Unit IX: Evolution - Ms. Shunkwiler`s Wiki!
... Evolution of Populations and Speciation 6. What does it mean to maintain genetic equilibrium? 7. What are the five conditions that must be met to maintain genetic equilibrium? 8. How is the Hardy-Weinberg equation used to measure genetic equilibrium? 9. Give the formula for the frequency of alleles ...
... Evolution of Populations and Speciation 6. What does it mean to maintain genetic equilibrium? 7. What are the five conditions that must be met to maintain genetic equilibrium? 8. How is the Hardy-Weinberg equation used to measure genetic equilibrium? 9. Give the formula for the frequency of alleles ...
SET 1A Darwin noticed that
... The species of finches that Charles Darwin found on the Galapagos Islands displayed different structural adaptations. One of the adaptations that Darwin noted was the Based on the adaptations Charles Darwin observed in finches and tortoises in the Galapagos, he wondered James Hutton’s and Charl ...
... The species of finches that Charles Darwin found on the Galapagos Islands displayed different structural adaptations. One of the adaptations that Darwin noted was the Based on the adaptations Charles Darwin observed in finches and tortoises in the Galapagos, he wondered James Hutton’s and Charl ...
Chapter 14
... successfully, soon the mutation spread throughout the population, rendering the insecticide ineffective Combat® had acted as an agent of natural selection ...
... successfully, soon the mutation spread throughout the population, rendering the insecticide ineffective Combat® had acted as an agent of natural selection ...
Finch?
... suited for the environment are more likely to survive – some may adapt to survive – this process results in the evolution of a new species – Affects all populations of organisms Adaptation – the changing of a species in response to its environment ...
... suited for the environment are more likely to survive – some may adapt to survive – this process results in the evolution of a new species – Affects all populations of organisms Adaptation – the changing of a species in response to its environment ...
EVPP 110 Lecture - Populations - Evoluti
... – in the late 1800s, industrial pollution from the Industrial Revolution killed large numbers of lichens, exposing the darker tree bark or rock • the dark variety of the moth became increasing more abundant since it now was camouflaged against the dark surface and the lighter variety was not • by th ...
... – in the late 1800s, industrial pollution from the Industrial Revolution killed large numbers of lichens, exposing the darker tree bark or rock • the dark variety of the moth became increasing more abundant since it now was camouflaged against the dark surface and the lighter variety was not • by th ...
Evolution Unit
... c. Genetic variation and mutation play roles in natural selection. A diverse gene pool is important for the survival of a species in a changing environment. d. Environments can be more or less stable or fluctuating, and this affects evolutionary rate and direction; different genetic variations can b ...
... c. Genetic variation and mutation play roles in natural selection. A diverse gene pool is important for the survival of a species in a changing environment. d. Environments can be more or less stable or fluctuating, and this affects evolutionary rate and direction; different genetic variations can b ...
File
... 1. Directional selection-in a given population there is variation, one extreme is now favored over the other phenotypes. This gives rise to an increase in the favored gene. The allelic frequency changes and moves to the more favored trait. Note-many traits are are controlled by many genes (multifact ...
... 1. Directional selection-in a given population there is variation, one extreme is now favored over the other phenotypes. This gives rise to an increase in the favored gene. The allelic frequency changes and moves to the more favored trait. Note-many traits are are controlled by many genes (multifact ...
Nerve activates contraction
... the idea that species were individually designed and did not evolve. • In the 1700’s, the dominant philosophy, natural theology, was dedicated toward studying the adaptations of organisms as evidence that the Creator had designed each species for a purpose. • At this time, Carolus Linnaeus, a Swedis ...
... the idea that species were individually designed and did not evolve. • In the 1700’s, the dominant philosophy, natural theology, was dedicated toward studying the adaptations of organisms as evidence that the Creator had designed each species for a purpose. • At this time, Carolus Linnaeus, a Swedis ...
CHAPTER 22 DESCENT WITH MODIFICATION: A DARWINIAN
... • The Origin of Species challenged a worldview that had been accepted for centuries. • The key classical Greek philosophers who influenced Western culture, Plato and Aristotle, opposed any concept of evolution. • Plato believed in two worlds: one real world that is ideal and perfect and an illusory ...
... • The Origin of Species challenged a worldview that had been accepted for centuries. • The key classical Greek philosophers who influenced Western culture, Plato and Aristotle, opposed any concept of evolution. • Plato believed in two worlds: one real world that is ideal and perfect and an illusory ...
File
... species that can produce viable offspring • Individuals that avoid breeding with members of other species will have a selective advantage • Any trait that contributes to avoidance of hybridization will be favored ...
... species that can produce viable offspring • Individuals that avoid breeding with members of other species will have a selective advantage • Any trait that contributes to avoidance of hybridization will be favored ...
A. Early Models of Evolution
... 1. Darwin’s ideas became known as the theory of evolution by natural selection. 2. Natural selection means that organisms with traits best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
... 1. Darwin’s ideas became known as the theory of evolution by natural selection. 2. Natural selection means that organisms with traits best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
Ch. 14 Principles of Evolution
... – Lamarck theorized that organisms are modified during their lifetime through use or disuse of different parts – These modifications are passed to offspring – The idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics was not rejected until long after Lamarck’s death, when geneticists such as Mendel began ...
... – Lamarck theorized that organisms are modified during their lifetime through use or disuse of different parts – These modifications are passed to offspring – The idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics was not rejected until long after Lamarck’s death, when geneticists such as Mendel began ...
BIO EXAM NOTES
... survive and reproduce in a particular environment mimicry: an adaptation in which a species resembles another, providing them with a survival advantage selective advantage: a genetic advantage that improves an organism’s chance of survival, usually in a changing environment selective pressure: condi ...
... survive and reproduce in a particular environment mimicry: an adaptation in which a species resembles another, providing them with a survival advantage selective advantage: a genetic advantage that improves an organism’s chance of survival, usually in a changing environment selective pressure: condi ...
Nerve activates contraction
... the idea that species were individually designed and did not evolve. • In the 1700s, the dominant philosophy, natural theology, was dedicated to studying the adaptations of organisms as evidence that the Creator had designed each species for a purpose. • At this time, Carolus Linnaeus, a Swedish bot ...
... the idea that species were individually designed and did not evolve. • In the 1700s, the dominant philosophy, natural theology, was dedicated to studying the adaptations of organisms as evidence that the Creator had designed each species for a purpose. • At this time, Carolus Linnaeus, a Swedish bot ...
Speciation
... phenotypes are so different that competition drives them towards different behaviors and food sources. ...
... phenotypes are so different that competition drives them towards different behaviors and food sources. ...
Homework - District 273 Technology Services
... refill the earth. •They were told to throw rocks behind their back, which then became humans. •Humans filled the earth once again. ...
... refill the earth. •They were told to throw rocks behind their back, which then became humans. •Humans filled the earth once again. ...
The origin of species
... • How do new species evolve? – An isolated population may become genetically unique as its gene pool is changed by natural selection, genetic drift, or mutation ...
... • How do new species evolve? – An isolated population may become genetically unique as its gene pool is changed by natural selection, genetic drift, or mutation ...
Niche construction, biological evolution, and cultural change
... the interior temperature of the nest may rise too high, organisms evolve behaviors to counteract these pressures. In reality, the causal relationship is the inverse; thanks to natural selection, those ancestral organisms that as an effect of random genetic mutation had traits that rendered them capa ...
... the interior temperature of the nest may rise too high, organisms evolve behaviors to counteract these pressures. In reality, the causal relationship is the inverse; thanks to natural selection, those ancestral organisms that as an effect of random genetic mutation had traits that rendered them capa ...
Evolution Test Review
... 23. Who is the naturalist that came up with the mechanism for evolution?_____________ 24. What process leads to evolution? 25. What are homologous structures? 26. Give an example of homologous structures. 27. What is a cladogram? 28. What is natural selection? 29. a)Over time, does natural selection ...
... 23. Who is the naturalist that came up with the mechanism for evolution?_____________ 24. What process leads to evolution? 25. What are homologous structures? 26. Give an example of homologous structures. 27. What is a cladogram? 28. What is natural selection? 29. a)Over time, does natural selection ...
What is Biology? - Winona State University
... Is it right to protect an endangered species at the expense of jobs? Is it ethical to use fetal tissue in biomedical research? Are there dangers in cloning humans? Are irradiated foods safe to eat? ...
... Is it right to protect an endangered species at the expense of jobs? Is it ethical to use fetal tissue in biomedical research? Are there dangers in cloning humans? Are irradiated foods safe to eat? ...
competition 2006
... • Do populations compete for resources, or are their needs sufficiently different that they can be said to occupy nonoverlapping niches • What are the consequences of competition for the distribution and abundance of species with similar needs • If there is any relationship between competition for a ...
... • Do populations compete for resources, or are their needs sufficiently different that they can be said to occupy nonoverlapping niches • What are the consequences of competition for the distribution and abundance of species with similar needs • If there is any relationship between competition for a ...
pdfx2 - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... traits since they separated from reptiles • Groups called grades have changed rapidly. May be an appropriate group even if paraphyletic • General tendency to eliminate paraphyletic groups as we learn more, but some familiar categories, such as reptiles, won’t disappear in a hurry ...
... traits since they separated from reptiles • Groups called grades have changed rapidly. May be an appropriate group even if paraphyletic • General tendency to eliminate paraphyletic groups as we learn more, but some familiar categories, such as reptiles, won’t disappear in a hurry ...
pdfx6 - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... Bird and bat wings are homoplastic ...
... Bird and bat wings are homoplastic ...
Charles Darwin + Natural Selection
... Finches seemed identical, but varied between islands. 10 different species occurred on one island. Each species had adapted its beak to eat a specific type of food. ...
... Finches seemed identical, but varied between islands. 10 different species occurred on one island. Each species had adapted its beak to eat a specific type of food. ...
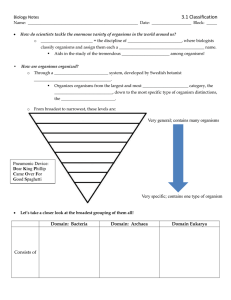
3.1 Classification
... _________________________ = the discipline of __________________________, where biologists classify organisms and assign them each a _________________________________________ name. ...
... _________________________ = the discipline of __________________________, where biologists classify organisms and assign them each a _________________________________________ name. ...