Second exam study questions
... 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? Ho ...
... 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? Ho ...
Regulation powerpoint File
... protected by skull, meninges (tough membrane) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Composed of 2 sides called hemispheres 3 major parts: a. cerebrum •largest part • right hemisphere controls the left side of the body & viceversa •the 2 hemispheres communicate via the nerves of the corpus callossum •is c ...
... protected by skull, meninges (tough membrane) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Composed of 2 sides called hemispheres 3 major parts: a. cerebrum •largest part • right hemisphere controls the left side of the body & viceversa •the 2 hemispheres communicate via the nerves of the corpus callossum •is c ...
Slide 1
... • Connects to brain and spinal cord via – 12 pairs of cranial nerves (connect to brain) – 31 pairs of spinal nerves (connect to spinal cord) ...
... • Connects to brain and spinal cord via – 12 pairs of cranial nerves (connect to brain) – 31 pairs of spinal nerves (connect to spinal cord) ...
lower back pain
... 1. If the conservative treatment options do not provide relief within two to three months. 2. If leg or back pain limits normal activity 3. If there is weakness or numbness in the legs 4. If it is difficult to walk or stand, or if medication or physical therapy are ineffective, surgery may be necess ...
... 1. If the conservative treatment options do not provide relief within two to three months. 2. If leg or back pain limits normal activity 3. If there is weakness or numbness in the legs 4. If it is difficult to walk or stand, or if medication or physical therapy are ineffective, surgery may be necess ...
Spinal Cord Review
... A 45 year old man noticed a weakness of his right hand which was progressing and causing him problems. He decided to see his doctor. On examination he demonstrated bilateral weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations of the intrinsic muscles of his hands and shoulders. Upper motor neuron syndrome signs, ...
... A 45 year old man noticed a weakness of his right hand which was progressing and causing him problems. He decided to see his doctor. On examination he demonstrated bilateral weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations of the intrinsic muscles of his hands and shoulders. Upper motor neuron syndrome signs, ...
Neurology - Porterville College
... Excitatory Neurotransmitters • Dopamine – Gross subconscious movement – Fine motor skills – Emotional responses ...
... Excitatory Neurotransmitters • Dopamine – Gross subconscious movement – Fine motor skills – Emotional responses ...
PATIENT POSITIONING IN OPERATING THEATRE
... Eye are well covered and fully protected by pads Position of spike must not harm patient’s ears and eyes Face is protected from pressure when in prone position Arms are in good anatomical alignments Bony prominences is protected whilst in all position ...
... Eye are well covered and fully protected by pads Position of spike must not harm patient’s ears and eyes Face is protected from pressure when in prone position Arms are in good anatomical alignments Bony prominences is protected whilst in all position ...
Principles of Sensory Coding
... Modality: the most basic mechanism for identifying the nature of a sensory input is via labeled lines. What this means is that input from the optic nerve is always interpreted by the brain as visual input etc. This extends to much finer discriminations: the connections of “pain” and “touch” fibers i ...
... Modality: the most basic mechanism for identifying the nature of a sensory input is via labeled lines. What this means is that input from the optic nerve is always interpreted by the brain as visual input etc. This extends to much finer discriminations: the connections of “pain” and “touch” fibers i ...
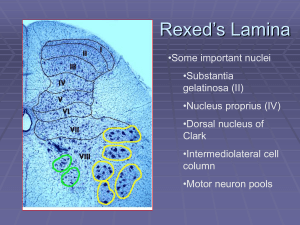
Rexed`s Lamina
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
Nervous System
... ► Many nerves are part of reflexes and can act automatically Patellar reflex – By passes the brain completely ...
... ► Many nerves are part of reflexes and can act automatically Patellar reflex – By passes the brain completely ...
sensation.
... Did you write “The cat was the rat”? If you did you were incorrect. The correct answer is: “The cat SAW the rat” ...
... Did you write “The cat was the rat”? If you did you were incorrect. The correct answer is: “The cat SAW the rat” ...
chapt12-nervous system
... sensory speech area) that are in communication. Interestingly enough, these two areas are located only in the left hemisphere. ...
... sensory speech area) that are in communication. Interestingly enough, these two areas are located only in the left hemisphere. ...
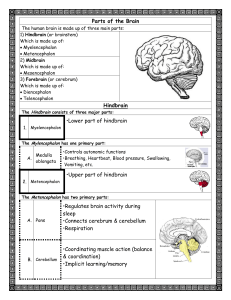
Parts of the Brain Hindbrain •Lower part of hindbrain •Upper part of
... •Network of nerves that passes through hindbrain •Extends from spinal cord to thalamus What it does: a. Alerts cortex to new stimuli b. Helps sift incoming stimulus so only important stuff sent to conscious mind c. Plays role in arousal (ability to receive stimuli) ...
... •Network of nerves that passes through hindbrain •Extends from spinal cord to thalamus What it does: a. Alerts cortex to new stimuli b. Helps sift incoming stimulus so only important stuff sent to conscious mind c. Plays role in arousal (ability to receive stimuli) ...
11_16_15- Day 1 - Kenwood Academy High School
... Behaviors can be made automatic. Our senses (hearing, olfaction, taste, sight, touch) do not work in isolation. Reflexes are different from responses. There are different stages of sleep. The left side of your brain controls the right side of your body. Neurons are lost (die) before you are born Cer ...
... Behaviors can be made automatic. Our senses (hearing, olfaction, taste, sight, touch) do not work in isolation. Reflexes are different from responses. There are different stages of sleep. The left side of your brain controls the right side of your body. Neurons are lost (die) before you are born Cer ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... 1. Mechanoreceptors are stimulated by mechanical force, such as touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch. 2. Thermoreceptors respond to changes in temperature. 3. Photoreceptors detect light. 4. Chemoreceptors are stimulated by chemicals, such as odorants, taste stimuli, or chemical components of bod ...
... 1. Mechanoreceptors are stimulated by mechanical force, such as touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch. 2. Thermoreceptors respond to changes in temperature. 3. Photoreceptors detect light. 4. Chemoreceptors are stimulated by chemicals, such as odorants, taste stimuli, or chemical components of bod ...
Sensation
... --certain # of each in “balance”…& if one goes on, its opposite goes OFF…then they fire to come back into balance “ON” “OFF” red green green red blue yellow yellow blue black white white black This causes an “afterimage”…remember the flag?? ...
... --certain # of each in “balance”…& if one goes on, its opposite goes OFF…then they fire to come back into balance “ON” “OFF” red green green red blue yellow yellow blue black white white black This causes an “afterimage”…remember the flag?? ...
The Nervous System - Valhalla High School
... your brain and spinal column. 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS): Consists of all the nerves that branch away from the central nervous system. (This is further divided into the somatic and autonomous nervous systems). ...
... your brain and spinal column. 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS): Consists of all the nerves that branch away from the central nervous system. (This is further divided into the somatic and autonomous nervous systems). ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.