Last Lecture http://www.umich.edu/~psycours/345/
... • Optic radiations to • AREA 17; Striate Cortex, Primary visual cortex Retinotopic Map ...
... • Optic radiations to • AREA 17; Striate Cortex, Primary visual cortex Retinotopic Map ...
Phase IIB / PHGY 825 Organization of the Brain Stem Organization
... the eyes will still respond to the head turns because of input from the other ear. Punctuate right lateral pontine lesion ...
... the eyes will still respond to the head turns because of input from the other ear. Punctuate right lateral pontine lesion ...
Cranial Nerves
... Ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular divisions •Sensory: Touch, pain, temp, proprioception for face, oral and nasal cavities. •Motor: Muscles for mastication. ...
... Ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular divisions •Sensory: Touch, pain, temp, proprioception for face, oral and nasal cavities. •Motor: Muscles for mastication. ...
BRAINSTEM Comprised of 4 components: • Grey matter = cranial
... Comprised of 4 components: Grey matter = cranial nerves and nuclei (one nerve can have many nuclei) Suprasegmental nuclei – motor/sensory functions or relays to cerebellum White matter = fiber tracts Reticular formation – interneurons integration 4 major levels of the brainstem: Caudal m ...
... Comprised of 4 components: Grey matter = cranial nerves and nuclei (one nerve can have many nuclei) Suprasegmental nuclei – motor/sensory functions or relays to cerebellum White matter = fiber tracts Reticular formation – interneurons integration 4 major levels of the brainstem: Caudal m ...
Dexterous Finger Movements in Primate Without Monosynaptic
... CS volley to the onset of the EPSPs (Fig. 2H) showed a monosynaptic range (from 0.4 to 1.0 ms) on the intact side (white area), but a disynaptic range (1.0 –1.8 ms) in 15 cells on the lesioned side (black area) and possibly a trisynaptic range (from 1.8 to 2.0 ms) in 3 cells. Figure 2, A–C, shows in ...
... CS volley to the onset of the EPSPs (Fig. 2H) showed a monosynaptic range (from 0.4 to 1.0 ms) on the intact side (white area), but a disynaptic range (1.0 –1.8 ms) in 15 cells on the lesioned side (black area) and possibly a trisynaptic range (from 1.8 to 2.0 ms) in 3 cells. Figure 2, A–C, shows in ...
5655.full - Journal of Neuroscience
... the fractal with the emotion in the presented video clip and were informed that they would be tested on the association. The association between fractals and emotional stimuli was tested after the learning session. Participants were presented with the fractal stimuli and tested on how quickly and ac ...
... the fractal with the emotion in the presented video clip and were informed that they would be tested on the association. The association between fractals and emotional stimuli was tested after the learning session. Participants were presented with the fractal stimuli and tested on how quickly and ac ...
The Five Senses - Flinn Scientific
... “non-tasters.” Not only is the difference in ability to taste this substance interesting, but it has also been found to be an inherited characteristic. Touch Mechanoreceptors are sensory receptors that are stimulated by touch, stretch, pressure, motion or sound. The density of mechanoreceptors diffe ...
... “non-tasters.” Not only is the difference in ability to taste this substance interesting, but it has also been found to be an inherited characteristic. Touch Mechanoreceptors are sensory receptors that are stimulated by touch, stretch, pressure, motion or sound. The density of mechanoreceptors diffe ...
Full Text
... Microscopic examination of the cerebral white matter in all cases demonstrated severe myelin loss and axonal damage (Figure 4). Regions beneath the association areas were most severely affected, and white matter axonal spheroids were most frequent in areas adjacent to areas of severe white matter in ...
... Microscopic examination of the cerebral white matter in all cases demonstrated severe myelin loss and axonal damage (Figure 4). Regions beneath the association areas were most severely affected, and white matter axonal spheroids were most frequent in areas adjacent to areas of severe white matter in ...
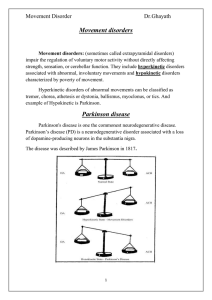
Movement disorders
... Link to pharmacology and psychiatry (This box were added by the students it is not included in the lecture): One of the side effects of anti-Parkinson medications is Psychosis because it was hypothesized that psychosis is related to increase level of dopamine. While one of the side effects of anti-p ...
... Link to pharmacology and psychiatry (This box were added by the students it is not included in the lecture): One of the side effects of anti-Parkinson medications is Psychosis because it was hypothesized that psychosis is related to increase level of dopamine. While one of the side effects of anti-p ...
pdf
... stimulation is fixed at 50% machine output in tonic mode. This is done because TMS with the double cone coil at high intensities is very unpleasant for the patient, more so than figure of eight coil stimulation. Furthermore it has been shown that the excitatory measurements of one specific cortex canno ...
... stimulation is fixed at 50% machine output in tonic mode. This is done because TMS with the double cone coil at high intensities is very unpleasant for the patient, more so than figure of eight coil stimulation. Furthermore it has been shown that the excitatory measurements of one specific cortex canno ...
Gaze effects in the cerebral cortex: reference frames for
... charge rate of a substantial proportion of PMd cells (Boussaoud et al. 1998), although we stress that the receptive fields were not studied in detail. Figure 2A shows an example of PMd cells whose discharge rate is tuned to the location of the visual cue (presented in polar coordinates) which instru ...
... charge rate of a substantial proportion of PMd cells (Boussaoud et al. 1998), although we stress that the receptive fields were not studied in detail. Figure 2A shows an example of PMd cells whose discharge rate is tuned to the location of the visual cue (presented in polar coordinates) which instru ...
1 Chapter 160: Trauma to the Middle Ear and Temporal Bone Sam E
... asked to make voluntary movements of the facial muscles, which then can be appropriately observed. If the patient's level of consciousness is somewhat depressed, one may observe facial nerve function by stimulating pain, as from applying pressure directly over the sternum, which will often cause the ...
... asked to make voluntary movements of the facial muscles, which then can be appropriately observed. If the patient's level of consciousness is somewhat depressed, one may observe facial nerve function by stimulating pain, as from applying pressure directly over the sternum, which will often cause the ...
BIo 218 Lecture Outline Tortora Ch18
... a. somatic reflexes involve contraction of skeletal muscles b. autonomic (visceral) reflexes involve responses of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands iii. The pathway followed by nerve impulses that produce a reflex response is called a reflex arc (reflex circuit), which includes five function ...
... a. somatic reflexes involve contraction of skeletal muscles b. autonomic (visceral) reflexes involve responses of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands iii. The pathway followed by nerve impulses that produce a reflex response is called a reflex arc (reflex circuit), which includes five function ...
Spinal Cord - Sydney University Medical Society
... Muscle Spindles (also known as Neuromuscular Spindles) – these are located parallel and adjacent to the muscle; this is carried via myelinated Type Ia Fibres (70120 m/s) Golgi Tendon Organs – these are carried via Type Ib fibres (70-120 m/s) Joint Receptors - these are carried via Type II fibr ...
... Muscle Spindles (also known as Neuromuscular Spindles) – these are located parallel and adjacent to the muscle; this is carried via myelinated Type Ia Fibres (70120 m/s) Golgi Tendon Organs – these are carried via Type Ib fibres (70-120 m/s) Joint Receptors - these are carried via Type II fibr ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.