the copies exclude important elements that appeared on the left side of the model, indicating that the patient was unable to process information abou ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... of the MNS interferes with the ability to imitate, leads to social impairment and communication difficulties. • Structural abnormalities in MNS regions of individuals with ASD exist, correlations between reduced MNS activity and severity of ASD. • But … in ASD abnormal brain activation in many other ...
... of the MNS interferes with the ability to imitate, leads to social impairment and communication difficulties. • Structural abnormalities in MNS regions of individuals with ASD exist, correlations between reduced MNS activity and severity of ASD. • But … in ASD abnormal brain activation in many other ...
Alzheimer`s Disease
... body formation and associated neuronal loss. • In Parkinson disease, the Lewy bodies are found in the substantia nigra of the midbrain, coupled with the loss of pigmented neurons. • In persons with the dementia of diffuse Lewy body disease, there are Lewy bodies in the neocortex. • Some persons have ...
... body formation and associated neuronal loss. • In Parkinson disease, the Lewy bodies are found in the substantia nigra of the midbrain, coupled with the loss of pigmented neurons. • In persons with the dementia of diffuse Lewy body disease, there are Lewy bodies in the neocortex. • Some persons have ...
While it may not be obvious from observing very young children
... of synapse loss) to incorporate new information from experience. This has been shown in studies of animals housed in complex, or “enriched,” environments. In the first such experiment, Hebb (1949) reared laboratory rats as pets in his home, then took them back to the laboratory to assess their learn ...
... of synapse loss) to incorporate new information from experience. This has been shown in studies of animals housed in complex, or “enriched,” environments. In the first such experiment, Hebb (1949) reared laboratory rats as pets in his home, then took them back to the laboratory to assess their learn ...
Final answers - Center for Neural Science
... b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. d) is a scientific hoax. 37) Although there have been many demonst ...
... b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. d) is a scientific hoax. 37) Although there have been many demonst ...
Visual7
... • Higher-order areas surround area 17 (areas 18 and 19), and can be distinguished as they lack a Stripe of Gennari. 1. Motion pathway – Magnocellular system 1° cortex higher-order areas for visual form in motion (including medial temporal projection). 2. Colour pathway – parvocellular system 1 ...
... • Higher-order areas surround area 17 (areas 18 and 19), and can be distinguished as they lack a Stripe of Gennari. 1. Motion pathway – Magnocellular system 1° cortex higher-order areas for visual form in motion (including medial temporal projection). 2. Colour pathway – parvocellular system 1 ...
Visual Field Defects - Northwestern Medical Review
... within the thalamus and they are the primary relay centers for visual information from the retina. Each LGN receives information from one half of the visual field. For example, the left LGN receives information from ganglion cells of the temporal retina of the left eye plus information from the nasa ...
... within the thalamus and they are the primary relay centers for visual information from the retina. Each LGN receives information from one half of the visual field. For example, the left LGN receives information from ganglion cells of the temporal retina of the left eye plus information from the nasa ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... • Color vision deficiency is an impairment in perceiving color differences. • Gene responsible is contained on the X chromosome. • Caused by either the lack of a type of cone or a cone has abnormal properties. • Most common form is difficulty distinguishing between red and green. – Results from the ...
... • Color vision deficiency is an impairment in perceiving color differences. • Gene responsible is contained on the X chromosome. • Caused by either the lack of a type of cone or a cone has abnormal properties. • Most common form is difficulty distinguishing between red and green. – Results from the ...
Top-down influence in early visual processing: a Bayesian perspective
... scheme can be applied again to higher areas recursively to form the whole hierarchy of inference. In this framework, each cortical area is an expert for inferring certain aspects of the visual scene, but its inference is made in consultation with the other brain areas, constrained by both incoming d ...
... scheme can be applied again to higher areas recursively to form the whole hierarchy of inference. In this framework, each cortical area is an expert for inferring certain aspects of the visual scene, but its inference is made in consultation with the other brain areas, constrained by both incoming d ...
The role of early visual cortex in visual integration: a neural model of
... Furthermore, as V1 is an area where all the information is implicitly available in retinotopic coordinates, it naturally provides a spatially registered common forum for all the higher order perceptual inferences to come back together. Thus, it could play the role of facilitating the integration of ...
... Furthermore, as V1 is an area where all the information is implicitly available in retinotopic coordinates, it naturally provides a spatially registered common forum for all the higher order perceptual inferences to come back together. Thus, it could play the role of facilitating the integration of ...
(1 Mark).
... commonly in the right hemisphere. 0 Patients demonstrate signs of contralesional (Describing the half of a patient's brain or body away from the site of a lesion) neglect. 0 For example, when searching through a visual scene patients with left neglect only tent to look at elements on the right side ...
... commonly in the right hemisphere. 0 Patients demonstrate signs of contralesional (Describing the half of a patient's brain or body away from the site of a lesion) neglect. 0 For example, when searching through a visual scene patients with left neglect only tent to look at elements on the right side ...
Neural Correlates of Selection
... appears, neurons tuned to the features of that stimulus are initially excited, but remain so only if attention is focused on that stimulus Chellazi et al. (1993). A neural basis for visual search in Inferior Temporal Cortex. Nature. 363, ...
... appears, neurons tuned to the features of that stimulus are initially excited, but remain so only if attention is focused on that stimulus Chellazi et al. (1993). A neural basis for visual search in Inferior Temporal Cortex. Nature. 363, ...
Cognitive Impairment www.AssignmentPoint.com Cognitive
... the study concluded that maintenance of cognitive functions with normal aging can be maintained by keeping an active lifestyle. The results also seemed to conclude that the correlation between lifestyle activities and cognition is not a simple one, as not all cognitive abilities were related to chan ...
... the study concluded that maintenance of cognitive functions with normal aging can be maintained by keeping an active lifestyle. The results also seemed to conclude that the correlation between lifestyle activities and cognition is not a simple one, as not all cognitive abilities were related to chan ...
Modulation of attentional inhibition by norepinephrine and cortisol
... One important way in which stress may affect attention is through inhibitory mechanisms. The negative priming ŽNP. paradigm is designed to assess the role of inhibition in selective attention ŽTipper, 1985.. NP is structurally similar to the phenomenon of latent inhibition ŽLubow, 1973. and involves ...
... One important way in which stress may affect attention is through inhibitory mechanisms. The negative priming ŽNP. paradigm is designed to assess the role of inhibition in selective attention ŽTipper, 1985.. NP is structurally similar to the phenomenon of latent inhibition ŽLubow, 1973. and involves ...
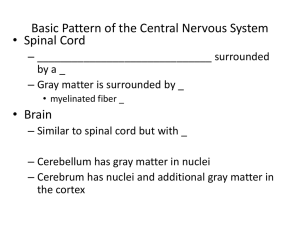
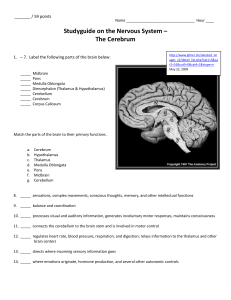
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 8. _____ sensations, complex movements, conscious thoughts, memory, and other intellectual functions 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain st ...
... 8. _____ sensations, complex movements, conscious thoughts, memory, and other intellectual functions 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain st ...
Chapter 21: Attention
... Slide 10 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... Slide 10 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
Attention maps in the brain - Site BU
... Over 20 distinct cerebral cortical areas contain spatial map representations of the visual field. These retinotopic, or visuotopic, cortical areas occur not only in the occipital lobe but also in the parietal, temporal, and frontal lobes. The cognitive influences of visuospatial attention operate vi ...
... Over 20 distinct cerebral cortical areas contain spatial map representations of the visual field. These retinotopic, or visuotopic, cortical areas occur not only in the occipital lobe but also in the parietal, temporal, and frontal lobes. The cognitive influences of visuospatial attention operate vi ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... preferred orientation of neurons encountered in a long microelectrode penetration through layers 2 + 3 (inset). There was a steady, slow progression of preferred orientations, although there were a few positions where the orientations changed more abruptly. (B) Schematic diagram of an electrode pene ...
... preferred orientation of neurons encountered in a long microelectrode penetration through layers 2 + 3 (inset). There was a steady, slow progression of preferred orientations, although there were a few positions where the orientations changed more abruptly. (B) Schematic diagram of an electrode pene ...