Atomic Theory Notes
... Atoms combine with each other in specific ratios to make compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but the atoms of one element are not changed into the atoms of another by chemical reaction ...
... Atoms combine with each other in specific ratios to make compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but the atoms of one element are not changed into the atoms of another by chemical reaction ...
File - GarzScience!
... • The law of conservation of mass (proposed by Lavoisier) • States that mass is conserved in any process, such as a chemical reaction. • Conservation is the result of the separation, combination, or rearrangement of atoms ...
... • The law of conservation of mass (proposed by Lavoisier) • States that mass is conserved in any process, such as a chemical reaction. • Conservation is the result of the separation, combination, or rearrangement of atoms ...
Notes - PowerPoint
... amounts of atoms and molecules, we use average masses in calculations. • Average mass is calculated from the isotopes of an element weighted by their relative abundances. ...
... amounts of atoms and molecules, we use average masses in calculations. • Average mass is calculated from the isotopes of an element weighted by their relative abundances. ...
1. Base your answer to the following question - Trupia
... However, an element that would be put between these two elements on the Periodic Table has not yet been produced. If produced, this element will be identified by the symbol Uut until an IUPAC name is approved. Identify one element that would be chemically similar to Uut. ...
... However, an element that would be put between these two elements on the Periodic Table has not yet been produced. If produced, this element will be identified by the symbol Uut until an IUPAC name is approved. Identify one element that would be chemically similar to Uut. ...
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
... Ion and Isotope. Both have something the same, something different. Both start with the letter “i". Don’t confuse them! Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have identical numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Ions are made when an atom gains or lose electrons. The mass number ...
... Ion and Isotope. Both have something the same, something different. Both start with the letter “i". Don’t confuse them! Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have identical numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Ions are made when an atom gains or lose electrons. The mass number ...
Chapter 3: Atoms
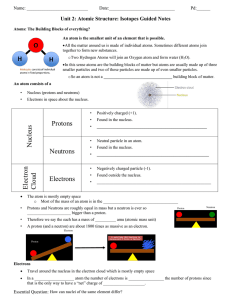
... A. Atoms consist of two regions: the nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons; and the region surrounding the nucleus, called the electron cloud, where the electrons are. Protons, neutrons, and electrons are also called subatomic particles. 1. Protons - Positively charged particles. 2. Neutrons ...
... A. Atoms consist of two regions: the nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons; and the region surrounding the nucleus, called the electron cloud, where the electrons are. Protons, neutrons, and electrons are also called subatomic particles. 1. Protons - Positively charged particles. 2. Neutrons ...
atomic theory of matter
... • Law of multiple proportions: when two elements form more than one compound, the ratio of the masses in one compound divided by the ratio of these masses in the other compound gives a ratio of small whole numbers. E.g. There are three binary compounds that form between barium and nitrogen. There wa ...
... • Law of multiple proportions: when two elements form more than one compound, the ratio of the masses in one compound divided by the ratio of these masses in the other compound gives a ratio of small whole numbers. E.g. There are three binary compounds that form between barium and nitrogen. There wa ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, IONS, AND COMPOUNDS
... – Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals, make up <0.005% of Earth's crust – Actinide series: Th-Lr, also called transuranium elements, generally all man-made and exist for only very short periods of time before decaying to other elements Periodic Law: ...
... – Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals, make up <0.005% of Earth's crust – Actinide series: Th-Lr, also called transuranium elements, generally all man-made and exist for only very short periods of time before decaying to other elements Periodic Law: ...
Chapter 3 - Vocabulary and Notes
... A. Substance – Matter that has the same composition and properties throughout B. Compound – Substance whose smallest unit is made up of more than one element 1. Chemical Formula – tells which elements make up a compound as well as how many atoms of each element are present a. The subscript number te ...
... A. Substance – Matter that has the same composition and properties throughout B. Compound – Substance whose smallest unit is made up of more than one element 1. Chemical Formula – tells which elements make up a compound as well as how many atoms of each element are present a. The subscript number te ...
Atomic structure
... Despite these differences, isotopes are chemically alike because they have identical numbers of protons and electrons, which are the subatomic particles responsible for chemical behavior. ...
... Despite these differences, isotopes are chemically alike because they have identical numbers of protons and electrons, which are the subatomic particles responsible for chemical behavior. ...
Atomic number, atomic mass and isotopes
... Appendix B and check out the atomic numbers and atomic masses of your favourite elements. Isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different atomic masses; they have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. Look at the element chlorine in Appendix B. Its atomi ...
... Appendix B and check out the atomic numbers and atomic masses of your favourite elements. Isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different atomic masses; they have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. Look at the element chlorine in Appendix B. Its atomi ...
Chapter 4 PPT
... equation” model of electrons Goes to Germany in 1927 but leaves in 1933 with rise of Nazis; ends up in Austria in 1937; recants opposition to Nazis but is harassed and escapes in 1938 1933 Nobel Prize in Physics with ...
... equation” model of electrons Goes to Germany in 1927 but leaves in 1933 with rise of Nazis; ends up in Austria in 1937; recants opposition to Nazis but is harassed and escapes in 1938 1933 Nobel Prize in Physics with ...
Chapter 3 – Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter - Hatboro
... This idea succeeded for about _______years. Neither view was supported by __________ _________ until ________. ...
... This idea succeeded for about _______years. Neither view was supported by __________ _________ until ________. ...
Counting Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... From the periodic table, the atomic number of chlorine is 17. Mass # - atomic # = # of neutrons 37 – 17 = 20 An atom of chlorine-37 is made up of 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 20 neutrons. ...
... From the periodic table, the atomic number of chlorine is 17. Mass # - atomic # = # of neutrons 37 – 17 = 20 An atom of chlorine-37 is made up of 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 20 neutrons. ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 70. Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? 71. Which subatomic particles are charged? 72. Name Rutherford’s famous experiment. What information did it contribute to atomic structure? 73. How many copper atoms would you have to line up side by side to form a line 1 m long? (re ...
... 70. Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? 71. Which subatomic particles are charged? 72. Name Rutherford’s famous experiment. What information did it contribute to atomic structure? 73. How many copper atoms would you have to line up side by side to form a line 1 m long? (re ...
mass number - KCPE-KCSE
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons. ...
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... Isotope – atoms of the same element that have the same number of _______________but a different number of _________________________ Ions – atoms of the same element that have the same number of __________________ but different number of _________________________ ...
... Isotope – atoms of the same element that have the same number of _______________but a different number of _________________________ Ions – atoms of the same element that have the same number of __________________ but different number of _________________________ ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... centuries later. Aristotle believed that empty space did not exist and that matter is made of earth, fire, air and water, not atoms. ...
... centuries later. Aristotle believed that empty space did not exist and that matter is made of earth, fire, air and water, not atoms. ...
Atomic Structure
... • Masses of atoms expressed in grams are very small. • For this reason, we use relative mass. – The standard used by scientists to govern units of atomic mass is carbon12 atom. It has been arbitrarily assigned a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu). ...
... • Masses of atoms expressed in grams are very small. • For this reason, we use relative mass. – The standard used by scientists to govern units of atomic mass is carbon12 atom. It has been arbitrarily assigned a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu). ...
Isotopes - Wando High School
... • We know that different elements have different number of protons. • However even atoms of the same element are not exactly the same. • Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. These are called Isotopes. ...
... • We know that different elements have different number of protons. • However even atoms of the same element are not exactly the same. • Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. These are called Isotopes. ...
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
... We know that atoms are made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. This sheet will discuss how we show the composition of atoms: How many p, e, and n a particular atom has. We will also relate the makeup of each element’s atoms to the periodic table. Key terms to know, covered on this sheet: Atomic nu ...
... We know that atoms are made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. This sheet will discuss how we show the composition of atoms: How many p, e, and n a particular atom has. We will also relate the makeup of each element’s atoms to the periodic table. Key terms to know, covered on this sheet: Atomic nu ...
atomic structure intro - Hood River County School District
... c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged; however, atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element when the a ...
... c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged; however, atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element when the a ...
Atomic History - Wylie High School Advanced Chemistry
... Dalton also claimed that atoms of different elements are different in all respects. This has been proven wrong in certain cases: argon and calcium atoms each have an atomic mass of 40 amu. These atoms are ...
... Dalton also claimed that atoms of different elements are different in all respects. This has been proven wrong in certain cases: argon and calcium atoms each have an atomic mass of 40 amu. These atoms are ...
Chapter 4 notes - Sussex Regional High School
... • Electron cloud‐ region where you might find an electron. ...
... • Electron cloud‐ region where you might find an electron. ...
Unit 1
... • Radioactive waste produced in nuclear reactors can take hundreds of thousands of years to decay. • Disposal of nuclear waste is done with the intention of never retrieving it. • There are 77 disposal sites around the country. A new one (Yucca Mountain) is being developed for the permanent disposal ...
... • Radioactive waste produced in nuclear reactors can take hundreds of thousands of years to decay. • Disposal of nuclear waste is done with the intention of never retrieving it. • There are 77 disposal sites around the country. A new one (Yucca Mountain) is being developed for the permanent disposal ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.