July 11, 1969 Report by Four Chinese Marshals, Chen Yi, Ye
... imperialists’ defeats in the Korean War and the Vietnam War have taught them a bitter lesson causing a deeper crisis both at home and abroad, thus forcing them to claim that they would never again be involved in wars similar to the ones in Korea and Vietnam. China is different from Korea and Vietna ...
... imperialists’ defeats in the Korean War and the Vietnam War have taught them a bitter lesson causing a deeper crisis both at home and abroad, thus forcing them to claim that they would never again be involved in wars similar to the ones in Korea and Vietnam. China is different from Korea and Vietna ...
The Bombing of Dresden
... The Allied bombing of Dresden during WWII was an extremely controversial piece of World War II, as the loss of life and tremendous damage caused an excessive amount of unnecessary destruction. The reason for targeting Dresden was mainly to attack any form of Nazi Germany, and to stop the production ...
... The Allied bombing of Dresden during WWII was an extremely controversial piece of World War II, as the loss of life and tremendous damage caused an excessive amount of unnecessary destruction. The reason for targeting Dresden was mainly to attack any form of Nazi Germany, and to stop the production ...
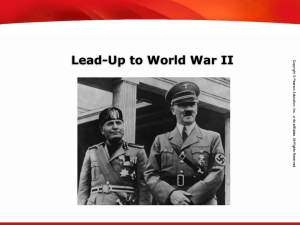
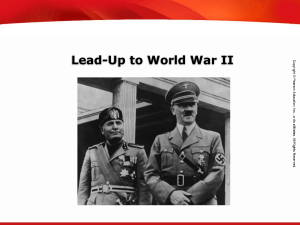
Essential Question: What are the causes and effects of World War II
... What are the causes and effects of World War II? Name____________________________ Period____________________________ ...
... What are the causes and effects of World War II? Name____________________________ Period____________________________ ...
The 1920`s and the Great Depression
... A. Hitler believed in GER world dominance. B. He wanted the “Third Reich” to last “a 1,000 years” C. He believed that certain people were “inferior” and a “master race” could control the rest. D. He believed the Nordic, blond, blue-eyed race was superior. E. Ethnics, Jews, Catholics, Gypsies, mental ...
... A. Hitler believed in GER world dominance. B. He wanted the “Third Reich” to last “a 1,000 years” C. He believed that certain people were “inferior” and a “master race” could control the rest. D. He believed the Nordic, blond, blue-eyed race was superior. E. Ethnics, Jews, Catholics, Gypsies, mental ...
(finding aid) to the scrapbook is created by Special Collections
... L 378 V R535 The following descriptions are only for the selected items: 1944 August 14 (p.17) Newspaper article details the invasion of southern France by the Allies (American, British, and French forces) by sea and air against the German troops ...
... L 378 V R535 The following descriptions are only for the selected items: 1944 August 14 (p.17) Newspaper article details the invasion of southern France by the Allies (American, British, and French forces) by sea and air against the German troops ...
1 HIST 388 – The Second World War FILM: Triumph of the Will
... o Conclusion: German armed forces must be ready in 4 years and so should the German economy Main features of 1930s, international relations and conflict o Japanese aggression in far east in 1931 o Italy’s colonial war against Ethiopia in 1935 o Spanish Civil War 1936-39 Italians send troops and Ge ...
... o Conclusion: German armed forces must be ready in 4 years and so should the German economy Main features of 1930s, international relations and conflict o Japanese aggression in far east in 1931 o Italy’s colonial war against Ethiopia in 1935 o Spanish Civil War 1936-39 Italians send troops and Ge ...
Essential Question: What are the causes and effects of World War II
... What are the causes and effects of World War II? Name____________________________ Period____________________________ ...
... What are the causes and effects of World War II? Name____________________________ Period____________________________ ...
US Chapter 17 section 3 notes
... War still raged in the Pacific, where the Allies were fighting their way toward Japan. ...
... War still raged in the Pacific, where the Allies were fighting their way toward Japan. ...
Introducing World War II
... Germany and Italy became allies in Europe. This alliance became known as the Axis Powers. Germany also signed a treaty with the Soviet Union’s new dictator, Joseph Stalin, that kept them from fighting each other. Japan began to increase its territory by attacking its neighbor, China. Of course, the ...
... Germany and Italy became allies in Europe. This alliance became known as the Axis Powers. Germany also signed a treaty with the Soviet Union’s new dictator, Joseph Stalin, that kept them from fighting each other. Japan began to increase its territory by attacking its neighbor, China. Of course, the ...
File - Mr Barck`s Classroom
... used propaganda to win support for the war. • Many Japanese Americans and Japanese Canadians lost their jobs and property and were interned in camps. • The British took similar action against German refugees. ...
... used propaganda to win support for the war. • Many Japanese Americans and Japanese Canadians lost their jobs and property and were interned in camps. • The British took similar action against German refugees. ...
5th Grade Social Studies Ch. 8 Vocabulary
... World War II the day after…? The Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor. ...
... World War II the day after…? The Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor. ...
Chap 32
... Germany invades an unprepared Soviet Union in June 1941 Soviet troops burn land as they retreat; Germans move into Russia Germans stopped at Leningrad, forced to undertake long siege Germans almost capture Moscow, but forced to pull back ...
... Germany invades an unprepared Soviet Union in June 1941 Soviet troops burn land as they retreat; Germans move into Russia Germans stopped at Leningrad, forced to undertake long siege Germans almost capture Moscow, but forced to pull back ...
Sample Responses Q7 - AP Central
... Hitler repudiates Versailles Treaty and League of Nations. March 7, 1936: Hitler remilitarizes Rhineland. October 1936: Germany allies with Italy, followed by Anti-Comintern Pact with Japan. September 1939: Having agreed to the absorption of the Czech Sudetenland the previous year, Chamberlain signe ...
... Hitler repudiates Versailles Treaty and League of Nations. March 7, 1936: Hitler remilitarizes Rhineland. October 1936: Germany allies with Italy, followed by Anti-Comintern Pact with Japan. September 1939: Having agreed to the absorption of the Czech Sudetenland the previous year, Chamberlain signe ...
World War II Paper - American History World War II (1939
... 7, 1941. Between those two events, President Franklin Roosevelt tried hard to prepare Americans for a conflict that he regarded as inevitable. In November 1939, he persuaded Congress to repeal the arms embargo provisions of the neutrality law so that arms could be sold to France and Britain. After t ...
... 7, 1941. Between those two events, President Franklin Roosevelt tried hard to prepare Americans for a conflict that he regarded as inevitable. In November 1939, he persuaded Congress to repeal the arms embargo provisions of the neutrality law so that arms could be sold to France and Britain. After t ...
Political Neutrality in Europe during World War II
... political and economic ties with fascist Franco’s Spain. Prime minister Antonio de Oliveria Salazar of Portugal had supported Franco during Spain’s civil war, and he had incorporated many facets of fascism into his government- including corporatist social and economic policies, the debasement of dem ...
... political and economic ties with fascist Franco’s Spain. Prime minister Antonio de Oliveria Salazar of Portugal had supported Franco during Spain’s civil war, and he had incorporated many facets of fascism into his government- including corporatist social and economic policies, the debasement of dem ...
Chapter 35 Focus Questions: Essay question: To what extent did the
... 32) Roosevelt’s and Churchill’s insistence on the absolute and “unconditional surrender” of Germany meant what would have to happen to them after the war? 33) Know the order of the wartime conferences. 34) What decisions were made at the Casablanca Conference by Churchill and Roosevelt and what was ...
... 32) Roosevelt’s and Churchill’s insistence on the absolute and “unconditional surrender” of Germany meant what would have to happen to them after the war? 33) Know the order of the wartime conferences. 34) What decisions were made at the Casablanca Conference by Churchill and Roosevelt and what was ...
From Appeasement to War - Trimble County Schools
... Western democracies denounced these invasions but chose a policy of appeasement. ...
... Western democracies denounced these invasions but chose a policy of appeasement. ...
17.1 from appeasement to war
... Western democracies denounced these invasions but chose a policy of appeasement. ...
... Western democracies denounced these invasions but chose a policy of appeasement. ...
Chapter 5
... 14. Define isolationism and appeasement. Which countries/leaders followed these policies? 15. Which countries/areas were invaded by Italy, Germany and Japan? 16. How is fascism and communism similar and different? 17. What two countries sign the non-aggression pact in 1939? What effect did it have o ...
... 14. Define isolationism and appeasement. Which countries/leaders followed these policies? 15. Which countries/areas were invaded by Italy, Germany and Japan? 16. How is fascism and communism similar and different? 17. What two countries sign the non-aggression pact in 1939? What effect did it have o ...
lithuanian prisoners of war in western
... ‘In the camps in Germany life is even harder: German food, living in stables, unusually cold weather, daily work for Germans in private apartments, sweeping the streets and uprooting stumps in the forests, and as payment for the work – a military loaf of bread, a couple of grams of butter for 30 peo ...
... ‘In the camps in Germany life is even harder: German food, living in stables, unusually cold weather, daily work for Germans in private apartments, sweeping the streets and uprooting stumps in the forests, and as payment for the work – a military loaf of bread, a couple of grams of butter for 30 peo ...
World War II Part One
... Hitler ignores the Treaty of Versailles • The failure of the League of Nations to take action against Japan did not escape the notice of Europe’s dictators. • In 1933, Hitler pulled Germany out of the League. • In 1935, he began a military buildup in violation of the Treaty of Versailles. ...
... Hitler ignores the Treaty of Versailles • The failure of the League of Nations to take action against Japan did not escape the notice of Europe’s dictators. • In 1933, Hitler pulled Germany out of the League. • In 1935, he began a military buildup in violation of the Treaty of Versailles. ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.