Introduction to Hinduism
... For Gandhi, social concern was deeply rooted in his conviction of the sacredness of life. He also believed in the people of any nation ruling themselves and helped greatly in the ending of British rule in India. Gandhi believed that human beings should strive to live as simply as possible since over ...
... For Gandhi, social concern was deeply rooted in his conviction of the sacredness of life. He also believed in the people of any nation ruling themselves and helped greatly in the ending of British rule in India. Gandhi believed that human beings should strive to live as simply as possible since over ...
Document
... Ordinary citizen of India – village life – born into a Hindu family, grows in secular / diverse culture, understand, accept and respect (tolerance) other’s beliefs & festivals, feel part of community (Unity in Diversity) ...
... Ordinary citizen of India – village life – born into a Hindu family, grows in secular / diverse culture, understand, accept and respect (tolerance) other’s beliefs & festivals, feel part of community (Unity in Diversity) ...
Ancient and Classical India
... us bound to this world (good and bad) • Ultimate goal of life – to release the soul and reunite with the divine, becoming as one with Brahman ...
... us bound to this world (good and bad) • Ultimate goal of life – to release the soul and reunite with the divine, becoming as one with Brahman ...
Indus Valley
... • Out of the clash between conqueror and conquered came a set of social institutions and class divisions that has lasted in India, with only minor changes, to the present day. • The caste system was a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person’s occupation and economic potentia ...
... • Out of the clash between conqueror and conquered came a set of social institutions and class divisions that has lasted in India, with only minor changes, to the present day. • The caste system was a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person’s occupation and economic potentia ...
Indus River Valley Civilizations
... • Out of the clash between conqueror and conquered came a set of social institutions and class divisions that has lasted in India, with only minor changes, to the present day. • The caste system was a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person’s occupation and economic potentia ...
... • Out of the clash between conqueror and conquered came a set of social institutions and class divisions that has lasted in India, with only minor changes, to the present day. • The caste system was a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person’s occupation and economic potentia ...
What is Hinduism?
... Tolerance and diversity: "Truth is one, paths are many" Many deities but a single, impersonal Ultimate Reality A philosophy and a way of life – focused both on this world and beyond ...
... Tolerance and diversity: "Truth is one, paths are many" Many deities but a single, impersonal Ultimate Reality A philosophy and a way of life – focused both on this world and beyond ...
File - Religious Studies Website
... This bronze sculpture, entitled Shiva as Nataraja (Lord of the Dance) (about ad 1000), is one of a number of sculptures of the Hindu god Shiva made during India’s Chola dynasty (10th century to 13th century). The sculpture shows Shiva dancing within a circle of fire. One of the god’s hands holds a f ...
... This bronze sculpture, entitled Shiva as Nataraja (Lord of the Dance) (about ad 1000), is one of a number of sculptures of the Hindu god Shiva made during India’s Chola dynasty (10th century to 13th century). The sculpture shows Shiva dancing within a circle of fire. One of the god’s hands holds a f ...
Two Main Religions of Ancient India
... Virupaksha Temple, dedicated to Shiva, in southern India ...
... Virupaksha Temple, dedicated to Shiva, in southern India ...
Hinduism: A Way of Life
... Does NOT have a specific founder, beginnings lie in the tradition of the Vedas. It appears polytheistic, but it is not…. ...
... Does NOT have a specific founder, beginnings lie in the tradition of the Vedas. It appears polytheistic, but it is not…. ...
The Hindu View of God
... widely believed to be a historical figure - "tribal hero of ancient India” Main character Hindu epic of Ramayana ...
... widely believed to be a historical figure - "tribal hero of ancient India” Main character Hindu epic of Ramayana ...
LECTURE NOTES
... Minister: "Hinduism is all things to all men", Hindus "live and let live' (1946, The Discovery of India New Delhi, OUP.) THE VEDAS (Sanskrit) RIGVEDA (hymns) YAJURVEDA (sacrificial formulas) SAMVEDA (chants) ATHARVEDA (incantations) feature Gods, demons (their frolics); creation stories, human origi ...
... Minister: "Hinduism is all things to all men", Hindus "live and let live' (1946, The Discovery of India New Delhi, OUP.) THE VEDAS (Sanskrit) RIGVEDA (hymns) YAJURVEDA (sacrificial formulas) SAMVEDA (chants) ATHARVEDA (incantations) feature Gods, demons (their frolics); creation stories, human origi ...
Answers
... Prayers are chanted and the god is invited to come and dwell within the image for the duration of worship. Flowers are placed before the image in offering. Then a seat, water and fresh clothes are symbolically offered to the deity. Other offerings include incense and sandalwood paste. Then worship t ...
... Prayers are chanted and the god is invited to come and dwell within the image for the duration of worship. Flowers are placed before the image in offering. Then a seat, water and fresh clothes are symbolically offered to the deity. Other offerings include incense and sandalwood paste. Then worship t ...
Gods and Goddesses of Hinduism
... vibration that is all pervading. It is the most common name of God. ...
... vibration that is all pervading. It is the most common name of God. ...
The Aryans
... • At constant peace • Is the foil of Shiva, but they work together • Wants humanity to find people with all living things • Avatar (human form) is Krishna ...
... • At constant peace • Is the foil of Shiva, but they work together • Wants humanity to find people with all living things • Avatar (human form) is Krishna ...
What is Hinduism? - cwwh
... • The religion of the Indian people • Many deities but a single, impersonal Ultimate Reality • A philosophy and a way of life – focused both on this world and beyond ...
... • The religion of the Indian people • Many deities but a single, impersonal Ultimate Reality • A philosophy and a way of life – focused both on this world and beyond ...
Hinduism - University of Windsor
... Hindus believe in one God, Brahman, who was the originator of everything. They believe that his work is now done, however, and the task of creating, maintaining and destroying the world is up to three main gods, Brahma, Vishnu and Shiva, and other lesser gods. Hindus worship various gods depending o ...
... Hindus believe in one God, Brahman, who was the originator of everything. They believe that his work is now done, however, and the task of creating, maintaining and destroying the world is up to three main gods, Brahma, Vishnu and Shiva, and other lesser gods. Hindus worship various gods depending o ...
Chapter 5 Crossword
... 25. The vast majority of the world’s Hindus live here 26. The Divine Mother 28. Comes from the Sanskrit word “sindhu” meaning river 31. A collection of stories about the three gods: Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva 32. The pursuit of liberation from the cycle of rebirth through actions, thoughts, and devot ...
... 25. The vast majority of the world’s Hindus live here 26. The Divine Mother 28. Comes from the Sanskrit word “sindhu” meaning river 31. A collection of stories about the three gods: Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva 32. The pursuit of liberation from the cycle of rebirth through actions, thoughts, and devot ...
Exploring Religions - Chapter 5 Large
... 25. The vast majority of the world’s Hindus live here 26. The Divine Mother 28. Comes from the Sanskrit word “sindhu” meaning river 31. A collection of stories about the three gods: Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva 32. The pursuit of liberation from the cycle of rebirth through actions, thoughts, and devot ...
... 25. The vast majority of the world’s Hindus live here 26. The Divine Mother 28. Comes from the Sanskrit word “sindhu” meaning river 31. A collection of stories about the three gods: Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva 32. The pursuit of liberation from the cycle of rebirth through actions, thoughts, and devot ...
File
... worshipped as the paramount lord by the Saivite sects of India. Shiva is one of the most complex gods of India, embodying seemingly contradictory qualities. He is the destroyer and the restorer, the great ascetic and the symbol of sensuality, the benevolent herdsman of souls and the wrathful avenger ...
... worshipped as the paramount lord by the Saivite sects of India. Shiva is one of the most complex gods of India, embodying seemingly contradictory qualities. He is the destroyer and the restorer, the great ascetic and the symbol of sensuality, the benevolent herdsman of souls and the wrathful avenger ...
Hindu handout - MELHS
... Untouchables. The greatest force for changing these laws and customs, which kept Untouchables in virtual slavery, as been the influence of Christian missionaries, who have played a major role in challenging the social-economic-religious power blocs in India. Still, the social reality in many Indian ...
... Untouchables. The greatest force for changing these laws and customs, which kept Untouchables in virtual slavery, as been the influence of Christian missionaries, who have played a major role in challenging the social-economic-religious power blocs in India. Still, the social reality in many Indian ...
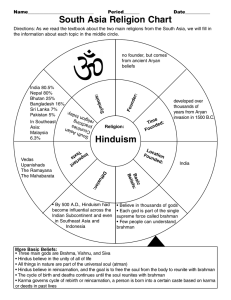
HinduismChart
... • All things in nature are part of the universal soul (atman) • Hindus believe in reincarnation, and the goal is to free the soul from the body to reunite with brahman • The cycle of birth and deaths continues until the soul reunites with brahman • Karma governs cycle of rebirth or reincarnation, a ...
... • All things in nature are part of the universal soul (atman) • Hindus believe in reincarnation, and the goal is to free the soul from the body to reunite with brahman • The cycle of birth and deaths continues until the soul reunites with brahman • Karma governs cycle of rebirth or reincarnation, a ...
Classical India
... Hindu Gods • Hinduism recognizes hundreds of gods and goddesses. • All are avatars, or incarnation of the Brahman. • 200s B.C.E. three gained large followings: Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva. • Brahma-The Creator-the most important and masculine personification. • Vishnu-The Preserver-A savior figure. A ...
... Hindu Gods • Hinduism recognizes hundreds of gods and goddesses. • All are avatars, or incarnation of the Brahman. • 200s B.C.E. three gained large followings: Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva. • Brahma-The Creator-the most important and masculine personification. • Vishnu-The Preserver-A savior figure. A ...