3rd Quarter Review
... 26. Which of the following describes the US attitude after World War I? a. Interventionist, pro-business, and pro-civil rights b. Isolationist, pro-worker, and anti-prohibition c. Isolationist, pro-business, and anti-foreigner d. Interventionist, pro-worker, and pro-immigration ...
... 26. Which of the following describes the US attitude after World War I? a. Interventionist, pro-business, and pro-civil rights b. Isolationist, pro-worker, and anti-prohibition c. Isolationist, pro-business, and anti-foreigner d. Interventionist, pro-worker, and pro-immigration ...
World_War_II_1942
... World War II Decision Making Activity By 1945, World War II was coming to an end. Germany surrendered in May and Japan had lost most of the lands it had conquered in the Pacific. The figh ...
... World War II Decision Making Activity By 1945, World War II was coming to an end. Germany surrendered in May and Japan had lost most of the lands it had conquered in the Pacific. The figh ...
Grade 11 Unit 8 - Amazon Web Services
... resist with force or risk being swallowed up by the dictators one nation at a time. Something had to be done about this brazen aggression. It was the Germans invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939 that touched off the most devastating global war this world had ever seen. Though the Poles fought bra ...
... resist with force or risk being swallowed up by the dictators one nation at a time. Something had to be done about this brazen aggression. It was the Germans invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939 that touched off the most devastating global war this world had ever seen. Though the Poles fought bra ...
Origins of World War 1
... c. In California, Hispanics often lived close to Naval Stations. i. Many worked for the government d. Relations between Mexican American civilians and Naval servicemen from these stations was hostile. i. In the summer of 1943, the “Zoot Suit Riot” erupted between Hispanics and servicemen 1. Believed ...
... c. In California, Hispanics often lived close to Naval Stations. i. Many worked for the government d. Relations between Mexican American civilians and Naval servicemen from these stations was hostile. i. In the summer of 1943, the “Zoot Suit Riot” erupted between Hispanics and servicemen 1. Believed ...
World War II Intro - mssarnelli
... avoiding further conflict. In 1938, Hitler demanded that Czechoslovakia give the Sudetenland to Germany. He claimed that the German population living there was being mistreated. The British and French prime ministers agreed to Hitler’s demands without consulting Czechoslovakian leaders, in the hopes ...
... avoiding further conflict. In 1938, Hitler demanded that Czechoslovakia give the Sudetenland to Germany. He claimed that the German population living there was being mistreated. The British and French prime ministers agreed to Hitler’s demands without consulting Czechoslovakian leaders, in the hopes ...
World War II Exam II
... 7. Which of the following World War II leaders was the President of the United States when the Japanese surrendered in August of 1945? a. Franklin Delano Roosevelt b. Winston Churchill c. Harry S. Truman d. Joseph Stalin 8. On D-Day, June 6, 1944, Allied forces a. Took control of many Japanese islan ...
... 7. Which of the following World War II leaders was the President of the United States when the Japanese surrendered in August of 1945? a. Franklin Delano Roosevelt b. Winston Churchill c. Harry S. Truman d. Joseph Stalin 8. On D-Day, June 6, 1944, Allied forces a. Took control of many Japanese islan ...
TRANSLATION OF EH.510/10, LUFTPOST, No. 10, 22. JULI 1941
... means a work pleasing to God. The same is true of the German bishops who, on July 6th, issued a Pastoral Letter, in which they opposed the anti-Christian measures of the III Reich. The Pope stated: “The Faithful suffer persecution for their religion and for their loyalty to the Church. Our anxiety a ...
... means a work pleasing to God. The same is true of the German bishops who, on July 6th, issued a Pastoral Letter, in which they opposed the anti-Christian measures of the III Reich. The Pope stated: “The Faithful suffer persecution for their religion and for their loyalty to the Church. Our anxiety a ...
File
... been based upon a decent respect for the rights and the dignity of all our fellow men within our gates, so our national policy in foreign affairs has been based on a decent respect for the rights and dignity of all nations, large and small. And the justice of morality must and will win in the end. ...
... been based upon a decent respect for the rights and the dignity of all our fellow men within our gates, so our national policy in foreign affairs has been based on a decent respect for the rights and dignity of all nations, large and small. And the justice of morality must and will win in the end. ...
The Potsdam Conference
... Union should be "friendly" to the Soviet regime while the Soviets pledged to allow free elections in all territories liberated from Nazi Germany. Negotiators also released a declaration on Poland, providing for the inclusion of Communists in the postwar national government. In discussions regarding ...
... Union should be "friendly" to the Soviet regime while the Soviets pledged to allow free elections in all territories liberated from Nazi Germany. Negotiators also released a declaration on Poland, providing for the inclusion of Communists in the postwar national government. In discussions regarding ...
War Conference Wkst
... governing of Germany, but also that Germany should assume some, but not all, responsibility for reparations following the war. The Americans and the British generally agreed that future governments of the Eastern European nations bordering the Soviet Union should be "friendly" to the Soviet regime w ...
... governing of Germany, but also that Germany should assume some, but not all, responsibility for reparations following the war. The Americans and the British generally agreed that future governments of the Eastern European nations bordering the Soviet Union should be "friendly" to the Soviet regime w ...
32 World_War_II Student
... 1. The U.S. declared war on both countries on the same day. 2. Represented a fatal blunder by Hitler: Germany was not obligated to declare war against the U.S. since it did not attack Japan first. 3. This guaranteed that the U.S. would focus most of its military might on Germany first, rather than J ...
... 1. The U.S. declared war on both countries on the same day. 2. Represented a fatal blunder by Hitler: Germany was not obligated to declare war against the U.S. since it did not attack Japan first. 3. This guaranteed that the U.S. would focus most of its military might on Germany first, rather than J ...
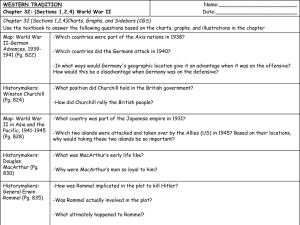
Ch 32 2010 Final CGS
... -In what ways would Germany's geographic location give it an advantage when it was on the offensive? How would this be a disadvantage when Germany was on the defensive? ...
... -In what ways would Germany's geographic location give it an advantage when it was on the offensive? How would this be a disadvantage when Germany was on the defensive? ...
Unit 4: The Twentieth-Century Crisis
... were given to France and Britain. 7. Germany and its allies received blame for the war, therefore, Germany was required to pay reparations to other nations, as compensation for property destroyed in the war. The price-$33 billion. Germany felt this was unfair. C. New nations formed from Germany & Au ...
... were given to France and Britain. 7. Germany and its allies received blame for the war, therefore, Germany was required to pay reparations to other nations, as compensation for property destroyed in the war. The price-$33 billion. Germany felt this was unfair. C. New nations formed from Germany & Au ...
The Allies Turn the Tide
... Germans Defeated at Stalingrad A major turning point occurred in the Soviet Union. After their lightning advance in 1941, the Germans were stalled outside Moscow and Leningrad. In 1942, Hitler launched a new offensive. This time, he aimed for the rich oil fields of the south. His troops, however, go ...
... Germans Defeated at Stalingrad A major turning point occurred in the Soviet Union. After their lightning advance in 1941, the Germans were stalled outside Moscow and Leningrad. In 1942, Hitler launched a new offensive. This time, he aimed for the rich oil fields of the south. His troops, however, go ...
Essential Question: What was the impact of World War II?
... War I, ruthless men used public anger and suffering to gain power in Europe and Asia. Fascist dictators, who had extremely nationalistic and racist views, arose in Italy and Germany. German dictator Adolf Hitler annexed (added) neighboring lands and greatly enlarged his military. The NAZI party led ...
... War I, ruthless men used public anger and suffering to gain power in Europe and Asia. Fascist dictators, who had extremely nationalistic and racist views, arose in Italy and Germany. German dictator Adolf Hitler annexed (added) neighboring lands and greatly enlarged his military. The NAZI party led ...
Ch.5 - SD43 Teacher Sites
... To get full marks, each response must be at least 2 sentences long! 1. GERMANY 1937 - Why did so many people attend a rally to see Hitler? ...
... To get full marks, each response must be at least 2 sentences long! 1. GERMANY 1937 - Why did so many people attend a rally to see Hitler? ...
22_The Consequences of World War II
... As the map demonstrates, the Auschwitz complex served as a concentration camp and an industrial centre for the exploitation of brutal slave labour - but it was the perpetration of genocide that became ...
... As the map demonstrates, the Auschwitz complex served as a concentration camp and an industrial centre for the exploitation of brutal slave labour - but it was the perpetration of genocide that became ...
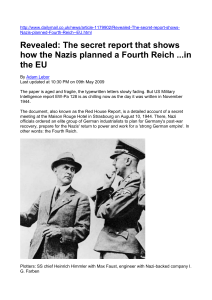
Nazi Fourth Reich - Friends of the Sabbath
... organisation, established in April 1951 by six European states. It created a common market for coal and steel which it regulated. This set a vital precedent for the steady erosion of national sovereignty, a process that continues today. But before the common market could be set up, the Nazi industri ...
... organisation, established in April 1951 by six European states. It created a common market for coal and steel which it regulated. This set a vital precedent for the steady erosion of national sovereignty, a process that continues today. But before the common market could be set up, the Nazi industri ...
World War II
... i. the old European Powers – France, Britain, and Germany – were exhausted by the war ii. two new powers – the USSR and the USA – assumed the dominant role in global politics C. conflicting ideologies and mutual distrust led to the Cold War, which pitted the western democracies, led by the United St ...
... i. the old European Powers – France, Britain, and Germany – were exhausted by the war ii. two new powers – the USSR and the USA – assumed the dominant role in global politics C. conflicting ideologies and mutual distrust led to the Cold War, which pitted the western democracies, led by the United St ...
World War Two: Allied vs. Axis Powers
... Power’s attempt to take over the world. – On the other hand the Axis were a group who planned on ruling the world, and having the world be populated entirely by their “perfect race.” ...
... Power’s attempt to take over the world. – On the other hand the Axis were a group who planned on ruling the world, and having the world be populated entirely by their “perfect race.” ...
Allied Control Council

The Allied Control Council or Allied Control Authority, known in the German language as the Alliierter Kontrollrat and also referred to as the Four Powers (German: Vier Mächte), was a military occupation governing body of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany after the end of World War II in Europe. The members were the Soviet Union, the United States, and the United Kingdom; France was later added with a vote, but had no duties. The organization was based in Berlin-Schöneberg.