Document
... As Hitler’s forces conquered most of Europe, the Nazis sent millions of Jews and political opponents to concentration camps. ...
... As Hitler’s forces conquered most of Europe, the Nazis sent millions of Jews and political opponents to concentration camps. ...
16. The Nuremberg Trials: Nazi Criminals Face Justice
... unexpectedly presented a proposal to the president two weeks before the War Department finished its own work. The two plans could not have been more different, and a bitter contest of ideas erupted in FDR’s cabinet. ...
... unexpectedly presented a proposal to the president two weeks before the War Department finished its own work. The two plans could not have been more different, and a bitter contest of ideas erupted in FDR’s cabinet. ...
World War II, 1939–1945
... targeted British airfields and aircraft factories. Then, on September 7, 1940, they began focusing on the cities, especially London—to break British morale. Bombs exploded daily in city streets. They killed civilians and set buildings ablaze. However, despite the destruction and loss of life, the Br ...
... targeted British airfields and aircraft factories. Then, on September 7, 1940, they began focusing on the cities, especially London—to break British morale. Bombs exploded daily in city streets. They killed civilians and set buildings ablaze. However, despite the destruction and loss of life, the Br ...
World War II
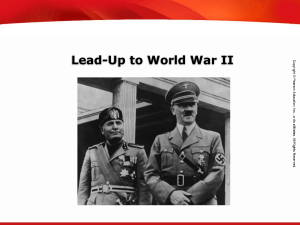
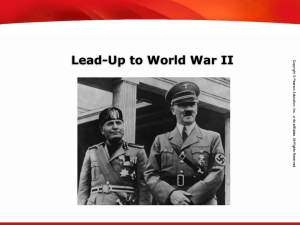
... What types of leaders came to power in Italy, Germany, and the Soviet Union before World War II? ...
... What types of leaders came to power in Italy, Germany, and the Soviet Union before World War II? ...
The Blitzkrieg Legend
... Even if you take issue with some of Mosier's interpretations, you'll find this a superb read. Contrary to myth, fortifications played an important role in prewar planning for both Germany (as the Allies ruefully discovered in 1944) and France. France had more tanks than Germany, and most were superi ...
... Even if you take issue with some of Mosier's interpretations, you'll find this a superb read. Contrary to myth, fortifications played an important role in prewar planning for both Germany (as the Allies ruefully discovered in 1944) and France. France had more tanks than Germany, and most were superi ...
Era of Global Wars
... • B It established permanent systems of government for the territories. • C It weakened the economies of countries that were supporting the territories. • D It was supposed to prepare territories for unification with the controlling country ...
... • B It established permanent systems of government for the territories. • C It weakened the economies of countries that were supporting the territories. • D It was supposed to prepare territories for unification with the controlling country ...
The Utility of Seapower: the Battle of the atlantic and the
... the continual attacks on merchant shipping by German U-boats to deny Allied Powers access to the Atlantic, and Allied efforts to counter this threat. The BA lasted through the Second World War (WWII), from September 1939, when a U-boat sunk passenger liner SS Athenia, to May 1945, when Germany capit ...
... the continual attacks on merchant shipping by German U-boats to deny Allied Powers access to the Atlantic, and Allied efforts to counter this threat. The BA lasted through the Second World War (WWII), from September 1939, when a U-boat sunk passenger liner SS Athenia, to May 1945, when Germany capit ...
Here we go again!
... D-Day lead by _____ Largest military engagement in history Separate HQ for what reason? Started with June 5th but what happened? So June 6th was the day. ...
... D-Day lead by _____ Largest military engagement in history Separate HQ for what reason? Started with June 5th but what happened? So June 6th was the day. ...
1 - Net Start Class
... 2. Great Britain and the Soviet city of Leningrad each fought off a German invasion. Other countries gave in to the Germans without much resistance. What factors do you think a country’s leaders consider when deciding whether to surrender or to fight? THINK ABOUT ...
... 2. Great Britain and the Soviet city of Leningrad each fought off a German invasion. Other countries gave in to the Germans without much resistance. What factors do you think a country’s leaders consider when deciding whether to surrender or to fight? THINK ABOUT ...
Holocaust Timeline
... Nazis targeted their hatred towards gypsies, blacks, homosexuals, Jehovah Witnesses, and physically and mentally handicapped along with Jews ...
... Nazis targeted their hatred towards gypsies, blacks, homosexuals, Jehovah Witnesses, and physically and mentally handicapped along with Jews ...
World War II, 1939–1945 Previewing Main Ideas
... targeted British airfields and aircraft factories. Then, on September 7, 1940, they began focusing on the cities, especially London, to break British morale. Despite the destruction and loss of life, the British did not waver. The RAF, although badly outnumbered, began to hit back hard. Two technolo ...
... targeted British airfields and aircraft factories. Then, on September 7, 1940, they began focusing on the cities, especially London, to break British morale. Despite the destruction and loss of life, the British did not waver. The RAF, although badly outnumbered, began to hit back hard. Two technolo ...
17.1 from appeasement to war
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
From Appeasement to War - Trimble County Schools
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
WWII Notes to Help You Study
... German offensive u-boat attack on America’s east coast. Aim was to prevent food and war materials from reaching Great Britain and Soviet Union. Germany was originally winning as they sank many of our ships. With eventual use of convoy system and new technology, we located and destroyed many German u ...
... German offensive u-boat attack on America’s east coast. Aim was to prevent food and war materials from reaching Great Britain and Soviet Union. Germany was originally winning as they sank many of our ships. With eventual use of convoy system and new technology, we located and destroyed many German u ...
Chapter 25 World War II
... segregation • Despite poor treatment many minority groups continued to serve in U.S. Military ...
... segregation • Despite poor treatment many minority groups continued to serve in U.S. Military ...
WWII - timeline 1939-1945
... Powers in WWII in November. Hungary was promised territorial gains by the Axis Powers, while Romania was seeking support against the Soviet Union, which had captured Moldova from them, and threatened the country as a whole. • Italy's Unsuccessful Invasion of Greece (Oct. 28, 1940): Italy invaded Gre ...
... Powers in WWII in November. Hungary was promised territorial gains by the Axis Powers, while Romania was seeking support against the Soviet Union, which had captured Moldova from them, and threatened the country as a whole. • Italy's Unsuccessful Invasion of Greece (Oct. 28, 1940): Italy invaded Gre ...
WORLD WAR II
... “ They’d halt us in front of these big artesian wells… so we could see the water and they wouldn’t let us have any. Anyone who would make a break for water would be shot or bayoneted. Then they were left there. Finally, it got so bad further along the road that you never got away from the ste ...
... “ They’d halt us in front of these big artesian wells… so we could see the water and they wouldn’t let us have any. Anyone who would make a break for water would be shot or bayoneted. Then they were left there. Finally, it got so bad further along the road that you never got away from the ste ...
Name:
... German offensive u-boat attack on America’s east coast. Aim was to prevent food and war materials from reaching Great Britain and Soviet Union. Germany was originally winning as they sank many of our ships. With eventual use of convoy system and new technology, we located and destroyed many German u ...
... German offensive u-boat attack on America’s east coast. Aim was to prevent food and war materials from reaching Great Britain and Soviet Union. Germany was originally winning as they sank many of our ships. With eventual use of convoy system and new technology, we located and destroyed many German u ...
World War II - Union High School
... met secretly and issued a joint declaration called the Atlantic Charter. It upheld free trade among nations and the right of people to choose their own government. The charter later served as the Allies’ peace plan at the end of World War II. On September 4, a German U-boat fired on a U.S. destroyer ...
... met secretly and issued a joint declaration called the Atlantic Charter. It upheld free trade among nations and the right of people to choose their own government. The charter later served as the Allies’ peace plan at the end of World War II. On September 4, a German U-boat fired on a U.S. destroyer ...
IB History Paper 1 Review - aise
... iii. Britain and US are outraged by France’s unilateral action and force France to accept the Dawes Plan f. Dawes Plan (1924) i. Major and ongoing American loans and investment to Germany ii. Reparations to be reduced for 5 years iii. Allied oversight of German railroads and other industries to ensu ...
... iii. Britain and US are outraged by France’s unilateral action and force France to accept the Dawes Plan f. Dawes Plan (1924) i. Major and ongoing American loans and investment to Germany ii. Reparations to be reduced for 5 years iii. Allied oversight of German railroads and other industries to ensu ...
June 2007 Mark Scheme The Causes and Impact of the First World
... No set answer is looked for but candidates will need to address the question. Answers will need to demonstrate a clear understanding of how the Treaty impacted on Germany up to 1923. Main issues that may be considered include: territorial disputes and the non-application of self determination (East ...
... No set answer is looked for but candidates will need to address the question. Answers will need to demonstrate a clear understanding of how the Treaty impacted on Germany up to 1923. Main issues that may be considered include: territorial disputes and the non-application of self determination (East ...
World War 2 - social studies
... you learn from the lesson. Follow the directions listed on the sheet of paper I provide for this assignment. ...
... you learn from the lesson. Follow the directions listed on the sheet of paper I provide for this assignment. ...
The European Campaign - Brookwood High School
... Franklin Roosevelt (USA) Winston Churchill (Britain) Joseph Stalin (USSR) ...
... Franklin Roosevelt (USA) Winston Churchill (Britain) Joseph Stalin (USSR) ...
Keeping Control (1933-1945) essay questions
... Was the depression the most important reason why the Nazis were able to come to power in 1933? Explain your answer using your knowledge. (8) Did the Nazis come to power in 1933 only because they promised to make Germany great once more? Explain your answer. (8) How far were working-class Germans bet ...
... Was the depression the most important reason why the Nazis were able to come to power in 1933? Explain your answer using your knowledge. (8) Did the Nazis come to power in 1933 only because they promised to make Germany great once more? Explain your answer. (8) How far were working-class Germans bet ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.