Chapter 4
... Strategy: In order to break a redox reaction down into an oxidation half-reaction and a reduction halfreaction, you should first assign oxidation numbers to all the atoms in the reaction. In this way, you can determine which element is oxidized (loses electrons) and which element is reduced (gains e ...
... Strategy: In order to break a redox reaction down into an oxidation half-reaction and a reduction halfreaction, you should first assign oxidation numbers to all the atoms in the reaction. In this way, you can determine which element is oxidized (loses electrons) and which element is reduced (gains e ...
Unit F325 - Equilibria, energetics and elements
... ALLOW: weak acid AND its conjugate base/salt present ...
... ALLOW: weak acid AND its conjugate base/salt present ...
INTEKNATIONAL ATOMIC WEIGHTS Aluminum... Antimony..., Argon
... particularly for more advanced work. It is designed not only to encourage students to undertake special work but to aid them in later years in the solution of practical problems. No claim whatsoever is made for completeness. In their selection of material the authors have been guided simply by their ...
... particularly for more advanced work. It is designed not only to encourage students to undertake special work but to aid them in later years in the solution of practical problems. No claim whatsoever is made for completeness. In their selection of material the authors have been guided simply by their ...
Mark scheme F325 Equilibria, Energetics and Elements June
... DO NOT ALLOW incorrect named particles, e.g. ‘atoms’, ‘molecules’, Na, Cl, Cl2, ‘atomic’, etc DO NOT ALLOW responses using nuclear size or attraction DO NOT ALLOW responses linked with loss of electrons IGNORE larger electron density ALLOW smaller sum of radii gives a greater ionic attraction ...
... DO NOT ALLOW incorrect named particles, e.g. ‘atoms’, ‘molecules’, Na, Cl, Cl2, ‘atomic’, etc DO NOT ALLOW responses using nuclear size or attraction DO NOT ALLOW responses linked with loss of electrons IGNORE larger electron density ALLOW smaller sum of radii gives a greater ionic attraction ...
Chemistry 11 Final Examination Review
... a) Electrons can absorb or emit energy only in whole numbers of photons. b) Atoms have a central positively charged nucleus. c) Electrons move around the nucleus as planets orbit the sun. d) Most of the volume of an atom is empty space. 10. Which of the following orbitals is spherical in shape? a) 3 ...
... a) Electrons can absorb or emit energy only in whole numbers of photons. b) Atoms have a central positively charged nucleus. c) Electrons move around the nucleus as planets orbit the sun. d) Most of the volume of an atom is empty space. 10. Which of the following orbitals is spherical in shape? a) 3 ...
Concept based notes Chemistry Lab Manual
... Q. 73. Why, H2S gas passed in presence of NH4OH? Ans. When H2S gas is passed in alkaline medium or in presence of NH4OH, the H+ ions from the dissociation of H2S gas combine with hydroxyl ions (OH-) from the dissociation of NH4OH to from nearly unionised H2O. The removal of H+ ions from the solutio ...
... Q. 73. Why, H2S gas passed in presence of NH4OH? Ans. When H2S gas is passed in alkaline medium or in presence of NH4OH, the H+ ions from the dissociation of H2S gas combine with hydroxyl ions (OH-) from the dissociation of NH4OH to from nearly unionised H2O. The removal of H+ ions from the solutio ...
B.Sc Chemistry - Calicut University
... behaviour of individual atoms and molecules. The laws of quantum mechanics decide the properties of the micro-world. There are two approaches for introducing quantum mechanics. One is to follow the historical development of the quantum theory and the other is to begin from the basic principles of th ...
... behaviour of individual atoms and molecules. The laws of quantum mechanics decide the properties of the micro-world. There are two approaches for introducing quantum mechanics. One is to follow the historical development of the quantum theory and the other is to begin from the basic principles of th ...
Chemistry Honours - SCS Autonomous College
... Bohr’s theory, its limitations and atomic spectrum of hydrogen atom. Wave mechanics: de Broglie equation, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle and its significance, Schrödinger’s wave equation, significance of ψ and ψ 2 . Quantum numbers and their significance. Normalized and orthogonal wave functions ...
... Bohr’s theory, its limitations and atomic spectrum of hydrogen atom. Wave mechanics: de Broglie equation, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle and its significance, Schrödinger’s wave equation, significance of ψ and ψ 2 . Quantum numbers and their significance. Normalized and orthogonal wave functions ...
Chemistry.of Organic Compounds
... Since 1860 the integrating theory behind the enormous mass of data that has been accumulated concerning organic compounds has been the theory of gross structure, that is, the theory correlating the reactions and physical properties of organic molecules with the kind of atoms present and with the ord ...
... Since 1860 the integrating theory behind the enormous mass of data that has been accumulated concerning organic compounds has been the theory of gross structure, that is, the theory correlating the reactions and physical properties of organic molecules with the kind of atoms present and with the ord ...
Cliffs Notes
... Technical Editor: Christopher Bushee Production Proofreader: Joel K. Draper Hungry Minds Indianapolis Production Services ...
... Technical Editor: Christopher Bushee Production Proofreader: Joel K. Draper Hungry Minds Indianapolis Production Services ...
Solutions Manual
... This produces long, straight chains of cellulose which are linked to each other by hydrogen bonding. In plants, cellulose acts as a structural material. Starch (both amylase and amylopectin) is made from long-chain repeating units of α-glucose, which are also highly branched. This results in tightly ...
... This produces long, straight chains of cellulose which are linked to each other by hydrogen bonding. In plants, cellulose acts as a structural material. Starch (both amylase and amylopectin) is made from long-chain repeating units of α-glucose, which are also highly branched. This results in tightly ...
Instructor`s Guide to General Chemistry: Guided
... element or one compound. A mixture, which is better called an inhomogeneous mixture, is matter consisting of two or more pure substances combined inhomogeneously, which means that one macroscopic region, as seen visually or with a microscope, differs from another. A solution is matter of two or more ...
... element or one compound. A mixture, which is better called an inhomogeneous mixture, is matter consisting of two or more pure substances combined inhomogeneously, which means that one macroscopic region, as seen visually or with a microscope, differs from another. A solution is matter of two or more ...
Supplementary Exercise 1B Topic 5
... In the electrochemical series, the position of calcium is higher than that of sodium. The order is different from that in the reactivity series. This is because calcium atom loses electrons more readily in cell reactions than in reaction with air, water and dilute acids. ...
... In the electrochemical series, the position of calcium is higher than that of sodium. The order is different from that in the reactivity series. This is because calcium atom loses electrons more readily in cell reactions than in reaction with air, water and dilute acids. ...
National German Competition
... Zinc organic compounds are longer known and more often used. These compounds are applied to synthesize alcohols, more exactly in the synthesis of hydroxy esters. Following this path you can get -hydroxy acids and then in follo-up reactions new unsaturated and saturated carboxylic acids. Adding zin ...
... Zinc organic compounds are longer known and more often used. These compounds are applied to synthesize alcohols, more exactly in the synthesis of hydroxy esters. Following this path you can get -hydroxy acids and then in follo-up reactions new unsaturated and saturated carboxylic acids. Adding zin ...
Chemistry - Department of Education and Skills
... authors have found beneficial over the years and gives details of student experiments and teacher demonstrations. Worked examples are included which the teacher may find useful in the class room or for homework. It is not intended that this book be used as a textbook or be read from cover to cover. ...
... authors have found beneficial over the years and gives details of student experiments and teacher demonstrations. Worked examples are included which the teacher may find useful in the class room or for homework. It is not intended that this book be used as a textbook or be read from cover to cover. ...
Chapter 2 1.Certain gases in the 293K and 9.97 × 104Pa when the
... 1. Try to use ionic bond theory to show a single mass of metal potassium and chlorine reaction, the formation of potassium chloride process? How to understand the ionic bond non-directional and saturation? Answer: Atoms derived from the two because of electrostatic attraction and the attraction betw ...
... 1. Try to use ionic bond theory to show a single mass of metal potassium and chlorine reaction, the formation of potassium chloride process? How to understand the ionic bond non-directional and saturation? Answer: Atoms derived from the two because of electrostatic attraction and the attraction betw ...
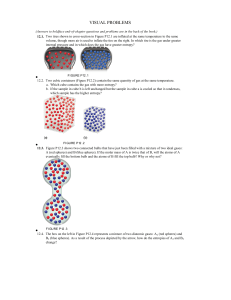
visual problems - Western Oregon University
... a. Use the appropriate ∆G°f value(s) from Appendix 4 to calculate ∆G°rxn for the reaction known as steam–methane reforming: CH4(g) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + 3 H2(g) b. To drive this nonspontaneous reaction the CO that is produced can be oxidized to CO 2 using more steam: CO(g) + H2O(g) → CO2(g) + H2(g) Us ...
... a. Use the appropriate ∆G°f value(s) from Appendix 4 to calculate ∆G°rxn for the reaction known as steam–methane reforming: CH4(g) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + 3 H2(g) b. To drive this nonspontaneous reaction the CO that is produced can be oxidized to CO 2 using more steam: CO(g) + H2O(g) → CO2(g) + H2(g) Us ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.