Smrti - www.BahaiStudies.net
... Vedāngas).[21] For example, the attempt to perfect the art of rituals led to the science of Kalpa, which branched into three Kalpa-sūtras: Srauta-sūtras, Grhya-sūtras, and Dharma-sūtras (estimated to have been composed between 600-200 BCE).[22] The Srauta-sutras became texts describing the perfect p ...
... Vedāngas).[21] For example, the attempt to perfect the art of rituals led to the science of Kalpa, which branched into three Kalpa-sūtras: Srauta-sūtras, Grhya-sūtras, and Dharma-sūtras (estimated to have been composed between 600-200 BCE).[22] The Srauta-sutras became texts describing the perfect p ...
Hinduism is the world`s 3rd largest religion after Christianity and
... dominant religion in India, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Hindus sometimes call their religion “Vedic religion” ______________(2) the ancient texts known as “Vedas”. Vedas contain religious texts of wisdom that had been ____________(3) orally and finally recorded in writing. They were not written by any sing ...
... dominant religion in India, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Hindus sometimes call their religion “Vedic religion” ______________(2) the ancient texts known as “Vedas”. Vedas contain religious texts of wisdom that had been ____________(3) orally and finally recorded in writing. They were not written by any sing ...
2017 Review Hinduism and Buddhism PowerPoint for Midterm Short
... • Reincarnation: after death, souls are reborn into another form; reincarnation is determined by karma and dharma; • Ahimsa: moral principle of nonviolence; Hindus believe that all things are aspects of Brahman, therefore they should be respected; ...
... • Reincarnation: after death, souls are reborn into another form; reincarnation is determined by karma and dharma; • Ahimsa: moral principle of nonviolence; Hindus believe that all things are aspects of Brahman, therefore they should be respected; ...
Hinduism PP
... Not easy to do. Believe it can take many lifetimes to reject maya. Because it can take many lifetimes to reject maya, souls must be reborn over and over. This is called reincarnation – the belief that the soul does not die, but can be reborn in the body of another human or animal. ...
... Not easy to do. Believe it can take many lifetimes to reject maya. Because it can take many lifetimes to reject maya, souls must be reborn over and over. This is called reincarnation – the belief that the soul does not die, but can be reborn in the body of another human or animal. ...
LECTURE NOTES
... ATHARVEDA (incantations) feature Gods, demons (their frolics); creation stories, human origins. each Veda has a Brahmana (priests' manuals). Gods require sacrifices (grain, milk, flesh - worshippers eat; these are also 'gods'). Later, when belief in atman as soul in all life forms developed, most Hi ...
... ATHARVEDA (incantations) feature Gods, demons (their frolics); creation stories, human origins. each Veda has a Brahmana (priests' manuals). Gods require sacrifices (grain, milk, flesh - worshippers eat; these are also 'gods'). Later, when belief in atman as soul in all life forms developed, most Hi ...
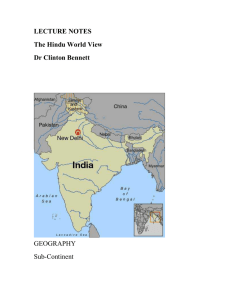
Full_India
... The Vedas: Brought to the Indian subcontinent by the Aryans. The Vedas are four collections of prayers and instructions for performing rituals. The Rig Veda is the most important, which includes Purusa. Mahabharata: A great epic Indian story that explains the struggles that took place in India as th ...
... The Vedas: Brought to the Indian subcontinent by the Aryans. The Vedas are four collections of prayers and instructions for performing rituals. The Rig Veda is the most important, which includes Purusa. Mahabharata: A great epic Indian story that explains the struggles that took place in India as th ...
Learning About Hindu Beliefs Chapter 15 History Alive!
... Dharma is a very important _________ in Hinduism. To follow one’s dharma means to perform one’s duties and so to live as one should. Hindu’s believed that when everyone followed the dharma of their class, _______ would be in harmony. Hinduism values ______________, sharing good with others a ...
... Dharma is a very important _________ in Hinduism. To follow one’s dharma means to perform one’s duties and so to live as one should. Hindu’s believed that when everyone followed the dharma of their class, _______ would be in harmony. Hinduism values ______________, sharing good with others a ...
Pastor`s Class October 21, 2009 World Religions
... Sanatana Dharma – eternal religion Vaidika Dharma – religion of the Vedas Hinduism -- the most commonly used name in North America Multiple Expressions and Variations of Hinduism The word "Hindu" is derived from the name of River Indus, which flows through northwestern India. In ancient times the ri ...
... Sanatana Dharma – eternal religion Vaidika Dharma – religion of the Vedas Hinduism -- the most commonly used name in North America Multiple Expressions and Variations of Hinduism The word "Hindu" is derived from the name of River Indus, which flows through northwestern India. In ancient times the ri ...
Hinduism - World History
... • In order to follow your dharma and achieve moksha you must have good karma. • Karma is: – Moral law which guides the universe – Good and bad actions, thoughts or words – The balance of karma in a previous life determines one’s present condition ...
... • In order to follow your dharma and achieve moksha you must have good karma. • Karma is: – Moral law which guides the universe – Good and bad actions, thoughts or words – The balance of karma in a previous life determines one’s present condition ...
Hinduism
... Something you didn’t know! Worlds oldest religion World’s third largest religion It is a way of life (dharma) The word ‘Hindu’ came from the river ‘Sindhu’ In Hinduism, they do not have any system or beliefs just ...
... Something you didn’t know! Worlds oldest religion World’s third largest religion It is a way of life (dharma) The word ‘Hindu’ came from the river ‘Sindhu’ In Hinduism, they do not have any system or beliefs just ...
Main beliefs and practices Language Key dates and festivals Points
... attributes are chanted, and divas are lit. ❖ Hindus live according to Dharma (literally ‘that which binds together’). It is both a religious philosophy and way of life. For Hindus, it means doing their duty towards their family and friends. ❖ A person’s Dharma affects their Karma (the cycle of birth ...
... attributes are chanted, and divas are lit. ❖ Hindus live according to Dharma (literally ‘that which binds together’). It is both a religious philosophy and way of life. For Hindus, it means doing their duty towards their family and friends. ❖ A person’s Dharma affects their Karma (the cycle of birth ...
Sample PDF
... about life. The texts themselves show that the collection is the result of the work of generations of poets, extending over many centuries. Books II to VII inclusive are each the work of a single poet, or ri'-shi (seer), and his descendants; hence they are aptly called “family books”. Book III is at ...
... about life. The texts themselves show that the collection is the result of the work of generations of poets, extending over many centuries. Books II to VII inclusive are each the work of a single poet, or ri'-shi (seer), and his descendants; hence they are aptly called “family books”. Book III is at ...
Hinduism - Global Dialogue Foundation
... Some Hindus define orthodoxy as compliance with the teachings of the Vedic texts (the four Vedas and their supplements). However, still others identify their tradition with 'Sanatana Dharma', the eternal order of conduct that transcends any specific body of sacred literature. Scholars sometimes draw ...
... Some Hindus define orthodoxy as compliance with the teachings of the Vedic texts (the four Vedas and their supplements). However, still others identify their tradition with 'Sanatana Dharma', the eternal order of conduct that transcends any specific body of sacred literature. Scholars sometimes draw ...
Document
... development of the idea of God in India. • The movement towards monotheism and monism may have been motivated in part by the concept of rita (law or order). Diversity in the universe Unity in the universe ...
... development of the idea of God in India. • The movement towards monotheism and monism may have been motivated in part by the concept of rita (law or order). Diversity in the universe Unity in the universe ...
Hinduism
... existence in the next life Dharma The moral & religious duties that are expected by of an individual ...
... existence in the next life Dharma The moral & religious duties that are expected by of an individual ...
Hinduism notes
... The _____________________________, or Untouchables, are even lower than the Sudras ...
... The _____________________________, or Untouchables, are even lower than the Sudras ...
Hinduism
... *Artha = worldly wealth and success (proper attitude); necessary for well-ordered society. *Kama = pleasure, desire (guided by dharma); Kama Sutra. *Dharma = virtue, duty; individual, universal. *Moksha = spiritual liberation, release from samsara. ...
... *Artha = worldly wealth and success (proper attitude); necessary for well-ordered society. *Kama = pleasure, desire (guided by dharma); Kama Sutra. *Dharma = virtue, duty; individual, universal. *Moksha = spiritual liberation, release from samsara. ...
Hindu Sacred Texts: Shruti and Smirti Every religion has either a
... As the title suggests, the Laws of Manu is a collection of 2685 verses which explain the rules or laws that members of Hindu society should live by. The text, which was eventually written down around 250 BCE, explains the four life stages or ‘Ashramas' and the four basic aims of life: Dharma (follow ...
... As the title suggests, the Laws of Manu is a collection of 2685 verses which explain the rules or laws that members of Hindu society should live by. The text, which was eventually written down around 250 BCE, explains the four life stages or ‘Ashramas' and the four basic aims of life: Dharma (follow ...
Hinduism Notes
... Unlike other religions, Hinduism is not based on one particular ___________________ or text. The earliest Hindu scriptures are called The Vedas, which means _______________________. The Bhagavad Gita is read ___________________ than any other Hindu scripture. ...
... Unlike other religions, Hinduism is not based on one particular ___________________ or text. The earliest Hindu scriptures are called The Vedas, which means _______________________. The Bhagavad Gita is read ___________________ than any other Hindu scripture. ...
"HINDUISM" The Religious Dimension of Indian Culture Professor
... pertaining to Vedic sacrifices and other religious matters. All four Vedas were transmitted orally from generation to generation. In later Hinduism, the Vedas are generally considered the highest of all scriptures, even by those whose beliefs and practices may be very different. ...
... pertaining to Vedic sacrifices and other religious matters. All four Vedas were transmitted orally from generation to generation. In later Hinduism, the Vedas are generally considered the highest of all scriptures, even by those whose beliefs and practices may be very different. ...
atman
... samsara – the lifecycle the atman is trapped in of birth, death, and reincarnation before achieving moksha shakti – cosmic energy, found in om and harnessed through meditation; personified in the great mother goddess sutra – religious text trimurthi – triad of main Hindu Gods, Brahma (creator), Vish ...
... samsara – the lifecycle the atman is trapped in of birth, death, and reincarnation before achieving moksha shakti – cosmic energy, found in om and harnessed through meditation; personified in the great mother goddess sutra – religious text trimurthi – triad of main Hindu Gods, Brahma (creator), Vish ...
The Vedas
... There are also appendices called Upangas. They include Ayurveda, the science of life (including medicine), Arthasastra, the science of economics, Dhanaveda, the science of war and of weapons, and Gandharvaveda, the treatises on the arts. The four basic Vedas are divided into three sections, the Samh ...
... There are also appendices called Upangas. They include Ayurveda, the science of life (including medicine), Arthasastra, the science of economics, Dhanaveda, the science of war and of weapons, and Gandharvaveda, the treatises on the arts. The four basic Vedas are divided into three sections, the Samh ...
Dharmaśāstra

Dharmaśāstra (Sanskrit: धर्मशास्त्र) is a genre of Sanskrit texts and refers to the śāstra, or Indic branch of learning, pertaining to Hindu dharma, religious and legal duty. The voluminous textual corpus of Dharmaśāstra is primarily a product of the Brahmanical tradition in India and represents the elaborate scholastic system of an expert tradition. Because of its sophisticated jurisprudence, Dharmaśāstra was taken by early British colonial administrators to be the law of the land for Hindus in India. Ever since, Dharmaśāstra has been linked with Hindu law, despite the fact that its contents deal as much or more with religious life as with law. In fact, a separation of religion and law within Dharmaśāstra is artificial and has been repeatedly questioned. Others have, however, argued for a distinction of religious and secular law within Dharmaśāstra. Dharmaśāstra is important within the Hindu tradition—first, as a source of religious law describing the life of an ideal householder and, second, as symbol of the summation of Hindu knowledge about religion, law and ethics.