Rajon, E. and Masel, J. (2013)
... relaxed selection. The full, unattenuated effects of such variants can later be revealed by single mutations, by recombination into a different genetic background, or by stress-responsive developmental mechanisms (Gibson and Dworkin, 2004; Hayden et al., 2011; Duveau and Félix, 2012). Hidden variat ...
... relaxed selection. The full, unattenuated effects of such variants can later be revealed by single mutations, by recombination into a different genetic background, or by stress-responsive developmental mechanisms (Gibson and Dworkin, 2004; Hayden et al., 2011; Duveau and Félix, 2012). Hidden variat ...
Science Review
... • What are these statements an integral part of? • Limited resources lead to struggle where less fit individuals do not survive. • Populations have varieties of traits that are genetically inherited. • Some members of a population have better chances at surviving and reproducing than others. ...
... • What are these statements an integral part of? • Limited resources lead to struggle where less fit individuals do not survive. • Populations have varieties of traits that are genetically inherited. • Some members of a population have better chances at surviving and reproducing than others. ...
modelling the ecological context of evolutionary change
... individual’s fitness is determined by the phenotypes of other individuals in the population as well. The introduction of game-theoretic ideas addressed this complexity, and it was motivated largely to model the evolution of social interactions for which optimality models were simply not tenable (May ...
... individual’s fitness is determined by the phenotypes of other individuals in the population as well. The introduction of game-theoretic ideas addressed this complexity, and it was motivated largely to model the evolution of social interactions for which optimality models were simply not tenable (May ...
Probabilistic causation and the explanatory role of natural selection
... 3. Explaining the propagation and maintenance of traits Since Darwin’s and Wallace’s (1858) and Darwin’s (1859) foundational works, the only consensus about the explanatory role of natural selection is that it explains the propagation of new mutant traits (and lost of the wild-type) and the maintena ...
... 3. Explaining the propagation and maintenance of traits Since Darwin’s and Wallace’s (1858) and Darwin’s (1859) foundational works, the only consensus about the explanatory role of natural selection is that it explains the propagation of new mutant traits (and lost of the wild-type) and the maintena ...
Epigenetic Inheritance, Genetic Assimilation and Speciation
... Epigenetic inheritance systems enable the environmentally induced phenotypes to be transmitted between generations. Jablonka and Lamb (1991, 1995) proposed that these systems have a substantial role during speciation. They argued that divergence of isolated populations may be "rst triggered by the a ...
... Epigenetic inheritance systems enable the environmentally induced phenotypes to be transmitted between generations. Jablonka and Lamb (1991, 1995) proposed that these systems have a substantial role during speciation. They argued that divergence of isolated populations may be "rst triggered by the a ...
Consilience, Historicity, and the Species Problem.
... And despite hundreds of years of work on this problem, there is still widespread disagreement over the correct answer. Michael Ruse, of course, has tackled the species problem (see Ruse 1969, 1971, 1973, 1987, 1988). (I say ‘of course’ because Ruse has written on every significant issue in the philos ...
... And despite hundreds of years of work on this problem, there is still widespread disagreement over the correct answer. Michael Ruse, of course, has tackled the species problem (see Ruse 1969, 1971, 1973, 1987, 1988). (I say ‘of course’ because Ruse has written on every significant issue in the philos ...
A Bayesian approach to the evolution of perceptual and cognitive systems
... process where each change must produce an increase in fitness; thus the real observer may correspond to a local maximum in the space of possible solutions, whereas the ideal observer corresponds to the global maximum in the space of possible solutions. Geisler and Diehl (2002) proposed an extended B ...
... process where each change must produce an increase in fitness; thus the real observer may correspond to a local maximum in the space of possible solutions, whereas the ideal observer corresponds to the global maximum in the space of possible solutions. Geisler and Diehl (2002) proposed an extended B ...
Chapter 16 Powerpoint
... Survival of the Fittest According to Darwin, differences in adaptations affect an individual’s fitness. Fitness describes how well an organism can survive and reproduce in its environment. Individuals with adaptations that are well-suited to their environment can survive and reproduce and are said t ...
... Survival of the Fittest According to Darwin, differences in adaptations affect an individual’s fitness. Fitness describes how well an organism can survive and reproduce in its environment. Individuals with adaptations that are well-suited to their environment can survive and reproduce and are said t ...
Negative frequency-dependent selection is frequently
... whether it is beneficial or detrimental – is dependent on the environmental context [12,13]. That is, alleles are advantageous and deleterious in different ecological contexts. Negative frequency-dependent selection has been called the most powerful selective force maintaining balanced polymorphisms ...
... whether it is beneficial or detrimental – is dependent on the environmental context [12,13]. That is, alleles are advantageous and deleterious in different ecological contexts. Negative frequency-dependent selection has been called the most powerful selective force maintaining balanced polymorphisms ...
Negative frequency-dependent selection is frequently confounding
... whether it is beneficial or detrimental – is dependent on the environmental context [12,13]. That is, alleles are advantageous and deleterious in different ecological contexts. Negative frequency-dependent selection has been called the most powerful selective force maintaining balanced polymorphisms ...
... whether it is beneficial or detrimental – is dependent on the environmental context [12,13]. That is, alleles are advantageous and deleterious in different ecological contexts. Negative frequency-dependent selection has been called the most powerful selective force maintaining balanced polymorphisms ...
Evolutionary Connectionism: Algorithmic Principles Underlying the
... side-effects on other traits? What is it about the organisation of an ecological community that causes some ecological relationships to remain stable over long periods of selection and applies a strong selective pressure for changes in other ecological relationships (e.g. between a particular herbiv ...
... side-effects on other traits? What is it about the organisation of an ecological community that causes some ecological relationships to remain stable over long periods of selection and applies a strong selective pressure for changes in other ecological relationships (e.g. between a particular herbiv ...
Review Evolution of Sex: Why Do Organisms Shuffle
... analogous to an ecological model of species competition. In such a case, long-term effects are of primary importance in determining the fate of the modifier. Consider again the example described above where, initially, all individuals are heterozygous at the A locus and wA/A = 1, wA/a = 0.9, and wa/ ...
... analogous to an ecological model of species competition. In such a case, long-term effects are of primary importance in determining the fate of the modifier. Consider again the example described above where, initially, all individuals are heterozygous at the A locus and wA/A = 1, wA/a = 0.9, and wa/ ...
Aesthetic evolution by mate choice: Darwin`s really dangerous idea
... Cronin [12, p. 123] documents in her excellent history of the Darwin– Wallace sexual selection debate, The ant and the peacock, Wallace never fully denied the possibility of evolution by mate choice. Most of his arguments merely advocated against its likelihood. However, the most relevant and forcef ...
... Cronin [12, p. 123] documents in her excellent history of the Darwin– Wallace sexual selection debate, The ant and the peacock, Wallace never fully denied the possibility of evolution by mate choice. Most of his arguments merely advocated against its likelihood. However, the most relevant and forcef ...
Aesthetic evolution by mate choice: Darwin`s really dangerous idea
... Cronin [12, p. 123] documents in her excellent history of the Darwin– Wallace sexual selection debate, The ant and the peacock, Wallace never fully denied the possibility of evolution by mate choice. Most of his arguments merely advocated against its likelihood. However, the most relevant and forcef ...
... Cronin [12, p. 123] documents in her excellent history of the Darwin– Wallace sexual selection debate, The ant and the peacock, Wallace never fully denied the possibility of evolution by mate choice. Most of his arguments merely advocated against its likelihood. However, the most relevant and forcef ...
Punctuated equilibrium in fact and theory
... controversy that punctuated equilibrium would generate (at most, we hoped to stir up some self-examination among palaeontologists). We had no hidden agenda (unless it was buried so deeply in our psyches that even we were not aware). Moreover, our reaction to the influence of our theory is a mixture ...
... controversy that punctuated equilibrium would generate (at most, we hoped to stir up some self-examination among palaeontologists). We had no hidden agenda (unless it was buried so deeply in our psyches that even we were not aware). Moreover, our reaction to the influence of our theory is a mixture ...
- Journal of Dentofacial Anomalies and Orthodontics
... number of teeth, and the differentiation of types of teeth, which is called heterodontia. These varied types of teeth in humans and primates are the incisors, the canine-first premolar complex, and the molars. We shall see that, even in primates, these fields may or may not embrace neighbouring teet ...
... number of teeth, and the differentiation of types of teeth, which is called heterodontia. These varied types of teeth in humans and primates are the incisors, the canine-first premolar complex, and the molars. We shall see that, even in primates, these fields may or may not embrace neighbouring teet ...
Ch 22 Notes - Dublin City Schools
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Presentation
... Assume no convergent evolution; and no derived traits have been lost. Lampreys are the outgroup—any species or group outside the group of interest. The group of interest is the ingroup. Comparison with the outgroup shows which traits of the ingroup are derived and which are ancestral. ...
... Assume no convergent evolution; and no derived traits have been lost. Lampreys are the outgroup—any species or group outside the group of interest. The group of interest is the ingroup. Comparison with the outgroup shows which traits of the ingroup are derived and which are ancestral. ...
Document
... might also result in the generation of new populations of mixed ancestry that remain distinct from both parental populations (hybrid speciation: Mallet, 2007; Abbott et al., 2010). These new populations may be sexual or asexual, homoploid or polyploid. We do not consider asexual hybrid lineages here ...
... might also result in the generation of new populations of mixed ancestry that remain distinct from both parental populations (hybrid speciation: Mallet, 2007; Abbott et al., 2010). These new populations may be sexual or asexual, homoploid or polyploid. We do not consider asexual hybrid lineages here ...
Darwin`s Theory of Natural Selection
... England’s peppered moth provides an example of natural selection in action. It also offers us a chance to study the sorts of experiments that can be used to test evolutionary theory. The story is as follows. The peppered moth spends much of the daytime resting on the bark of oak trees. In the beginn ...
... England’s peppered moth provides an example of natural selection in action. It also offers us a chance to study the sorts of experiments that can be used to test evolutionary theory. The story is as follows. The peppered moth spends much of the daytime resting on the bark of oak trees. In the beginn ...
PRACTICE TEST 1
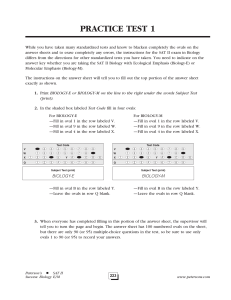
... 26. There are three alleles of the gene that controls the inheritance of the ABO blood groups; the A and B alleles are co-dominant, and O is recessive to both the A and B alleles. A man with type B blood and a women with type A blood could have children showing which of the following phenotype(s)? ( ...
... 26. There are three alleles of the gene that controls the inheritance of the ABO blood groups; the A and B alleles are co-dominant, and O is recessive to both the A and B alleles. A man with type B blood and a women with type A blood could have children showing which of the following phenotype(s)? ( ...
Genome-wide patterns of divergence during speciation: the lake
... recent (less than 12 000 yr BP) and involves both a phase of allopatry (geographical isolation) and sympatry (secondary contact) [31,37,38]. This system is especially well suited to study the genetics of species boundaries for several reasons. First, lake whitefish represents a rare illustration of ...
... recent (less than 12 000 yr BP) and involves both a phase of allopatry (geographical isolation) and sympatry (secondary contact) [31,37,38]. This system is especially well suited to study the genetics of species boundaries for several reasons. First, lake whitefish represents a rare illustration of ...
POSSIBLE LARGEST-SCALE TRENDS IN ORGANISMAL
... disordered collisions among fluid molecules (i.e. by conduction) from source below to sink above. If the gradient is increased above the threshold, however, the fluid flow spontaneously becomes structured at a large scale. Viewed from above, the surface of the fluid is no longer a smooth sheet but r ...
... disordered collisions among fluid molecules (i.e. by conduction) from source below to sink above. If the gradient is increased above the threshold, however, the fluid flow spontaneously becomes structured at a large scale. Viewed from above, the surface of the fluid is no longer a smooth sheet but r ...
The Contribution of Selection and Genetic Constraints to Phenotypic
... and variation in directional selection. Zeng (1988) explicitly assumed in this model that genetic constraints would not be important in determining the pattern of divergence in the longer term. In contrast, model 2 assumed that stabilizing selection was absent and that population divergence in multi ...
... and variation in directional selection. Zeng (1988) explicitly assumed in this model that genetic constraints would not be important in determining the pattern of divergence in the longer term. In contrast, model 2 assumed that stabilizing selection was absent and that population divergence in multi ...