Introductory Psychology: Sensation
... The incoming vibrations cause movement in the cochlea’s oval window, which then creates motion in the cochlea’s fluid This motion causes movement in the basilar membrane and its hair cells Eventually, the hair cells trigger an impulse in adjacent nerve fibers; converge to form the auditory nerve ...
... The incoming vibrations cause movement in the cochlea’s oval window, which then creates motion in the cochlea’s fluid This motion causes movement in the basilar membrane and its hair cells Eventually, the hair cells trigger an impulse in adjacent nerve fibers; converge to form the auditory nerve ...
潓慭潴敳獮牯⁹祓瑳浥
... Posterior column lesions. The posterior columns mainly transmit impulses arising in the proprioceptors and cutaneous receptors. If they are dysfunctional, the individual can no longer feel the position of his or her limbs; nor can he or she recognize an object laid in the hand by the sense of touch ...
... Posterior column lesions. The posterior columns mainly transmit impulses arising in the proprioceptors and cutaneous receptors. If they are dysfunctional, the individual can no longer feel the position of his or her limbs; nor can he or she recognize an object laid in the hand by the sense of touch ...
L6. Thalamus (László Acsády) All cortical areas receive thalamic
... All cortical areas receive thalamic inputs and no cortical area is functional without intact thalamocortical connections. The thalamus has multiple functions. It may be thought of as a kind of hub of information. The thalamus is generally believed to act as a relay between different subcortical area ...
... All cortical areas receive thalamic inputs and no cortical area is functional without intact thalamocortical connections. The thalamus has multiple functions. It may be thought of as a kind of hub of information. The thalamus is generally believed to act as a relay between different subcortical area ...
Ch 8 (Student MCQs etc)
... cones are of three types, which are selective to different, if overlapping, ranges of light wavelength. The information from the cones is reorganized in the retina to give green–red and blue–yellow opponent channels (see chapter 7). There is, in addition, a group of large retinal cells alongside the ...
... cones are of three types, which are selective to different, if overlapping, ranges of light wavelength. The information from the cones is reorganized in the retina to give green–red and blue–yellow opponent channels (see chapter 7). There is, in addition, a group of large retinal cells alongside the ...
10 Control of Movement
... involves ONLY one synapse – Sensory neuron from the extensor muscle synapses with the motor neuron for that extensor muscle – Only found in the stretch reflex ...
... involves ONLY one synapse – Sensory neuron from the extensor muscle synapses with the motor neuron for that extensor muscle – Only found in the stretch reflex ...
Somatosensory System
... Posterior column lesions. The posterior columns mainly transmit impulses arising in the proprioceptors and cutaneous receptors. If they are dysfunctional, the individual can no longer feel the position of his or her limbs; nor can he or she recognize an object laid in the hand by the sense of touch ...
... Posterior column lesions. The posterior columns mainly transmit impulses arising in the proprioceptors and cutaneous receptors. If they are dysfunctional, the individual can no longer feel the position of his or her limbs; nor can he or she recognize an object laid in the hand by the sense of touch ...
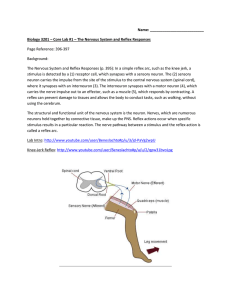
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
Module 3 The integration of postural control and selective movement
... Dysynergic patterns of co contraction Spasms ...
... Dysynergic patterns of co contraction Spasms ...
Parathyroidectomy • Everybody has 4 parathyroid glands, 2
... In other patients, there is the possibility of a precipitous fall in calcium levels while still in hospital, or in the first few days after discharge, which may lead to symptoms of pins and needles or muscle spasm, a longer than expected hospital stay and/or readmission to hospital, and/or require c ...
... In other patients, there is the possibility of a precipitous fall in calcium levels while still in hospital, or in the first few days after discharge, which may lead to symptoms of pins and needles or muscle spasm, a longer than expected hospital stay and/or readmission to hospital, and/or require c ...
File
... bilateral projections from the retina to the pretectum and projections from the pretectum to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. Neurons in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus terminate in the ciliary ganglion, and neurons in the ciliary ganglion innervate the pupillary constrictor muscles. Notice that the affer ...
... bilateral projections from the retina to the pretectum and projections from the pretectum to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. Neurons in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus terminate in the ciliary ganglion, and neurons in the ciliary ganglion innervate the pupillary constrictor muscles. Notice that the affer ...
3 - smw15.org
... separate families act like one another more than say two adopted children into the same family who have no genetic influences? Lets look at some case study research to help us determine this… ...
... separate families act like one another more than say two adopted children into the same family who have no genetic influences? Lets look at some case study research to help us determine this… ...
Control and Coordination -Organ systems
... EFFECTORS (muscles, glands) which cause a response 3. INTERNEURONS: link sensory and motor neurons - these neurons make up the CENTRAL nervous system v The REFLEX ARC: also known as the Withdrawl Reflex ...
... EFFECTORS (muscles, glands) which cause a response 3. INTERNEURONS: link sensory and motor neurons - these neurons make up the CENTRAL nervous system v The REFLEX ARC: also known as the Withdrawl Reflex ...
Spasticity in the Podiatric Patient
... arthrodesis may be warranted of the GreenGrice type. If using a fibuiar graft it should be taken from the middle to upper 1/3rd of the fibula to prevent ankle valgus. In the event of ankle valgus supramalleolar osteotomies may need to be considered. Tibialis anterior transfers require specific thoug ...
... arthrodesis may be warranted of the GreenGrice type. If using a fibuiar graft it should be taken from the middle to upper 1/3rd of the fibula to prevent ankle valgus. In the event of ankle valgus supramalleolar osteotomies may need to be considered. Tibialis anterior transfers require specific thoug ...
Nervous System
... bodies outside the CNS) • Ventral (anterior) horns (left and right) – motor information exits the cord on the ventral aspect where they control effectors (muscle or glands) – extend into motor roots • Dorsal and ventral roots merge together to form spinal nerves ...
... bodies outside the CNS) • Ventral (anterior) horns (left and right) – motor information exits the cord on the ventral aspect where they control effectors (muscle or glands) – extend into motor roots • Dorsal and ventral roots merge together to form spinal nerves ...
Nervous System
... bodies outside the CNS) • Ventral (anterior) horns (left and right) – motor information exits the cord on the ventral aspect where they control effectors (muscle or glands) – extend into motor roots • Dorsal and ventral roots merge together to form spinal nerves ...
... bodies outside the CNS) • Ventral (anterior) horns (left and right) – motor information exits the cord on the ventral aspect where they control effectors (muscle or glands) – extend into motor roots • Dorsal and ventral roots merge together to form spinal nerves ...
Pontine tegmental cap dysplasia
... colour coding and fibre tracking revealed an ectopic transverse fibre bundle at the site of the pontine tegmentum and complete absence of transverse fibres in the ventral pons.The combined findings indicate an embryonic defect in axonal growth and guidance. Phenotypic analogy to mice with homozygous ...
... colour coding and fibre tracking revealed an ectopic transverse fibre bundle at the site of the pontine tegmentum and complete absence of transverse fibres in the ventral pons.The combined findings indicate an embryonic defect in axonal growth and guidance. Phenotypic analogy to mice with homozygous ...
Physiology 1B
... Send out hormones to the body Hormone- A chemical substance formed in the body that is carried in the bloodstream to affect another part of the body ...
... Send out hormones to the body Hormone- A chemical substance formed in the body that is carried in the bloodstream to affect another part of the body ...
mspn4a
... circuitry which may have been involved. Coticospinal fibers of the pyramidal tract, corticobulber fibers and other motor pathways descending to the spinal cord may have been affected. Thalamocortical somatosensory fibers (dorsal column-medial lemniscus, anterolateral pathways) ascending in the inter ...
... circuitry which may have been involved. Coticospinal fibers of the pyramidal tract, corticobulber fibers and other motor pathways descending to the spinal cord may have been affected. Thalamocortical somatosensory fibers (dorsal column-medial lemniscus, anterolateral pathways) ascending in the inter ...
Module9ClassicalCond..
... – a kind of learning that involves mental processes, such as attention and memory; may be learned through observation or imitation; and may not involve any persons to perform any observable behaviors • Albert Bandura – found that children who had watched the film of an adult modeling aggressive beha ...
... – a kind of learning that involves mental processes, such as attention and memory; may be learned through observation or imitation; and may not involve any persons to perform any observable behaviors • Albert Bandura – found that children who had watched the film of an adult modeling aggressive beha ...
Movement control system
... of primary motor cortex caused movements of specific muscles. The studies demonstrate Somatotopic Organization. ...
... of primary motor cortex caused movements of specific muscles. The studies demonstrate Somatotopic Organization. ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.