6. Divisibility of atoms: from radioactivity to particle physics
... theories for the four different fundamental forces. (But it would not mean the end of physics!) • Electro-magnetic and weak nuclear force have been unified: electro-weak theory. Theories unifying electro-weak theory with the strong nuclear force are ...
... theories for the four different fundamental forces. (But it would not mean the end of physics!) • Electro-magnetic and weak nuclear force have been unified: electro-weak theory. Theories unifying electro-weak theory with the strong nuclear force are ...
Inside A Particle Physicist`s Toolbox
... From each tube’s drift time we obtain the drift radius or drift circle. ...
... From each tube’s drift time we obtain the drift radius or drift circle. ...
ERC-focus (English)
... particles, which have large masses coming from the Higgs field. The recent likely discovery of the excitation of this field is an important step in our quest what is beyond the so-called Standard Model of particle physics describing all these forces. This question has come up earlier with the discov ...
... particles, which have large masses coming from the Higgs field. The recent likely discovery of the excitation of this field is an important step in our quest what is beyond the so-called Standard Model of particle physics describing all these forces. This question has come up earlier with the discov ...
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the Higgs boson and
... design of the Al-stabilized thin SC (superconducting) solenoid of the ZEUS detector (HERA at Desy, Hamburg); the development in 1998 of record Jc Nb3Sn superconductor with Europa Metalli, the construction of the first prototype of the LHC 9 T magnet dipole for CERN; the development of the super-stab ...
... design of the Al-stabilized thin SC (superconducting) solenoid of the ZEUS detector (HERA at Desy, Hamburg); the development in 1998 of record Jc Nb3Sn superconductor with Europa Metalli, the construction of the first prototype of the LHC 9 T magnet dipole for CERN; the development of the super-stab ...
Dr. Saskia Mioduszewski Quark-Gluon Plasma
... part of the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) ...
... part of the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) ...
PPT
... So, are there other characteristics of quarks? The two lightest are 'up' and 'down' quarks They combine to form protons and neutrons. The heavier quarks aren't found in nature and have so far only been observed in particle accelerators. ...
... So, are there other characteristics of quarks? The two lightest are 'up' and 'down' quarks They combine to form protons and neutrons. The heavier quarks aren't found in nature and have so far only been observed in particle accelerators. ...
Accelerators
... Quite simply, accelerators give high energy to subatomic particles, which then collide with targets. Out of this interaction come many other subatomic particles that pass into detectors. From the information gathered in the detectors, physicists can determine properties of the particles and their in ...
... Quite simply, accelerators give high energy to subatomic particles, which then collide with targets. Out of this interaction come many other subatomic particles that pass into detectors. From the information gathered in the detectors, physicists can determine properties of the particles and their in ...
Study Notes Lesson 23 Atomic and Nuclear Physics
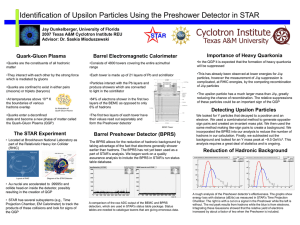
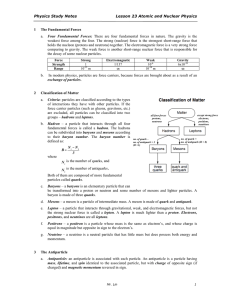
... Criteria: particles are classified according to the types of interactions they have with other particles. If the force carrier particles (such as gluons, gravitons, etc.) are excluded, all particles can be classified into two groups – hadrons and leptons. Hadron – a particle that interacts through a ...
... Criteria: particles are classified according to the types of interactions they have with other particles. If the force carrier particles (such as gluons, gravitons, etc.) are excluded, all particles can be classified into two groups – hadrons and leptons. Hadron – a particle that interacts through a ...
Particle Physics Design Group Studies Worksheet Introduction
... the particles with the detector material. Several different types of interactions are important, the main ones being: ionisation and excitation of atoms by charged particles; electromagnetic interactions in nuclear electric fields; and hadronic interactions of strongly-interacting particles with nuc ...
... the particles with the detector material. Several different types of interactions are important, the main ones being: ionisation and excitation of atoms by charged particles; electromagnetic interactions in nuclear electric fields; and hadronic interactions of strongly-interacting particles with nuc ...
conceptual design of a polarized medium energy electron
... Pocatello, ID 83209; A. Kondratenko, GOO Zaryad, Novosibirsk, Russian Federation Abstract A medium energy electron-ion collider is envisioned as the primary future of the JLab nuclear science program beyond the 12 GeV upgraded CEBAF. The present conceptual design selects a ring-ring collider option, ...
... Pocatello, ID 83209; A. Kondratenko, GOO Zaryad, Novosibirsk, Russian Federation Abstract A medium energy electron-ion collider is envisioned as the primary future of the JLab nuclear science program beyond the 12 GeV upgraded CEBAF. The present conceptual design selects a ring-ring collider option, ...
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (english German Electron Synchrotron) commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany that operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter. It conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science; and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen.