ppt - Jefferson Lab
... It was observed strong RF signal induced by proton beam with a gap ( one long bunch). For intensity of proton beam Qb< 4E12 p electron current to the VIPM plate is low ( Qe< 0.1 V~ 1E-7 A) as corresponded to electron production by residual gas ionization by proton beam. For higher proton beam intens ...
... It was observed strong RF signal induced by proton beam with a gap ( one long bunch). For intensity of proton beam Qb< 4E12 p electron current to the VIPM plate is low ( Qe< 0.1 V~ 1E-7 A) as corresponded to electron production by residual gas ionization by proton beam. For higher proton beam intens ...
dynamics and acceleration in linear structures
... However TM modes (with an electric field in the direction of propagation) in rectangular or cylindrical guides have phase velocities bigger than c. Then it was necessary to bring the phase velocity at the level of the particle velocity (vp ~ c) and to do so the simplest method consists of loading th ...
... However TM modes (with an electric field in the direction of propagation) in rectangular or cylindrical guides have phase velocities bigger than c. Then it was necessary to bring the phase velocity at the level of the particle velocity (vp ~ c) and to do so the simplest method consists of loading th ...
A beam of antimatter could help to unravel the secrets of
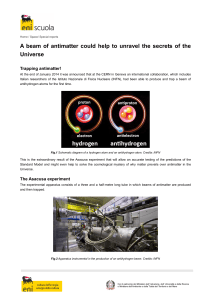
... How is antimatter generated? When matter and antimatter meet, they annihilate each other releasing electromagnetic radiation. Hence, it follows that, in theory, inverting the process it should be possible to create pairs of particles and antiparticles from energy in the form of electromagnetic radia ...
... How is antimatter generated? When matter and antimatter meet, they annihilate each other releasing electromagnetic radiation. Hence, it follows that, in theory, inverting the process it should be possible to create pairs of particles and antiparticles from energy in the form of electromagnetic radia ...
phys3313-fall12-112812
... Nucleons contain both quarks and glue particles (gluons) both described by individual characteristic momentum distributions (Parton Distribution Functions) Monday, Nov. 27, 2006 ...
... Nucleons contain both quarks and glue particles (gluons) both described by individual characteristic momentum distributions (Parton Distribution Functions) Monday, Nov. 27, 2006 ...
L3_interactions_matter_riegler09 - Indico
... How do we find the energy loss distribution ? If f(E) is the probability to lose the energy E’ in an interaction, the probability p(E) to lose an energy E over the distance D ? ...
... How do we find the energy loss distribution ? If f(E) is the probability to lose the energy E’ in an interaction, the probability p(E) to lose an energy E over the distance D ? ...
POINT/COUNTERPOINT Intensity-modulated conformal radiation
... volume because they stop, whereas photons will irradiate all structures in their path distal to the target !and also deliver more dose upstream of the target". Up to medium depths, lateral penumbra is comparable for photons and protons and, except for small, spherical volumes, the photon penumbra ca ...
... volume because they stop, whereas photons will irradiate all structures in their path distal to the target !and also deliver more dose upstream of the target". Up to medium depths, lateral penumbra is comparable for photons and protons and, except for small, spherical volumes, the photon penumbra ca ...
Slide 1
... Hadron RAA is pt independent as expected by the radiative energy loss (LPM). Direct photons follow the binary scaling. Number of binary scaling works! Unexpected level of suppression for the heavy quarks. Equark,m=0 Equark,m>0 No sign for the color factor effect on energy loss. E CR Egluo ...
... Hadron RAA is pt independent as expected by the radiative energy loss (LPM). Direct photons follow the binary scaling. Number of binary scaling works! Unexpected level of suppression for the heavy quarks. Equark,m=0 Equark,m>0 No sign for the color factor effect on energy loss. E CR Egluo ...
Strangeness production in Heavy Ion Collisions
... This means that strange antiquarks are most likely to combine with a light quark to form a K+ or Ko while strange quarks are more likely to combine with light quarks to form a hyperon. ...
... This means that strange antiquarks are most likely to combine with a light quark to form a K+ or Ko while strange quarks are more likely to combine with light quarks to form a hyperon. ...
ppt
... production of mesons-and baryon resonances and their decay, exotic resonances ( e.g. pentaquark ) • experiments at COSY / FZ Jülich • data analysis in Tübingen ...
... production of mesons-and baryon resonances and their decay, exotic resonances ( e.g. pentaquark ) • experiments at COSY / FZ Jülich • data analysis in Tübingen ...
non-relativistic Breit
... around m⊥ ≈ mW . The fact that the decay is more or less evenly distributed in azimuth angle the peak will become smeared and slightly shifted towards lower m⊥ (a Jacobian peak). Then we have the spin properties of the W which can be checked. We know that W + only couples to left-handed (spin oposit ...
... around m⊥ ≈ mW . The fact that the decay is more or less evenly distributed in azimuth angle the peak will become smeared and slightly shifted towards lower m⊥ (a Jacobian peak). Then we have the spin properties of the W which can be checked. We know that W + only couples to left-handed (spin oposit ...
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (english German Electron Synchrotron) commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany that operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter. It conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science; and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen.