Notes-16-End-of-WWII
... several nations, and if so, what borders and interrelationships the new German states were to have. • The eventual partition of Germany into Allied Occupation Zones: British zone, French zone (two exclaves), American zone, Soviet zone, and Allied-administered Austria ...
... several nations, and if so, what borders and interrelationships the new German states were to have. • The eventual partition of Germany into Allied Occupation Zones: British zone, French zone (two exclaves), American zone, Soviet zone, and Allied-administered Austria ...
Aim: How did the U.S. try to contain the Communist threat
... life. Since the achievements of Socialism in our country meant the victory of the policy of the Party and the utter bankruptcy of their own policy, these gentry, instead of admitting the obvious facts and joining the common cause, began to revenge themselves on the Party and the people for their own ...
... life. Since the achievements of Socialism in our country meant the victory of the policy of the Party and the utter bankruptcy of their own policy, these gentry, instead of admitting the obvious facts and joining the common cause, began to revenge themselves on the Party and the people for their own ...
Europe Erupts in War
... Why did Stalin sign the nonaggression pact with Hitler in 1939? What was the blitzkrieg? What was Germany planning during the sitzkrieg? ...
... Why did Stalin sign the nonaggression pact with Hitler in 1939? What was the blitzkrieg? What was Germany planning during the sitzkrieg? ...
war!
... -Japanese American Peter Ota (whose family were sent to an internment camp in Colorado) recalled how his father ...
... -Japanese American Peter Ota (whose family were sent to an internment camp in Colorado) recalled how his father ...
Ch. 24.2 War in Europe Section Objectives: 1. Explain Hitler`s
... A lightning war, attack your enemy as fast as possible to overwhelm them Who declared war on Germany two days after the attack on Poland? Britain and France How was the blitzkrieg successful? What had now started? Major fighting was over in three weeks, before France and Britain could mount a def ...
... A lightning war, attack your enemy as fast as possible to overwhelm them Who declared war on Germany two days after the attack on Poland? Britain and France How was the blitzkrieg successful? What had now started? Major fighting was over in three weeks, before France and Britain could mount a def ...
1st Semester Where did human life begin? What is the period, of
... 59. What battle stopped the German advance towards Paris? 60. Which country betrayed its allies in WWI? 61. What was Woodrow Wilson’s plan for after WWI? 62. What was the Schlieffen Plan? 63. Who was Karl.Marx? The Rise of Dictators 64. What is a totalitarian state? 65. In what country did Benito Mu ...
... 59. What battle stopped the German advance towards Paris? 60. Which country betrayed its allies in WWI? 61. What was Woodrow Wilson’s plan for after WWI? 62. What was the Schlieffen Plan? 63. Who was Karl.Marx? The Rise of Dictators 64. What is a totalitarian state? 65. In what country did Benito Mu ...
`Origins and Beginnings of WWII Dictator Chart (Who was the worst
... declared that any further attacks by Germany on small states would trigger war France and Britain followed through with their original announcement and declared war on Germany ...
... declared that any further attacks by Germany on small states would trigger war France and Britain followed through with their original announcement and declared war on Germany ...
TEST NINE NOTES
... Great Britain’s prime minister was Neville Chamberlain and he had continued pushing for Great Britain to stay out of the war. Now Great Britain was in danger of being attacked by Germany and the British people wanted a change. In May of 1940 he was forced to resign and the new prime minister was Wi ...
... Great Britain’s prime minister was Neville Chamberlain and he had continued pushing for Great Britain to stay out of the war. Now Great Britain was in danger of being attacked by Germany and the British people wanted a change. In May of 1940 he was forced to resign and the new prime minister was Wi ...
World War II - Mrs. Curtis`s Social Studies Classroom
... The Axis and Ally Powers Axis Powers Germany Italy Japan ...
... The Axis and Ally Powers Axis Powers Germany Italy Japan ...
World War II and Its Aftermath
... Soviet Union to provide food products as well as raw materials to Germany in exchange for furnished products such as machinery from Germany. During the first years of the war, this economic agreement helped Germany bypass the British blockade. On August 23, 1939, four days after the economic agreeme ...
... Soviet Union to provide food products as well as raw materials to Germany in exchange for furnished products such as machinery from Germany. During the first years of the war, this economic agreement helped Germany bypass the British blockade. On August 23, 1939, four days after the economic agreeme ...
totalitarian - White Plains Public Schools
... build empires so they invaded other nations – Responses to Fascist Aggression • Appeasement: giving into a nation’s demands in order to avoid war – To avoid war with Germany, Great Britain & France allowed Hitler to rebuild his military and invade other nations ...
... build empires so they invaded other nations – Responses to Fascist Aggression • Appeasement: giving into a nation’s demands in order to avoid war – To avoid war with Germany, Great Britain & France allowed Hitler to rebuild his military and invade other nations ...
World War II Summary - socialstudiesguy.com
... Facts of the Case: Supreme Court’s Ruling: President Franklin Roosevelt issued an Executive Order excluding/removing all Japanese-Americans from the West Coast of the United States. After the 1941 Japanese attack on the U.S. Japanese-Americans were forced to sell their homes and businesses. They wer ...
... Facts of the Case: Supreme Court’s Ruling: President Franklin Roosevelt issued an Executive Order excluding/removing all Japanese-Americans from the West Coast of the United States. After the 1941 Japanese attack on the U.S. Japanese-Americans were forced to sell their homes and businesses. They wer ...
The Coming of the Second World War
... segments of the populace don't want war • Munich Agreement: Czechoslovakia forced to give away Sudetenland • Chamberlain returns to Britain a hero, boasting: "we have secured peace in our time" • German invasion of Czechoslovakia, spring1939: Hitler double-crosses Chamberlain ...
... segments of the populace don't want war • Munich Agreement: Czechoslovakia forced to give away Sudetenland • Chamberlain returns to Britain a hero, boasting: "we have secured peace in our time" • German invasion of Czechoslovakia, spring1939: Hitler double-crosses Chamberlain ...
Unit 4B Part One Chapter 15.2, 15.3,15.4 & 16.1
... • He hopes to strengthen allies so they can resist Germany • “Cash-and-carry” program Allowed nations to buy weapons with cash if they shipped them on their own ships. • Congress passed the first peacetime military draft in 1940. • Roosevelt wins 3rd Presidential election, breaks the 2-term ...
... • He hopes to strengthen allies so they can resist Germany • “Cash-and-carry” program Allowed nations to buy weapons with cash if they shipped them on their own ships. • Congress passed the first peacetime military draft in 1940. • Roosevelt wins 3rd Presidential election, breaks the 2-term ...
World War II
... • In 1940, Hitler took Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Belgium. • German forces bypassed France’s Maginot Line. • British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. • In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. • French were forced to surrender. • Germ ...
... • In 1940, Hitler took Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Belgium. • German forces bypassed France’s Maginot Line. • British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. • In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. • French were forced to surrender. • Germ ...
Chapter 7 Notes and Answers
... • Germany had to pay 33 billion dollars to pay for the war (reparations) • Reduce their army • It wasn’t created to promote peace, but to punish Germany. • The reparation payments, combined with the Great Depression, created terrible conditions for the German people. • These conditions created polit ...
... • Germany had to pay 33 billion dollars to pay for the war (reparations) • Reduce their army • It wasn’t created to promote peace, but to punish Germany. • The reparation payments, combined with the Great Depression, created terrible conditions for the German people. • These conditions created polit ...
Part II
... 2. Division of Germany into 4 occupied zones 3. Demilitarization and denazification of Germany 4. Germany’s reparations, including by forced labour of its soldiers 5. A new govt in Poland, including non-Communists 6. Changes of Poland’s borders 7. Return of citizens to USSR and Yugoslavia 8. Soviet ...
... 2. Division of Germany into 4 occupied zones 3. Demilitarization and denazification of Germany 4. Germany’s reparations, including by forced labour of its soldiers 5. A new govt in Poland, including non-Communists 6. Changes of Poland’s borders 7. Return of citizens to USSR and Yugoslavia 8. Soviet ...
Chap 29-30 Dictators Threaten World Peace
... he staged a mock takeover by marching his black shirts through the streets of Rome in October, 1922 ...
... he staged a mock takeover by marching his black shirts through the streets of Rome in October, 1922 ...
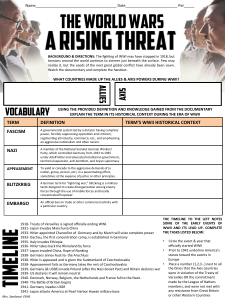
term definition term`s wwii historical context fascism nazi blitzkrieg
... A member of the Na9onal Socialist German Workers' Party, which controlled Germany from 1933 to 1945 under Adolf Hitler and advocated totalitarian government, territorial expansion, an9-‐Semi9sm, and Aryan suprema ...
... A member of the Na9onal Socialist German Workers' Party, which controlled Germany from 1933 to 1945 under Adolf Hitler and advocated totalitarian government, territorial expansion, an9-‐Semi9sm, and Aryan suprema ...
World War II (1939
... Munich agreement, invades rest of Czechoslovakia August 1939- Hitler signs nonaggression pact with rival USSR, turns attention west September 1, 1939“blitzkrieg” invasion of Poland; Britain and France declare war on Germany ...
... Munich agreement, invades rest of Czechoslovakia August 1939- Hitler signs nonaggression pact with rival USSR, turns attention west September 1, 1939“blitzkrieg” invasion of Poland; Britain and France declare war on Germany ...
Hitler Defies the Treaty of Versailles
... A. Hitler in Munich about his actions and decided that they would again appease Hitler and agreed NOT to get in his way if he agreed that this would be his last breach of the treaty and told Czechoslovakia they were on their own. ...
... A. Hitler in Munich about his actions and decided that they would again appease Hitler and agreed NOT to get in his way if he agreed that this would be his last breach of the treaty and told Czechoslovakia they were on their own. ...
Intro WWII Forum Lecture
... Casablanca Conference (1943)—unconditional surrender of Axis Battle of Atlantic—won by U. S. in 1943 Sicily invaded on July 10, 1943 September 1944, Italy mainland invaded ...
... Casablanca Conference (1943)—unconditional surrender of Axis Battle of Atlantic—won by U. S. in 1943 Sicily invaded on July 10, 1943 September 1944, Italy mainland invaded ...
World War II powerpoint
... • Spanish Civil War- Franco, fascist dictator takes power, US sends volunteers and relief aid, not enough, Germany, Italy send troops • Isolationism – The US believed they were dragged into war by business men making $, want to avoid Europe’s problems, public opinion against war, marches and rallies ...
... • Spanish Civil War- Franco, fascist dictator takes power, US sends volunteers and relief aid, not enough, Germany, Italy send troops • Isolationism – The US believed they were dragged into war by business men making $, want to avoid Europe’s problems, public opinion against war, marches and rallies ...
German–Soviet Axis talks

In October and November 1940, German–Soviet Axis talks occurred concerning the Soviet Union's potential entry as a fourth Axis Power in World War II. The negotiations included a two-day Berlin conference between Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov, Adolf Hitler and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, followed by both countries trading written proposed agreements. Germany never responded to a November 25, 1940, Soviet proposal, leaving the negotiations unresolved. Germany broke the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact in June 1941 by invading the Soviet Union.